Many business leaders mistakenly view product development as purely a technical challenge—something to hand off to the engineering team while focusing on sales and marketing. This narrow perspective misses a critical truth: product development strategy drives competitive advantage and long-term business success far beyond what technical implementation alone can deliver.
This guide is for executives, product managers, and development teams who want to understand how strategic product development creates measurable business value. You'll discover why treating product development as business strategy prevents costly missteps that drain resources and delay market entry.
We'll explore how a strategic framework prevents common development pitfalls that sink promising products before they reach customers. You'll also learn why user-centered design business value extends beyond user satisfaction to create sustainable competitive advantages. Finally, we'll examine how systems engineering scalability and collaborative product strategy deliver outcomes that pure technical execution simply cannot match.
Product Strategy Creates Business Value Beyond Technical Implementation
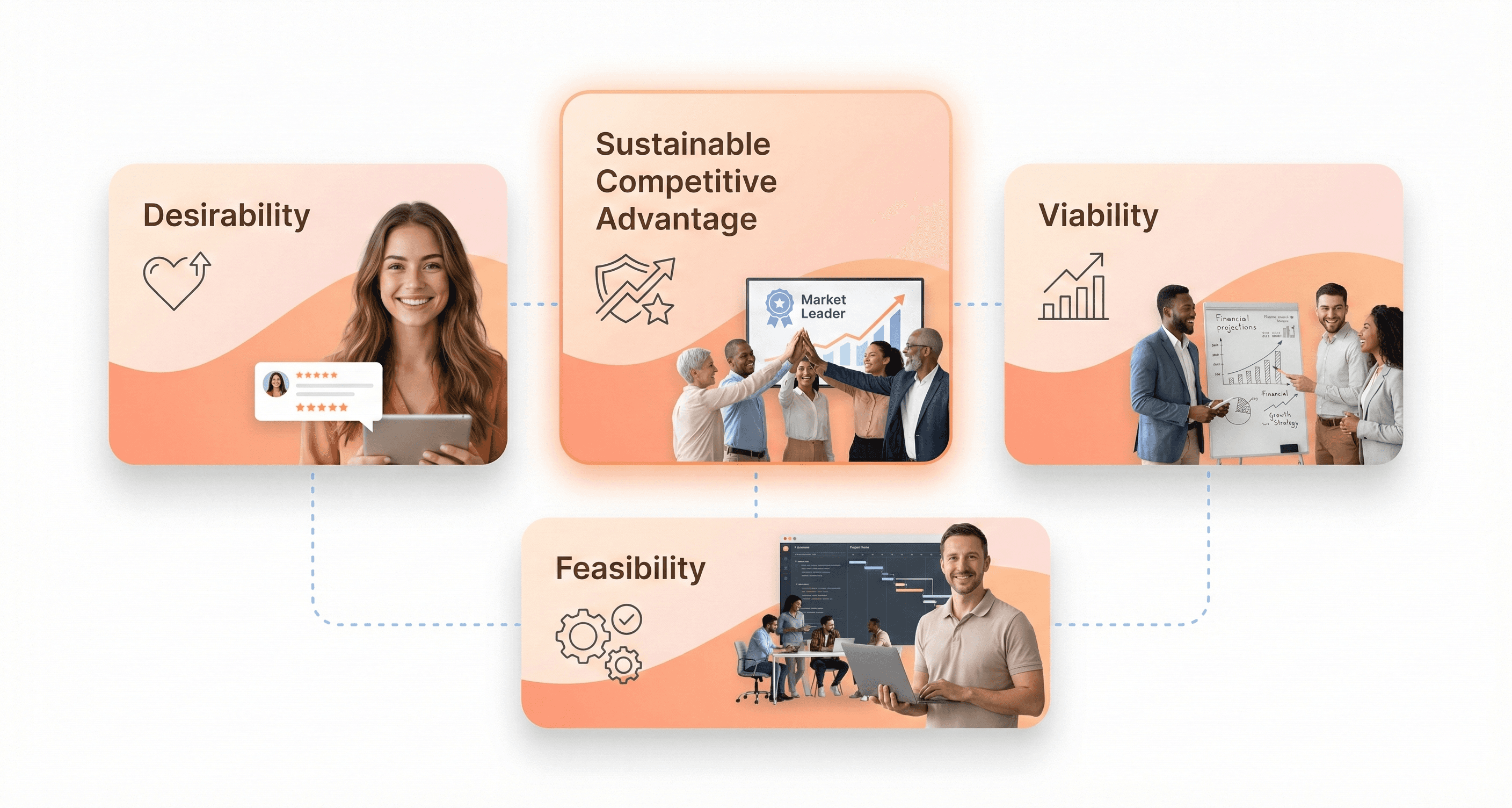
Balances product desirability, business viability, and engineering feasibility
Strategic product development recognizes that successful products exist at the intersection of three critical dimensions. Product desirability ensures that what you're building addresses genuine customer needs and pain points. Rather than developing features in isolation, a strategic framework evaluates whether customers actually want and will use the proposed functionality. This customer-centric approach prevents teams from building technically impressive solutions that nobody actually needs.
Business viability examines whether the product can generate sustainable value for the organization. This goes beyond basic profitability to consider factors like customer acquisition cost (CAC), customer lifetime value (CLV), monthly recurring revenue (MRR), and market positioning. A strategic product development approach ensures that engineering efforts align with measurable business outcomes rather than pursuing technical excellence for its own sake.
Engineering feasibility evaluates whether the proposed solution can be built within technical constraints, resource limitations, and timeline requirements. This dimension prevents teams from committing to unrealistic deliverables that could derail entire product initiatives. By balancing all three elements, product teams avoid the common trap of optimizing for only one dimension at the expense of the others.
Provides objective frameworks for decision-making alignment
Strategic frameworks eliminate the guesswork and subjective decision-making that often plague product development efforts. When teams operate without clear strategic guidelines, they frequently make decisions based on personal preferences, internal politics, or the loudest voice in the room. A well-defined product strategy framework creates objective criteria for evaluating competing priorities and feature requests.
These frameworks establish measurable goals and key performance indicators (KPIs) that serve as reference points for all product decisions. Teams can compare potential initiatives against established success metrics such as user engagement, retention rates, or conversion improvements. This data-driven approach ensures that resource allocation decisions support the overall product vision rather than short-term tactical considerations.
The framework also facilitates cross-functional alignment by providing a common language and set of priorities that all stakeholders can reference. When engineering, marketing, sales, and product teams all understand the strategic objectives, they can make autonomous decisions that still support the broader business goals. This alignment accelerates development cycles and reduces the need for constant escalation and re-alignment meetings.
Reduces costly iterations and accelerates time to market
Strategic product development significantly reduces the expensive trial-and-error cycles that characterize many development efforts. By conducting thorough market research, competitor analysis, and user needs assessment upfront, teams can identify potential issues before they become costly problems during development. This front-loaded strategic work prevents teams from building entire feature sets that ultimately don't resonate with target customers.
The strategic approach also prioritizes high-impact activities that drive the product forward most effectively. Rather than spreading development resources across multiple simultaneous initiatives, teams focus on the critical path items that will generate the greatest business value. This focused execution approach enables faster delivery of core functionality that customers actually want.
Additionally, strategic frameworks establish clear success criteria and measurement guidelines that enable teams to course-correct quickly when needed. Instead of continuing down unproductive development paths for months, teams can identify misalignment early and adjust their approach. This rapid feedback loop reduces wasted development cycles and ensures that engineering efforts consistently contribute to business objectives rather than becoming expensive technical experiments.
Strategic Framework Prevents Common Development Pitfalls
Avoids premature solution fixation that creates blind spots
A strategic product development framework prevents teams from rushing into manufacturing or technical implementation before truly understanding the problem space. As highlighted by industry experts, one of the most common pitfalls is rushing into manufacturing without fully aligning on the process across marketing, design, engineering, and manufacturing teams. This premature fixation on solutions creates dangerous blind spots that can derail entire projects.
When teams focus solely on the "race to market," critical steps get bypassed, leading to costly misunderstandings and unforeseen complications. The strategic framework requires honest conversations and checkpoints throughout the development process, ensuring that feature sets, target markets, and overall market positioning remain aligned with the original vision. Without this structured approach, even small misalignments can lead to costly adjustments later in the development cycle.
The framework also prevents the dangerous trap of product development by committee without strong leadership. While collaboration is essential, strategic frameworks establish dedicated leadership that bridges knowledge gaps across teams, ensuring alignment and minimizing miscommunication that could lead to solution fixation on unfeasible concepts.
Ensures products meet actual user needs and market demands
Now that we've covered solution fixation, the strategic framework's most critical function is maintaining focus on actual user requirements rather than assumed market demands. The reference to Google Glass serves as a powerful example of what happens when teams ignore customer needs - despite Google's technical prowess and significant investment, the product failed because there was no consensus among creators about core use cases.
Google Glass demonstrated how assumptions about user acceptance can be fatal. Both development groups believed the product's "hype" would compel users to adopt it, but they failed to validate whether users actually wanted to wear the device in public or found it socially acceptable. This lack of proper product/market fit analysis doomed the project from the outset.
A strategic product development framework incorporates the definition and validation of user requirements before embarking on costly development journeys. This includes regular opportunities for re-evaluation to ensure those needs are being met as the project continues. High-tech companies working at the edge of possibility particularly benefit from this approach, as they can avoid the expensive mistake of building technically impressive products that customers simply don't want.
The framework prevents teams from retreating into silos where developers obfuscate with complex technical explanations while business leads fixate on unrealistic solutions, ensuring continuous alignment with actual market demands.
Eliminates wasteful resource allocation on unfeasible concepts
With this strategic foundation in mind, the framework's third critical function is preventing the waste of resources on concepts that cannot deliver profitable, marketable products. The Magic Leap case study illustrates this perfectly - despite $4.5 billion in funding and seven years of development, the company struggled to release a viable consumer product that met market expectations.
Magic Leap's failure stemmed from embarking on product development without clear deliverables or completion criteria. The team kept tinkering and tweaking in a constant state of ongoing development, eventually running out of resources and market enthusiasm. Their AR product, which promised to "bend the digital world to your physical life," ultimately delivered a compromised experience where digital objects were poorly integrated with the physical environment.
A strategic framework eliminates this waste by establishing clear project governance and defined deliverables from the outset. It prevents the open-ended development cycles that characterized Magic Leap's approach, instead prioritizing return on investment in a structured and realistic way. The framework ensures teams can decide not just what to build, but when to stop - preventing the endless refinement cycles that drain resources without delivering market value.
This structured approach also addresses the fragmentation of processes across platforms that can create accountability gaps. Instead of losing track of decisions and requirements across multiple communication tools, strategic frameworks maintain centralized documentation and approval processes that prevent errors from amplifying over time.
User-Centered Design Acts as the Business User Advocate
Translates marketing vision into actionable engineering requirements
User-centered design serves as the critical bridge between marketing promises and technical implementation, ensuring that ambitious business visions become tangible product features. When marketing teams articulate value propositions about user experience, customer satisfaction, and product benefits, UCD translates these high-level concepts into specific, measurable requirements that engineering teams can execute.
This translation process involves conducting comprehensive user research to understand actual needs beyond marketing assumptions. Through interviews, surveys, and usability testing, UCD practitioners gather concrete data about user behaviors, pain points, and expectations. These insights transform abstract marketing concepts like "seamless experience" or "user-friendly interface" into precise technical specifications such as load times under 2 seconds, accessibility compliance standards, or specific interaction patterns.
User personas and journey mapping become the foundation for this translation, providing engineering teams with detailed profiles representing key audience segments. Each persona includes demographics, goals, challenges, behaviors, and decision-making patterns that directly inform technical architecture decisions. When engineers understand that their target user is a 45-year-old logistics manager working on mobile devices with limited bandwidth, they can make informed choices about data compression, offline functionality, and interface optimization.
Creates empathy-driven solutions that reinforce brand promise
The strategic value of user-centered design extends beyond functional requirements to emotional resonance between brands and their customers. UCD creates solutions that generate trust, loyalty, and emotional connection by designing from concrete user data rather than internal assumptions or business-centric viewpoints.
This empathy-driven approach directly supports business objectives by reducing customer acquisition costs and increasing lifetime value. When products genuinely address user needs and pain points, they create positive experiences that translate into higher conversion rates, reduced churn, and stronger brand loyalty. Users who feel understood and valued by a product experience are more likely to become brand advocates, driving organic growth through referrals and positive reviews.
The business impact becomes measurable through improved Net Promoter Scores, reduced customer service costs, and higher user satisfaction ratings. Companies implementing user-centered design strategies consistently achieve better results than those relying on assumption-based development approaches. The iterative nature of UCD ensures continuous alignment between evolving user needs and product capabilities, maintaining competitive advantage in dynamic markets.
Establishes shared understanding across cross-functional teams
User-centered design creates a unified vision that aligns diverse stakeholders around common user objectives, eliminating the siloed thinking that often derails product development initiatives. When UX designers, product managers, engineers, marketers, and business stakeholders all reference the same user personas, journey maps, and research insights, decision-making becomes more efficient and strategically coherent.
This shared understanding manifests through collaborative workshops where cross-functional teams participate in persona creation, journey mapping, and usability testing sessions. Marketing teams gain realistic perspectives on user capabilities and constraints, while engineering teams develop deeper appreciation for user context and emotional drivers. Product managers can make informed prioritization decisions based on actual user impact rather than internal politics or assumptions.
The collaborative strategy process delivers competitive advantages by ensuring all team members design with empathy and awareness of real user needs. When everyone understands the personas and their specific contexts, teams avoid costly design mistakes, reduce development iterations, and create products with long-term market viability. This alignment prevents common development pitfalls where different departments work toward conflicting objectives, ultimately delivering a cohesive product that serves both user needs and business goals effectively.
Systems Engineering Ensures Product Viability and Scalability
Maintains holistic oversight of complex product requirements
Systems engineering provides the critical framework for maintaining comprehensive oversight of intricate product requirements throughout the development lifecycle. Unlike traditional engineering approaches that may focus on individual components, systems engineering takes a holistic view that considers how all elements interact within the broader product ecosystem.
This approach becomes essential when dealing with complex products that must satisfy multiple stakeholders, technical constraints, and business objectives simultaneously. Systems engineers ensure that requirements from different domains—whether technical, regulatory, user experience, or business—are properly integrated and balanced against each other. They identify potential conflicts early in the development process, preventing costly redesigns and ensuring that the final product meets all specified requirements.
The holistic oversight extends beyond immediate technical requirements to encompass long-term considerations such as maintainability, upgradability, and integration with existing systems. This comprehensive perspective helps product teams avoid the common pitfall of optimizing individual components at the expense of overall system performance.
Balances technical feasibility with manufacturing constraints
One of the most critical aspects of systems engineering in product development is the ability to balance ambitious technical goals with real-world manufacturing limitations. This balance requires deep understanding of both cutting-edge technical possibilities and practical production realities.
Systems engineers work closely with manufacturing teams to ensure that innovative designs can be produced at scale without compromising quality or significantly inflating costs. They evaluate trade-offs between technical performance and manufacturing complexity, helping teams make informed decisions about which features to prioritize and which constraints to accept.
This balancing act extends to supply chain considerations, material availability, and production timelines. By considering these factors early in the design process, systems engineering prevents the common scenario where technically sound designs prove impossible or prohibitively expensive to manufacture at commercial scale.
The approach also involves continuous assessment of emerging manufacturing technologies and processes that might enable new design possibilities or reduce production constraints over time.
Supports long-term business goals through scalable solutions
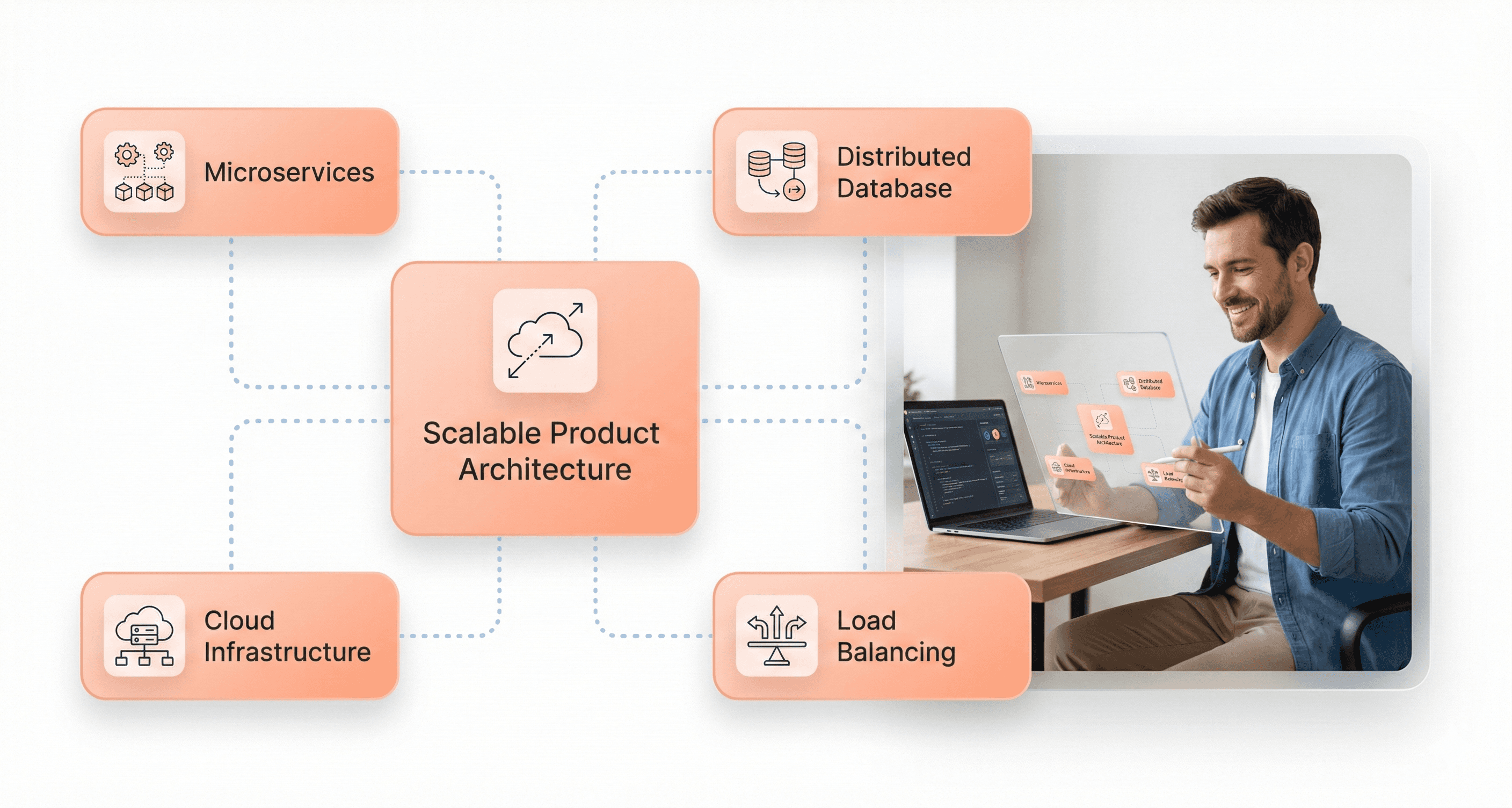
Systems engineering serves as a strategic enabler by ensuring that product development efforts align with and support broader business objectives. This involves architecting solutions that can scale efficiently as demand grows and business requirements evolve.
Scalable solutions require careful consideration of system architecture from the earliest design phases. As demonstrated in modern distributed systems, proper architectural decisions—such as implementing microservices, distributed databases, and cloud-native approaches—enable products to handle exponential growth in users and data without requiring complete system redesigns.
Systems engineers evaluate multiple scaling scenarios and build flexibility into the product architecture to accommodate future growth. This includes planning for horizontal scaling capabilities, implementing proper load balancing strategies, and ensuring that individual components can be upgraded or replaced without disrupting the entire system.
The strategic value extends to supporting business expansion into new markets, geographies, or customer segments. By building adaptable systems that can accommodate different regulatory environments, languages, or business models, systems engineering creates the foundation for sustainable business growth and competitive advantage in evolving markets.
Collaborative Strategy Process Delivers Competitive Advantages
Creates solution-neutral frameworks that guide development decisions
Building collaborative product strategy competitive advantage begins with establishing solution-neutral frameworks that prevent teams from jumping to premature technical solutions. These frameworks serve as guardrails that keep development focused on customer value rather than engineering preferences. When teams operate without clear strategic boundaries, they often pursue technically interesting solutions that may not align with business objectives or user needs.
Solution-neutral frameworks force teams to clearly articulate problems before exploring solutions. This approach prevents the common pitfall where engineering teams become attached to specific technologies or architectures before fully understanding the business context. By maintaining neutrality about implementation approaches, teams can evaluate multiple pathways and select the most appropriate solution based on strategic criteria rather than technical familiarity.
These frameworks also create shared language between business stakeholders and technical teams. When everyone understands the strategic parameters and success metrics, decision-making becomes more collaborative and less siloed. This collaborative approach ensures that technical decisions support broader business goals while maintaining engineering excellence.
Enables faster market entry through reduced redesign cycles
Now that we have covered how frameworks guide decisions, let's examine how collaborative strategy processes accelerate time-to-market through strategic alignment. When teams embrace collaborative advantage over competitive advantage approaches, they significantly reduce costly redesign cycles that plague traditional product development.
The collaborative strategy process creates alignment between stakeholders before development begins, eliminating the expensive back-and-forth that occurs when different groups have conflicting assumptions about product requirements. Instead of discovering misalignments during development or testing phases, collaborative frameworks surface these issues during strategic planning.
This upfront investment in alignment pays dividends throughout the development lifecycle. Teams spend less time reworking features that don't meet business requirements or user expectations. The collaborative approach also enables parallel workstreams, as different team members can work confidently knowing their efforts align with the overall strategic direction.
Furthermore, collaborative strategies help teams identify potential market disruptions and opportunities that might not be visible through competitive analysis alone. As noted in the reference material, the biggest disruptions often don't come from direct competitors, making collaborative market understanding more valuable than purely competitive positioning.
Maximizes resource efficiency by clarifying requirements upfront
With this foundation of collaborative alignment established, teams can maximize resource efficiency through clear upfront requirements definition. The collaborative strategy process ensures that all stakeholders contribute their perspectives during the planning phase, creating comprehensive requirements that reflect both business needs and technical constraints.
This comprehensive requirements gathering prevents the resource waste that occurs when teams build features that don't align with business objectives or user needs. By engaging all relevant parties in the strategy process, teams avoid the costly cycle of building, testing, and rebuilding that characterizes less collaborative approaches.
The collaborative process also helps teams identify opportunities for resource sharing and partnership development. Rather than trying to build every capability internally, teams can identify strategic partnerships that extend their capabilities while reducing resource requirements. This approach leverages the broader business ecosystem to create value more efficiently than isolated competitive strategies.
Additionally, clear upfront requirements enable better resource allocation across different aspects of product development. Teams can prioritize features based on strategic importance and resource constraints, ensuring that limited resources focus on the highest-value activities. This strategic resource allocation is particularly important in today's environment where the ability to maintain competitive advantage has diminished over time, making efficient resource utilization even more critical for sustainable success.
Strategic Outsourcing Enhances Product Development Outcomes
Brings neutral third-party perspective to balance competing priorities
Strategic outsourcing product development provides an invaluable external viewpoint that helps organizations navigate complex internal dynamics and competing priorities. When companies develop products in-house, they often face challenges from politics, clashing personalities, unequal contributions, and different ways of working that can be time-consuming hurdles before teams function efficiently. An outsourced development partner brings objectivity to decision-making processes, helping companies see the forest through the trees.
External teams constantly stress-test assumptions and risk factors to ensure de-risking at every step of development. They challenge internal thinking, bring fresh perspectives, and uncover risks that may not be visible from inside the organization. This neutral stance prevents costly redesigns, delays, and setbacks that often arise when risks are overlooked early on due to internal biases or blind spots.
Rather than following a linear, rigid development plan influenced by internal politics or established ways of thinking, outsourced teams focus on tackling the biggest risks first. This approach allows for early course-correction, ensuring that subsequent design iterations are built on a strong foundation. Whether addressing feasibility concerns, technical bottlenecks, or supply chain constraints, external partners address risks head-on to keep projects on track and within budget.
Leverages specialized expertise to eliminate development blind spots
Many companies have a strong product vision and clear technical and financial goals, but often lack a full understanding of the risks involved in bringing products to life. They may not have tested assumptions, examined potential failure points, or gained experience moving from concept to production. Strategic outsourcing provides access to specialized expertise that eliminates these critical knowledge gaps.
The multidisciplinary approach offered by outsourcing partners addresses one of the most significant challenges in product development: the need for expertise across multiple engineering disciplines—mechanical, electrical, software, automation, and more. Hiring specialists for each discipline is costly and complex, but outsourcing provides access to a complete, integrated team that has already solved similar challenges.
Companies gain access to a team of 40+ professionals for the cost of hiring just one or two full-time employees. This expertise comes with proven processes, refined development methodologies, and experience across industries that helps navigate uncertainties and avoid common pitfalls. External partners also provide access to advanced tools and simulation capabilities like Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) and Finite Element Analysis (FEA) that many companies cannot justify investing in for a single project.
Integrates manufacturing readiness into early-stage planning
One of the most critical advantages of strategic outsourcing product development is the integration of manufacturing considerations from the earliest stages of product planning. External development partners bring manufacturing readiness expertise that prevents costly redesigns and delays later in the development cycle.
Experienced outsourcing teams understand the critical importance of designing for manufacturability from the outset. They eliminate structural weaknesses in fabrication processes, optimize production dynamics through advanced simulation tools, and implement automation to ensure precision and scalability. This early integration of manufacturing considerations ensures that products can move smoothly from prototype to production without major design overhauls.
The manufacturing readiness approach includes evaluating supply chain constraints, material selection, production scalability, and quality control measures during the design phase. This comprehensive view prevents the common scenario where products must be redesigned because manufacturing requirements were not considered early enough in the development process.
External partners also bring experience with different manufacturing methods and can recommend the most cost-effective and scalable approaches for specific product requirements. This expertise is particularly valuable for companies developing outside their core competency, as they may not fully understand the manufacturing implications of their design decisions.
Conclusion
Product development that treats strategy as an afterthought risks creating technically sound products that fail in the marketplace. The most successful companies recognize that product strategy must drive every development decision, from initial concept through final manufacturing. By establishing frameworks that balance user needs, business objectives, and technical feasibility upfront, organizations avoid costly redesigns and accelerate their path to market success.
The collaboration between User-Centered Design and Systems Engineering creates the foundation for products that not only function well but truly resonate with their intended audience. Whether executed by internal teams or through strategic partnerships with experienced engineering services providers, this approach ensures that every product delivers on its brand promise while meeting real user needs. Companies that invest in formal product strategy processes don't just bring products to market—they bring solutions that drive sustainable competitive advantage and meaningful growth.

About the author
Author Name:
Parth G
|
Founder of
Hashbyt
I’m the founder of Hashbyt, an AI-first frontend and UI/UX SaaS partner helping 200+ SaaS companies scale faster through intelligent, growth-driven design. My work focuses on building modern frontend systems, design frameworks, and product modernization strategies that boost revenue, improve user adoption, and help SaaS founders turn their UI into a true growth engine.