
Enterprise leaders are investing billions in AI, yet most initiatives fail to move beyond pilot programs. This AI adoption checklist for enterprise application modernization helps IT leaders, operations managers, and enterprise architects navigate the complex journey from experimentation to production-scale AI integration.
Who this guide serves: CIOs, IT directors, enterprise architects, and operations teams responsible for modernizing legacy systems while building AI-ready infrastructure that delivers measurable business value.
This comprehensive framework covers three critical areas that determine AI success. First, we'll explore how to establish clear business objectives and assess your data foundation before writing a single line of code. Next, you'll learn to prepare your technical infrastructure and build the right talent mix within existing teams. Finally, we'll walk through implementing governance frameworks and designing strategic pilot programs that scale from proof-of-concept to enterprise-wide deployment.
Skip the common pitfalls that trap 70% of AI projects in development limbo. This practical roadmap ensures your AI implementation strategy aligns with real business outcomes, not just technological possibilities.
Establish Clear Business Objectives Before AI Implementation
Define specific business problems that AI will solve
Enterprise AI transformation must begin with precise problem identification rather than technology-first thinking. According to research findings, the winners will not be the companies that try the most pilots, but those that connect an AI business strategy to revenue, cost, and risk outcomes the board already cares about.
Successful AI implementation strategy requires mapping AI opportunities directly to measurable business pain points. This involves identifying business units with the highest value potential and connecting AI initiatives to specific operational challenges such as:
Revenue uplift opportunities through improved forecasting, pricing optimization, or customer personalization
Cost reduction initiatives via process automation, predictive maintenance, or resource optimization
Risk mitigation through fraud detection, compliance automation, or safety prediction systems
Operational efficiency gains by eliminating manual workflows, reducing errors, or accelerating decision-making
The most effective approach involves facilitating cross-functional workshops that extract business pain points and translate them into high-ROI candidate use cases. Enterprise leaders should engage business owners early in this process to ensure eventual adoption and alignment with existing workflows.
Determine if AI is the right approach versus traditional automation
Not every business problem requires AI intervention. Enterprise application modernization teams must distinguish between scenarios that benefit from intelligent systems versus those better served by traditional automation or process improvements.
AI proves most valuable when dealing with:
Complex pattern recognition in large datasets where traditional rules-based systems fall short
Predictive scenarios requiring analysis of multiple variables and historical trends
Unstructured data processing such as document intelligence, image analysis, or natural language understanding
Dynamic optimization where conditions change frequently and require continuous adaptation
Traditional automation remains more appropriate for:
Well-defined, repeatable processes with clear business rules
Simple data transformations or scheduled batch operations
Scenarios with limited data availability or static conditions
Cost-sensitive applications where simpler solutions provide adequate results
The decision framework should evaluate data availability, process complexity, regulatory requirements, and cost-benefit ratios. Organizations should prefer the simplest effective method, using classical approaches where signals are stable and reserving AI for scenarios requiring sophisticated pattern recognition or predictive capabilities.
Set measurable success criteria for ROI and efficiency gains
Enterprise AI readiness depends on establishing clear, quantifiable metrics before any development begins. Every AI initiative must tie directly to measurable business outcomes rather than technical achievements or model performance alone.
Effective success criteria should encompass:
Financial Metrics:
Revenue impact through improved conversion rates, pricing optimization, or new service capabilities
Cost reduction via automated processes, reduced manual effort, or operational efficiency
Risk mitigation value through prevented losses, compliance improvements, or safety enhancements
Operational KPIs:
Process efficiency gains measured in time savings, throughput improvements, or error reduction
Quality improvements in decision-making, forecasting accuracy, or customer satisfaction
Scalability metrics demonstrating the system's ability to handle increased volume or complexity
Adoption and Change Metrics:
User engagement with AI-enabled workflows
Training completion rates and competency development
Integration success across existing systems and processes
The measurement framework should include both leading indicators (usage metrics, data quality scores) and lagging indicators (revenue impact, cost savings achieved). Establishing baseline measurements before AI implementation ensures accurate ROI calculation and provides clear benchmarks for success evaluation.
Organizations should set realistic timelines for value realization, typically expecting initial gains within 90-180 days for well-scoped use cases, with full impact measurable within 12-18 months. This approach ensures AI adoption checklist items remain tied to business value rather than technical milestones alone.
Assess Your Data Foundation and Quality Standards
Evaluate data accessibility, completeness, and reliability
Before implementing any AI initiative, organizations must thoroughly assess their existing data foundation. According to industry research, between 33% and 38% of AI initiatives suffer delays or failures from inadequate data quality, making this evaluation critical for enterprise AI readiness.
Data accessibility involves ensuring that relevant data can be easily retrieved and utilized across different systems and departments. This means breaking down data silos and creating unified datasets that AI models can effectively leverage. Organizations need to map out where their data resides, who has access to it, and how quickly it can be retrieved for AI processing.
Completeness assessment focuses on identifying gaps in your datasets that could compromise AI model performance. Incomplete data can cause AI models to make incorrect conclusions, particularly in critical business applications. For example, in the financial sector, an AI-driven credit scoring model with incomplete historical data may exhibit bias toward particular demographics, resulting in unfair lending decisions.
Reliability evaluation examines whether your data accurately reflects current business conditions. In industries like retail and banking, obsolete data can lead to missed opportunities or incorrect risk assessments. AI models require current, accurate data to function effectively, making reliability a cornerstone of successful AI implementation.
Establish data governance policies and ownership
Data governance serves as the foundation for AI readiness by establishing defined policies and regulations over how data is collected, stored, and accessed within an organization. This structured approach ensures that data deployed in AI projects will be ethical, unbiased, and trustworthy.
Effective data governance involves defining clear data ownership, establishing access controls, and ensuring compliance with relevant regulations. By creating these frameworks, organizations can prevent data misuse and ensure high-quality datasets for training AI models. This structured approach not only protects sensitive information but also helps build reliable and accurate information systems that support compliant decisions and drive innovation with confidence.
Organizations should designate data stewards responsible for maintaining data quality standards and implementing governance policies across different departments. These policies should address data collection protocols, storage requirements, access permissions, and usage guidelines that align with your AI implementation strategy.
Identify and address data quality issues and biases
Data quality encompasses several critical elements that directly impact AI performance. Accuracy ensures that data correctly reflects real-world scenarios - inaccurate customer data can cause AI models to make faulty predictions, leading to poor marketing strategies or customer service decisions.
Consistency requires that data remains uniform across systems and datasets. Inconsistent data can produce contradictory findings and make AI-driven conclusions untrustworthy. For example, a global retailer with inconsistent inventory data across countries may cause AI-driven supply chain models to overestimate or underestimate stock needs.
Data cleansing becomes essential for eliminating inaccuracies and inconsistencies that could compromise AI model performance. This process involves identifying and correcting errors such as duplicate entries, missing values, or incorrect data formats. Clean data helps AI models generate more accurate insights and informed predictions while avoiding biases that could arise from poor data quality.
Organizations should implement automated data quality monitoring systems that can detect anomalies and inconsistencies before they impact AI initiatives. These systems should use unsupervised machine learning to learn historical patterns in data and identify unexpected changes or quality issues.
Ensure compliance with privacy and regulatory requirements
Compliance considerations become particularly crucial in highly regulated industries like finance and healthcare, where data privacy and accuracy requirements are stringent. Poor data quality can lead to regulatory violations, investigations, penalties, and legal action, especially when AI algorithms produce biased or incorrect results.
Organizations must establish frameworks that address data privacy regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or industry-specific compliance requirements. These frameworks should include data anonymization procedures, consent management processes, and audit trails that demonstrate compliance with regulatory standards.
Privacy protection measures should be built into data collection, storage, and processing workflows from the beginning. This includes implementing encryption protocols, access logging, and data retention policies that align with regulatory requirements while supporting AI implementation goals.
Regular compliance audits should be conducted to ensure that data governance policies remain effective and up-to-date with evolving regulatory landscapes. These audits should assess both technical compliance measures and organizational adherence to established data governance frameworks.
Prepare Your Technical Infrastructure for AI Integration
Assess current systems integration capabilities and API availability
With your business objectives and data foundation evaluated, the next critical step in your AI adoption checklist involves conducting a thorough assessment of your existing technical infrastructure. Enterprise AI integration connects artificial intelligence systems with existing enterprise applications, data sources, and workflows so AI can actively participate in how the organization operates.
Begin by evaluating your current systems integration capabilities across key enterprise platforms. Common enterprise systems that require AI integration include CRM platforms for customer engagement, ERP systems for operations and finance, contact center platforms for service and support, case management and ticketing systems, and knowledge management repositories. Document your existing API landscape and determine which systems already offer REST APIs, streaming capabilities, or event-driven architectures that can support AI connectivity.
Modern enterprise AI integration relies heavily on API-first and event-driven architectures. Your assessment should identify systems that support REST and streaming APIs for system connectivity, event-based triggers for real-time AI responses, microservices for modular integration, and asynchronous messaging for scalability. These patterns allow AI to respond dynamically to enterprise events and operational changes.
Integration spans multiple architectural layers that must be evaluated: the data integration layer that aggregates enterprise data, the application integration layer connecting AI to business systems, the workflow integration layer embedding AI into processes, the API and event layer enabling real-time interaction, and the monitoring layer providing visibility and control.
Determine cloud, on-premises, or hybrid deployment strategy
Now that you've assessed your integration capabilities, determining the optimal deployment strategy becomes crucial for your AI infrastructure requirements. The choice between cloud, on-premises, or hybrid deployment significantly impacts performance, cost, and scalability of your AI initiatives.
Cloud-hosted AI infrastructure offers quick deployment and burst capacity but introduces several considerations for enterprise application modernization. Significant subscription costs, substantial data transit expenses, and introduced latencies can impact performance. Many organizations experience cost spirals when multiple teams instantiate separate AI cloud subscriptions, leading to lost resources, limited service features, poor collaboration, and data governance gaps.
On-premises AI infrastructure provides greater control and can be more cost-effective at scale. Enterprise data centers offer resource maximization, cost efficiency, centralized data management, enhanced security and governance, standardization, and skills leverage. However, traditional enterprise infrastructure often cannot support deep AI processing at the required speed and scale without significant upgrades.
A hybrid approach combining on-premises core infrastructure with cloud burst capacity often provides the optimal balance. This strategy enables organizations to maintain control over sensitive data and critical workloads while leveraging cloud resources for peak demands and specialized AI services. The hybrid model supports both real-time integration for live recommendations and in-workflow automation, as well as asynchronous integration for background processing and batch analysis.
Consider implementing an AI center of excellence that consolidates high-performance AI infrastructure. This centralized approach can reduce overall costs while accelerating AI initiatives across the organization through resource sharing, common tooling, and enhanced collaboration.
Establish MLOps capabilities and model management systems
Moving beyond deployment strategy, establishing robust MLOps capabilities becomes essential for sustainable AI operations. MLOps encompasses the practices and technologies needed to deploy, monitor, and manage machine learning models throughout their lifecycle in production environments.
Your MLOps framework must support both real-time and asynchronous AI execution models. Real-time integration supports live recommendations, in-workflow automation, customer-facing interactions, and conversational AI for immediate responses. Asynchronous integration handles background processing, batch analysis, long-running workloads, and compute-intensive operations that don't require immediate responses.
Model management systems should provide version control for AI models, automated deployment pipelines, performance monitoring, and rollback capabilities. These systems must integrate with your existing enterprise applications while maintaining security and compliance standards. The infrastructure should support model retraining, A/B testing of different model versions, and seamless updates without disrupting business operations.
Enterprise AI platforms are specifically designed to support these integration layers, enabling scalable, secure, and adaptable AI integration across the organization. Your MLOps capabilities should align with enterprise AI governance frameworks to ensure controlled execution paths, approved data sources, and policy adherence throughout the model lifecycle.
Implement monitoring, logging, and audit frameworks
Finally, comprehensive monitoring, logging, and audit frameworks form the foundation of reliable AI operations and governance compliance. These frameworks provide essential visibility into AI system performance, decision-making processes, and business impact across your enterprise application modernization initiative.
Your monitoring strategy should encompass multiple dimensions of AI system performance. Infrastructure monitoring tracks compute resources, storage utilization, and network performance to ensure optimal system operation. Model performance monitoring evaluates prediction accuracy, drift detection, and business metric alignment to maintain AI effectiveness over time.
Implement logging mechanisms that capture AI decision paths, input data characteristics, and output rationales. This audit trail becomes crucial for regulatory compliance, particularly when AI systems can initiate actions within enterprise workflows. Governance-aligned integration requires auditability of AI-driven actions, monitoring for policy adherence, and ensuring data quality through integrity checks and governance controls.
Security monitoring must address the unique challenges introduced by AI integration with enterprise systems. Key considerations include secure authentication and authorization, encryption of data in transit between systems, segmentation of AI workloads, monitoring for unauthorized access, and compliance with regional and industry regulations. This is particularly important for protecting sensitive data and ensuring data privacy when AI systems access customer information.
Your audit framework should provide comprehensive reporting capabilities that demonstrate AI system compliance with governance policies, security standards, and business objectives. This includes tracking AI system usage patterns, performance metrics, and business outcomes to support continuous improvement and stakeholder reporting requirements.
Build Skills and Talent Readiness Within Existing Teams
Identify required skills across data, engineering, and domain expertise
Building AI readiness within your existing teams requires a strategic assessment of skill requirements across three critical areas. Based on enterprise research, organizations need foundational skills spanning data professionals, developers, IT professionals, and business stakeholders to ensure successful AI adoption.
Data professionals must develop advanced prompt engineering fundamentals and context-setting abilities to effectively communicate with AI systems. This includes writing clear, specific instructions that produce accurate outputs and understanding how to provide background information AI needs to comprehend complex business requirements.
Engineering teams require technical skills for AI integration, including system prompts, structured prompting techniques, and automation capabilities. Developers need hands-on experience with AI platforms and the ability to build department-specific AI workflows that integrate seamlessly with existing enterprise applications.
Domain expertise becomes equally critical as business users must understand AI limitations and develop role-specific applications. According to industry data, trained employees demonstrate 2.7x higher proficiency than self-taught workers, highlighting the importance of formal skill development programs.
Develop training programs for business stakeholders on AI literacy
Enterprise AI literacy programs should address three proficiency tiers to maximize organizational readiness. Research shows that only 35% of employees have received any AI training, despite 94% of CEOs prioritizing AI skills as essential for business transformation.
Tier 1 foundational training should cover all employees with core competencies including understanding AI capabilities and limitations, writing clear prompts, providing context and background information, specifying output formats, and basic iteration techniques. This foundational layer also encompasses company AI policies and compliance requirements essential for enterprise governance.
Tier 2 advanced training targets knowledge workers with role-specific prompt templates, multi-step prompting for complex tasks, few-shot learning with examples, and integration with existing workflows. This level focuses on building personal prompt libraries and developing quality control processes for output verification.
Tier 3 expert training creates internal AI champions who can build department-specific workflows, train colleagues, and evaluate AI tools for enterprise adoption. These power users develop advanced automation capabilities and serve as bridges between technical teams and business stakeholders.
Create coordination strategies to maximize existing team capabilities
Successful AI adoption relies on structured coordination that leverages existing organizational strengths while building new capabilities. The most effective approach involves identifying internal AI champions within each department who can support peer learning and knowledge transfer.
Weekly 45-minute team learning sessions drive the highest adoption rates, with teams completing short lessons together, practicing prompting in real work scenarios, and sharing discoveries. This collaborative approach builds momentum as a community rather than relying on isolated individual learning through self-service courses.
Cross-departmental knowledge sharing becomes essential for maximizing AI implementation across enterprise applications. Organizations should establish internal prompt libraries and templates that teams can access and contribute to, creating a collaborative knowledge base that grows with organizational experience.
The coordination strategy should include regular skill assessments and continuous learning paths that align with career development goals. Research indicates that 77% of employees expect AI to affect their careers within five years, making coordination with professional development crucial for retention and engagement.
Plan for change management and adoption support
Effective change management for AI adoption requires addressing the significant skills gap that currently costs businesses $5.5 trillion in lost productivity globally. Only 6% of employees feel comfortable using AI tools, indicating substantial change management needs for enterprise transformation.
The implementation roadmap should begin with assessment phases that audit current AI tool usage, identify high-impact roles, and establish baseline skill measurements. Pilot programs with 20-50 employees from priority departments allow organizations to gather feedback, refine approaches, and document early productivity gains before broad rollout.
Change management must address generational disparities in AI comfort levels, with only 20% of Baby Boomers receiving AI training compared to 50% of Gen Z workers. Support structures should accommodate different learning preferences and comfort levels while maintaining consistent enterprise standards.
Organizations implementing comprehensive AI training report 27% average productivity improvements and $8,700 per employee annually in efficiency gains. These metrics demonstrate that proper change management and adoption support deliver measurable ROI of $3.70 per dollar invested, making the business case for structured transformation programs compelling for enterprise application modernization initiatives.
Implement Governance, Ethics, and Security Frameworks
Establish responsible AI policies and acceptable use guidelines
Implementing robust AI governance frameworks begins with developing comprehensive responsible AI policies that define acceptable use parameters across your organization. These policies must establish clear boundaries for AI system deployment, outlining what constitutes appropriate AI usage within your enterprise environment. According to industry frameworks, responsible AI policies should encompass key principles including human oversight, transparency, accountability, safety, fairness and non-discrimination, privacy and data protection, proportionality, and human-centric design.
Your acceptable use guidelines should clearly define prohibited AI applications, such as social scoring systems or other high-risk uses that regulatory frameworks like the EU AI Act explicitly ban. These policies must also establish approval processes for AI implementations, requiring structured review workflows that evaluate potential risks before deployment. Organizations should develop tiered policies that correspond to different risk levels - from minimal risk applications requiring basic oversight to high-risk systems demanding extensive governance controls.
The policy framework should integrate seamlessly with existing organizational governance structures rather than operating in isolation. This means aligning AI policies with current data management practices, security protocols, and business objectives. Effective policies also require clear ownership assignment, with designated data stewards overseeing data quality, AI leads managing implementation, and compliance officers handling regulatory risks.
Ensure model transparency, fairness, and explainability standards
Model transparency forms the foundation of trustworthy AI systems, requiring organizations to implement comprehensive documentation practices throughout the AI lifecycle. This includes maintaining clear, accessible records of data sources, model assumptions, training methodologies, and evaluation processes. Systematic tracking of lineage, versioning, and model behaviors enables teams to trace decision-making processes and identify contributing factors when issues arise.
Fairness standards demand proactive bias identification and mitigation strategies across data collection, model training, and production monitoring phases. Organizations must implement techniques such as disparate impact analysis, bias detection metrics, and representative sampling strategies to understand how model outputs vary across different user groups. Continuous fairness assessments allow teams to identify drift or inequities as real-world usage patterns evolve.
Explainability requirements vary based on the AI system's risk classification and industry context. For regulated industries like healthcare and finance, both technical and non-technical stakeholders must be able to understand and assess AI-driven outputs. This necessitates implementing transparency tools such as execution graphs, confidence scores, and traceable reasoning chains. Organizations should embed explainability mechanisms directly into their AI development workflows, ensuring that interpretability is built-in rather than added retrospectively.
Create risk assessment and mitigation strategies
Comprehensive risk assessment frameworks must evaluate multiple dimensions of AI-related risks, including bias, model drift, data leakage, privacy breaches, and performance degradation. Organizations should adopt structured risk assessment methodologies that map AI use cases against associated risk levels, enabling proportionate application of safeguards based on potential impact.
Risk mitigation strategies should encompass both preventive measures and responsive controls. Preventive strategies include implementing differential privacy techniques, adversarial testing protocols, red-teaming exercises tailored to domain-specific risks, and representative training dataset requirements. These measures help identify and address potential issues before AI systems reach production environments.
Organizations must establish automated monitoring pipelines to track performance metrics, fairness indicators, and policy compliance in production environments. When risks materialize, structured incident response procedures ensure rapid identification, containment, and remediation of issues. This includes implementing retraining procedures, conducting structured incident reviews, and maintaining updated documentation to support continuous improvement.
Risk management requires ongoing evaluation and adaptation as AI systems evolve. Regular audits against established governance frameworks verify continued compliance with risk management requirements. Organizations should implement versioning and audit trails to track system evolution, enabling teams to understand how changes impact risk profiles over time.
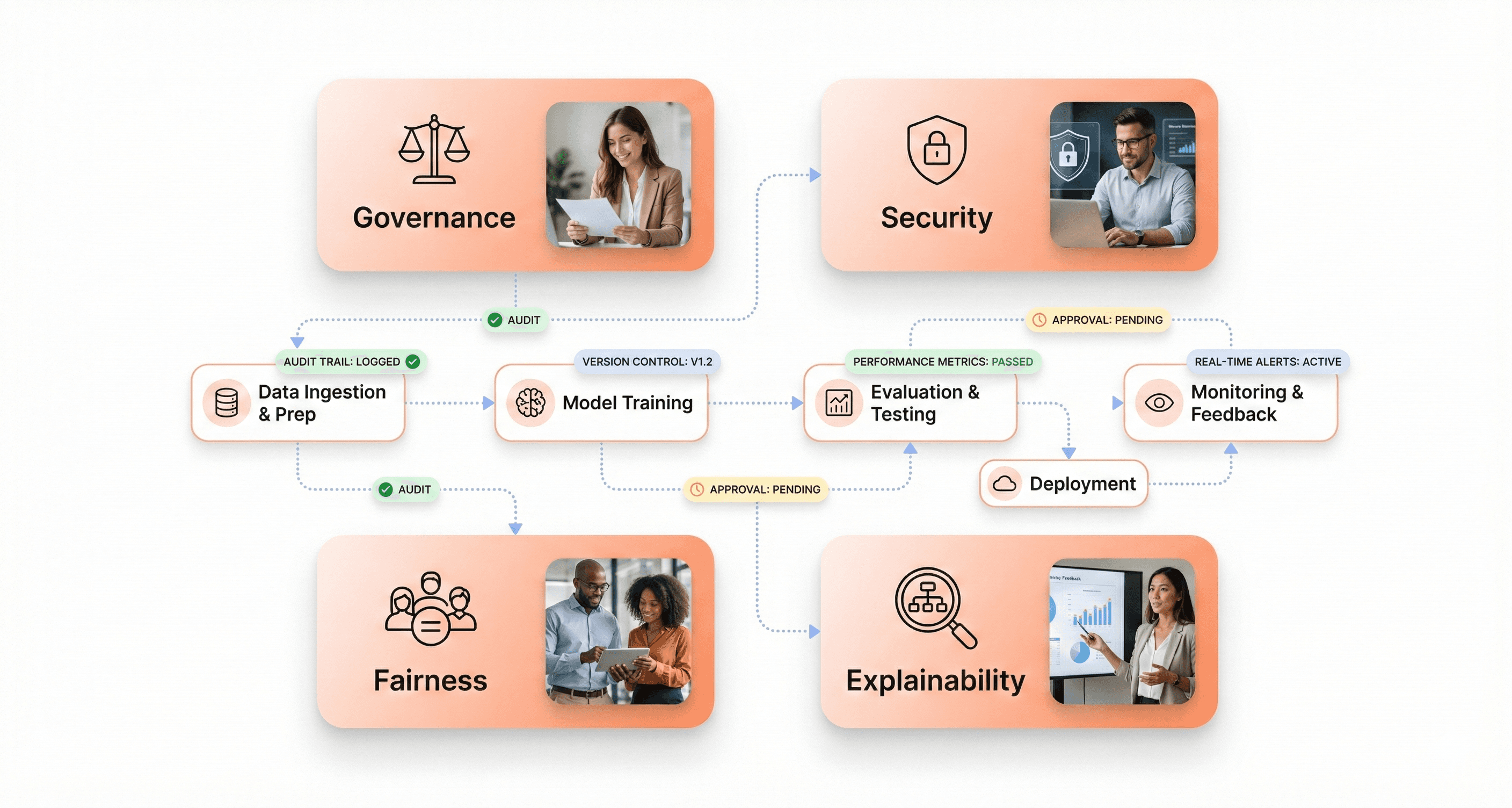
Implement end-to-end security for AI pipelines
End-to-end AI pipeline security requires implementing comprehensive protection measures across every stage of the AI lifecycle, from initial data ingestion through model deployment and ongoing operations. Organizations must deploy AI systems in secure environments, utilizing virtual private clouds (VPCs) or on-premises infrastructure to maintain control over data access, model behavior, and system integrity.
Access controls form the cornerstone of AI pipeline security, requiring implementation of role-based permissions that restrict system access based on job responsibilities and business requirements. Security frameworks must include output validation mechanisms that verify AI system responses meet established quality and safety standards before reaching end users. Comprehensive audit logging enables oversight, accountability, and traceability throughout the AI lifecycle.
Data protection measures must address both data at rest and data in transit, implementing encryption protocols that safeguard sensitive information throughout processing pipelines. Organizations should establish secure data sourcing practices that verify data provenance and maintain data quality standards. This includes implementing schema enforcement, lineage tracking, and controlled access mechanisms that prevent unauthorized data usage.
Infrastructure security extends beyond traditional cybersecurity measures to address AI-specific vulnerabilities. This includes protecting against adversarial attacks designed to compromise model behavior, implementing model versioning controls that prevent unauthorized modifications, and establishing secure model serving environments that isolate production systems from development workflows. Organizations must also implement continuous monitoring systems that detect anomalous behavior patterns that might indicate security breaches or system compromises.
Design Human-Centric Workflows and Operational Integration
Map how AI recommendations will integrate into existing workflows
With established business objectives and technical infrastructure in place, organizations must thoughtfully map how AI recommendations will integrate into current operational workflows. The most successful enterprise AI implementations focus on augmenting human capabilities rather than replacing them entirely. According to research referenced in collaborative intelligence studies, companies using AI to augment human workers outperform those pursuing automation-only approaches by a factor of three.
Start by breaking down existing workflows into individual tasks and identifying where AI can add the most value. AI excels at processing massive datasets, performing repetitive work, and providing rapid analysis, while humans contribute creativity, strategic thinking, and ethical judgment. For example, AI might analyze customer data and generate preliminary recommendations, but human experts should review these insights, apply contextual knowledge, and make final strategic decisions.
Design workflows where AI handles the initial processing or "grunt work," allowing employees to focus on exceptions, quality control, and complex problem-solving. A practical approach involves creating checkpoints where humans review AI outputs before finalization, particularly when outcomes impact customers or require value judgments. This ensures that AI contributes efficiency without compromising quality or accountability.
Define human-in-the-loop processes and escalation procedures
Building on workflow integration, establishing clear human-in-the-loop processes becomes critical for maintaining control and accountability in AI-driven operations. These processes ensure that human oversight remains embedded throughout automated workflows, creating fail-safes and maintaining quality standards.
Design escalation procedures that automatically route complex, sensitive, or unusual scenarios to human experts. For instance, in customer service applications, AI chatbots can handle routine inquiries instantly, but should immediately escalate to human agents when issues become complex or customers express dissatisfaction. The AI should provide full context to the human agent, enabling seamless handoffs that improve rather than disrupt the customer experience.
Three emerging roles are particularly valuable for human-in-the-loop processes:
Role | Responsibility | Key Function |
|---|---|---|
AI Trainers | Teach AI systems to perform better | Curate data, fine-tune interactions, apply human insights |
AI Explainers | Translate AI outputs into human terms | Ensure transparency, accountability, and stakeholder trust |
AI Sustainers | Monitor and maintain AI systems | Watch for bias, performance drift, and ethical issues |
Establish clear decision-making authority where humans remain accountable for final outcomes. AI may inform decisions with data-driven insights, but people must sign off on actions, especially in high-stakes areas like finance, healthcare, or security.
Plan user training and change management communications
Now that human-in-the-loop processes are defined, comprehensive user training and change management communications become essential for successful AI adoption. According to World Economic Forum projections, approximately 50% of workers remaining in their roles will need reskilling to adapt to new AI-integrated workflows.
Develop training programs that cover both technical skills and AI literacy. Employees need to understand how to interpret AI-driven insights, recognize AI limitations, and know when human judgment is required as a backstop. Training should emphasize that AI serves as a tool for empowerment rather than replacement, helping staff build confidence in using these new capabilities.
Create clear communication strategies that frame AI integration positively. Instead of saying "we're automating customer support," position it as "AI will handle routine queries so our representatives can focus on solving complex customer problems." This messaging helps alleviate fears about job displacement and encourages adoption.
Leadership at all levels should model an AI-augmented mindset, demonstrating willingness to use AI in their own workflows and encouraging experimentation. Mid-level managers are particularly crucial as they translate high-level digital strategies into daily practices. Provide them with the authority and resources to identify AI opportunities within their teams and advocate for necessary training or tools.
Create feedback loops for continuous improvement
With training programs underway, establishing robust feedback loops ensures continuous improvement of AI-integrated workflows. These mechanisms allow organizations to refine their human-AI collaboration based on real-world performance and user experiences.
Involve employees early in the design of AI integrations, as their on-the-ground insights help identify where AI genuinely helps and where it doesn't. When people help shape the AI tools they'll use, they're more likely to trust and adopt them. Regular feedback sessions should capture both quantitative performance metrics and qualitative user experiences.
Set up cross-functional AI governance committees that include representatives from different departments and levels of the organization. These committees should regularly review AI performance, gather user feedback, and make iterative improvements to workflows. Encourage employees to flag issues or suggest enhancements to AI systems, creating shared ownership of AI initiatives.
Implement monitoring systems that track both AI performance and human satisfaction with the collaborative process. Key metrics might include task completion times, error rates, employee engagement scores, and customer satisfaction levels. Use this data to continuously refine the balance between automated and human-driven tasks.
Start with pilot programs in focused areas to test human-AI workflows before full deployment. Gather comprehensive feedback from participants, analyze what works well, and identify areas for improvement. This iterative approach allows organizations to refine their collaborative intelligence model based on practical experience rather than theoretical assumptions.
Execute Strategic Pilot Programs with Clear Success Metrics
Design tightly scoped proof-of-concepts with defined timelines
Successful enterprise AI pilot programs begin with carefully crafted proof-of-concepts that prioritize high-impact, low-risk use cases. Organizations should focus on automating repetitive tasks, optimizing logistics, and enhancing customer service as popular starting points for their AI adoption checklist. These tightly scoped initiatives allow businesses to test AI solutions in real-world scenarios while identifying their strengths and limitations before full-scale deployment.
A structured approach requires defining clear objectives aligned with business goals. Decision-makers must identify specific pain points and establish measurable KPIs such as cost savings, time reduction, or revenue growth. For example, companies can implement AI pilot programs in two main functions: marketing and sales, as well as product and service development, reflecting the broader shift where AI adoption has risen to 72 percent over the past six years.
The Department of Homeland Security exemplifies this approach by testing three Generative AI pilot programs across USCIS, HSI, and FEMA by October 2024, providing valuable insights into practical applications and limitations of GenAI tools within defined timeframes.
Test usability and adoption alongside technical accuracy
Beyond technical performance metrics, enterprise AI transformation requires comprehensive evaluation of user experience and adoption rates. User feedback from both internal stakeholders and end-users provides critical insights into the practical usability of AI solutions and satisfaction levels of those interacting with them.
Organizations must regularly collect and analyze feedback to understand how AI solutions integrate with existing workflows and operational processes. This dual focus ensures that technical accuracy aligns with real-world usability, addressing common challenges such as resistance to change and employee concerns about job displacement or skepticism about effectiveness.
Testing should evaluate how well AI systems can scale to handle larger datasets or adapt to new variables without significant redevelopment, ensuring long-term viability of the AI initiative.
Establish baseline metrics and measurement frameworks
Evaluating the success of AI pilot programs involves a comprehensive approach to metrics and outcomes. Key performance indicators must include accuracy metrics comparing AI performance to human benchmarks or predefined standards, while efficiency improvements should measure time savings and resource optimization.
Financial metrics like ROI provide insights into economic benefits gained from AI deployment. For instance, a retail company might measure AI's impact on inventory management, observing reduced waste and improved stock levels. These metrics collectively inform businesses about tangible benefits and areas needing further refinement.
Comparing pre- and post-implementation scenarios provides a clear picture of AI's impact. Businesses can track performance metrics before the AI pilot and then compare these to results during and after the pilot phase. This comparative analysis highlights specific gains achieved through AI, guiding future investment decisions for enterprise application modernization.
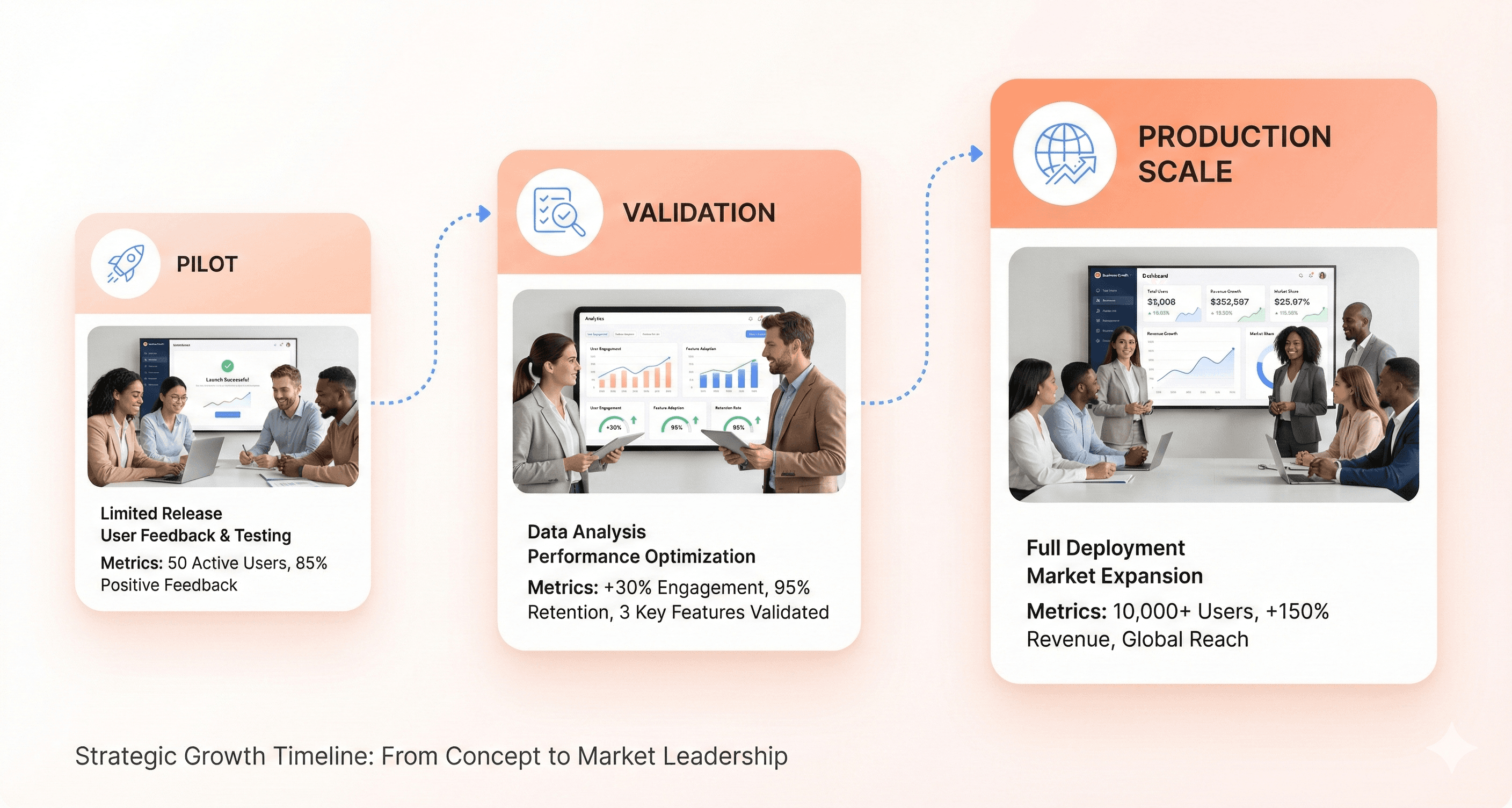
Plan scalable transition from pilot to production deployment
Once a pilot program demonstrates value, scaling requires robust planning and infrastructure investments. Organizations must document learnings and best practices, capturing insights from pilots including successes, challenges, and areas for improvement. This documentation serves as a blueprint for future deployments across the enterprise.
Securing stakeholder buy-in becomes critical at this stage. Demonstrating ROI and aligning AI initiatives with strategic objectives helps gain support from leadership and stakeholders. Organizations should invest in scalable infrastructure, including cloud computing, data pipelines, and integration tools, assessing and upgrading IT systems accordingly.
An agile approach proves essential for scaling AI successfully. Organizations must adopt iterative methodologies that allow refinement of solutions based on feedback and evolving needs. Training and upskilling employees ensures the workforce can effectively work alongside AI technologies, addressing the common challenge of lacking technical expertise to develop, implement, and manage AI solutions across the enterprise.
Conclusion
AI success isn't measured by the sophistication of your models, it's determined by your organization's readiness before implementation begins. This comprehensive checklist covering business objectives, data foundations, technical infrastructure, talent development, governance frameworks, human-centric workflows, and strategic pilots provides the roadmap for transforming AI from experimental technology into operational capability.
The enterprises that will thrive in the AI-driven future won't be those with the most AI experiments, but those with the clearest foundations and most thoughtful preparation. AI is not a project to be completed, but an operational capability to be built systematically. By working through each element of this checklist, your organization moves beyond proof-of-concept paralysis toward scalable, sustainable AI integration that delivers real business outcomes.

About the author
Author Name:
Parth G
|
Founder of
Hashbyt
I’m the founder of Hashbyt, an AI-first frontend and UI/UX SaaS partner helping 200+ SaaS companies scale faster through intelligent, growth-driven design. My work focuses on building modern frontend systems, design frameworks, and product modernization strategies that boost revenue, improve user adoption, and help SaaS founders turn their UI into a true growth engine.
Is a clunky UI holding back your growth?
Is a clunky UI holding back your growth?
▶︎
Transform slow, frustrating dashboards into intuitive interfaces that ensure effortless user adoption.
▶︎
Transform slow, frustrating dashboards into intuitive interfaces that ensure effortless user adoption.






