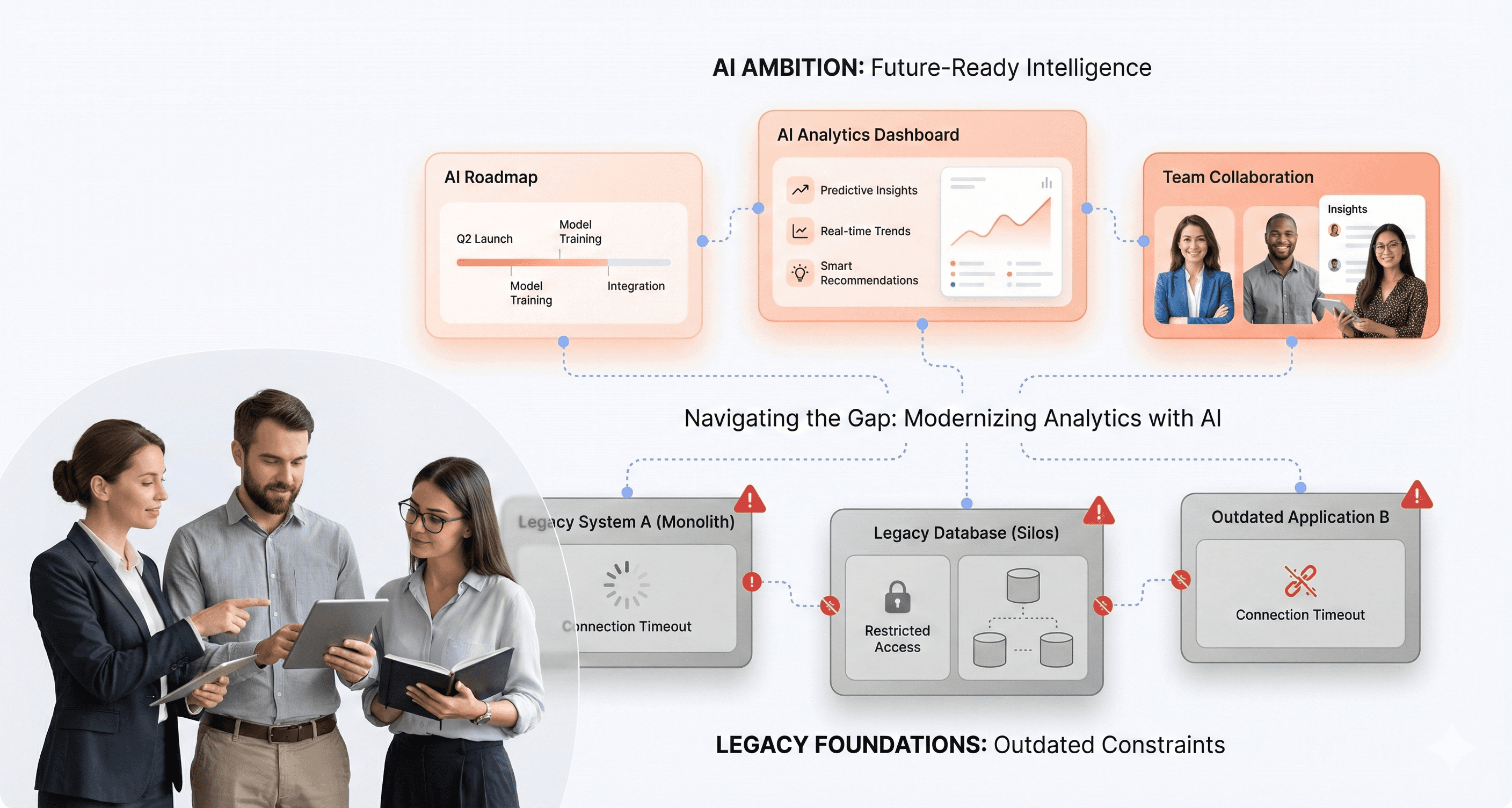
Organizations are pouring millions into AI initiatives while their outdated applications create bottlenecks that prevent real business results. This disconnect between AI ambition and application readiness is costing companies more than just money, it's limiting growth, customer experience, and competitive advantage.
This guide is for CTOs, engineering leaders, and business executives who are frustrated with AI projects that fail to deliver promised outcomes and want to understand why their technology modernization efforts aren't translating into business value.
We'll explore why AI implementation fails without proper foundation, revealing how legacy systems create invisible barriers that no amount of AI can overcome. You'll discover critical warning signs your technology is limiting business growth, from roadmaps dictated by system constraints to small changes requiring massive effort. Finally, we'll cover essential components of effective modernization strategy that focus on business outcomes rather than technical features, including risk-managed migration approaches that unlock data and build AI-ready infrastructure.
The gap between AI potential and actual results isn't about the technology itself, it's about the foundation your applications provide for that technology to succeed.
Why AI Implementation Fails Without Proper Foundation
Legacy systems create architectural barriers that block AI capabilities
Legacy systems were fundamentally designed for structured transactions and traditional enterprise workflows, not the complex computational demands of modern AI implementation. These systems lack the architectural flexibility needed for AI application modernization, creating significant technical gaps that prevent effective integration.
The core incompatibilities manifest in several critical ways. Rigid architectures prevent the integration of modern AI components, while outdated APIs and data formats severely limit interoperability with contemporary AI frameworks. Monolithic applications cannot support the distributed workloads that AI systems require, making it nearly impossible to deploy intelligent capabilities without extensive overhauls.
Enterprise systems like SAP ECC exemplify these challenges perfectly. As experts note, "SAP ECC was never designed for real-time, high-volume data processing or native AI embedding. Its architecture makes it hard to support the kind of intelligent, self-learning applications enterprises need today." The system's complex data model, reliance on aggregate tables, and layers of custom code make AI adoption slow and fragile.
Outdated applications lack the agility and infrastructure needed for AI integration
Modern AI implementation demands elastic compute resources, high-speed data access, and robust memory management capabilities that legacy infrastructure simply cannot provide. These systems were never built to handle the intensive workloads required by AI models, especially those leveraging deep learning or processing large datasets.
The performance barriers become particularly acute when organizations attempt to run AI workloads on-premises or in tightly coupled environments. This architectural mismatch leads to severe performance degradation and unreliable results, often stalling AI-ready infrastructure initiatives before they can generate measurable business impact.
Legacy environments also struggle with the operational complexity of AI deployment. They typically lack the infrastructure and processes needed to support lifecycle management of AI assets, resulting in version sprawl, retraining gaps, and inconsistent outputs across business units. This operational complexity increases risk and undermines trust in AI-driven decisions.
Technical debt prevents organizations from scaling AI solutions effectively
Years of accumulated technical modifications and customizations create substantial barriers to AI transformation. What may have been clever fixes implemented decades ago now act as walls preventing new AI technologies from integrating effectively. This technical debt multiplies exponentially when organizations attempt to scale AI solutions across their enterprise.
Data complexity represents one of the most significant scaling challenges. Legacy systems often operate with multiple company codes, languages, and currencies within a single environment, producing vast amounts of redundant and inconsistent information. Add years of modifications, add-on tools, and third-party integrations, and these systems behave more like patchwork quilts than efficient platforms for AI deployment.
The data fragmentation problem is particularly acute for business outcomes AI implementation. When information is scattered across departments, formats, and platforms in isolated silos, achieving consistent and trustworthy AI outputs becomes nearly impossible. These silos compromise not only the accuracy of predictions but also the speed of insight delivery and the organization's ability to govern data effectively.
As one expert emphasizes, "Neglecting data profiling and quality in legacy systems is like building a skyscraper on swampy ground. No matter how good your AI model is, if the foundation is messy, the project will fail." This foundation problem prevents organizations from realizing the full potential of their modernization business alignment efforts, as AI initiatives become constrained by the very systems they're meant to transform.
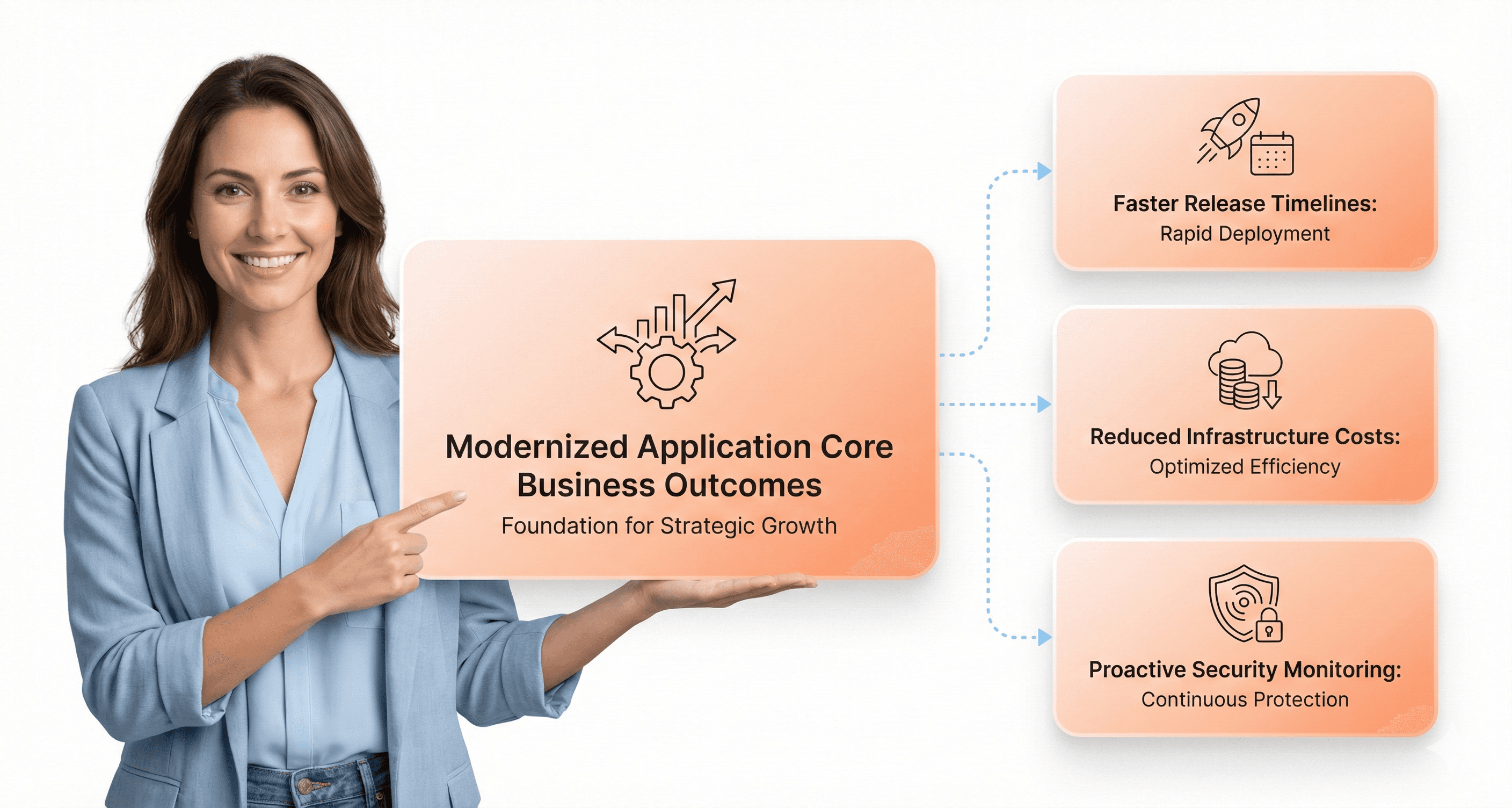
Focus on Business Outcomes Rather Than Technical Features
Reduce feature delivery time from months to weeks through modernization
When organizations focus on business outcomes over technical features, they unlock dramatic improvements in their time-to-market capabilities. Modern application architectures enable development teams to deploy features up to 80% faster than traditional legacy systems, transforming delivery cycles from months to weeks.
The key lies in implementing microservices architecture and DevOps practices that create continuous integration and deployment pipelines. These methodologies allow for rapid feature rollouts while maintaining system stability and quality. Organizations leveraging these approaches have consistently reported significant reductions in lead time for changes and dramatically improved deployment frequency.
Business-driven modernization prioritizes scalable and flexible systems that can handle increased traffic and expand user bases without major overhauls. This scalability directly translates to faster feature delivery, as teams no longer face the bottlenecks and technical debt associated with legacy system dependencies.
Achieve 30-80% cost savings depending on modernization approach
Cost optimization represents one of the most tangible business outcomes from strategic modernization initiatives. Organizations can realize substantial savings across multiple areas, with total reductions ranging from 30% to 80% depending on their specific modernization approach and current technical debt levels.
Hardware and Software Cost Reductions:
Cost Category | Potential Savings | Impact Area |
|---|---|---|
Infrastructure costs | 30-50% reduction | Lower operational expenses, better resource utilization |
Maintenance costs | Up to 74% reduction | Reduced system maintenance demands |
Licensing expenses | 15-35% decrease | Streamlined software portfolio |
Modern cloud-native architectures eliminate the need for expensive on-premises hardware while providing dynamic resource allocation that scales with actual business needs. Organizations moving from outdated mainframes to cloud-based setups have reported annual savings of millions of dollars through reduced hardware, software, and staffing costs.
Process efficiency improvements contribute significantly to these savings. By streamlining workflows and eliminating manual processes, businesses can achieve immediate operational cost reductions. Automation capabilities reduce task completion times by up to 74% while cutting manual data entry requirements by 65%.
The financial impact extends beyond immediate cost savings. Organizations typically see 55% cost savings over three years when implementing structured modernization with proper measurement and optimization cycles.
Transform from reactive to proactive security and operational models
Modern infrastructure fundamentally shifts organizations from reactive troubleshooting to proactive system management, delivering measurable improvements in security posture and operational efficiency. This transformation represents a critical business outcome that directly impacts risk management and operational resilience.
Security Enhancement Metrics:
Security Improvement | Performance Gain | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|
Threat Detection | 92% faster identification | Reduced security incident impact |
Patch Management | 85% quicker deployment | Minimized vulnerability windows |
Incident Response | 76% faster containment | Lower operational disruption |
Proactive security models built into modern systems provide automated security patches, advanced threat detection, and continuous monitoring capabilities. These systems enable businesses to identify and respond to threats before they impact operations, rather than reacting after damage has occurred.
Operational transformation includes automated monitoring, reduced dependence on outdated hardware, and improved disaster recovery solutions. Organizations implementing these proactive models typically experience 30-50% lower application maintenance and operational costs while building stronger technology foundations for future growth.
The shift to proactive operations also improves system reliability metrics, with modern infrastructure achieving 99.9% uptime compared to legacy systems' frequent downtime. This reliability translates directly to improved customer experience and reduced revenue loss from system failures.
Critical Warning Signs Your Technology Is Limiting Business Growth
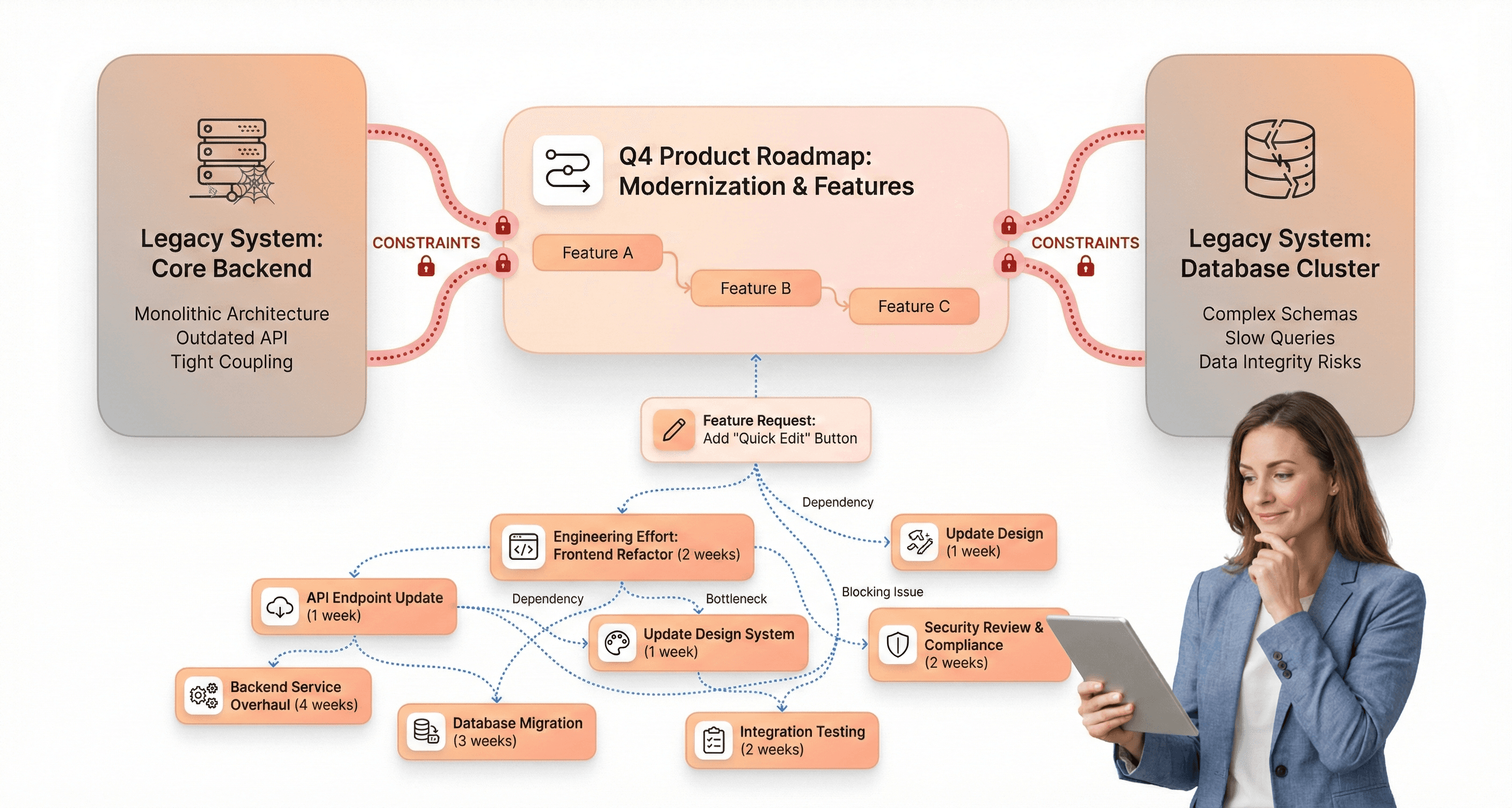
Product roadmaps become constrained by system limitations instead of market needs
One of the most telling signs that legacy technology is constraining business growth is when product development decisions are driven by system limitations rather than market opportunities. Organizations find themselves asking "Can our system handle this?" instead of "What do our customers need?" This fundamental shift in decision-making represents a critical warning sign that outdated infrastructure is actively limiting business potential.
Legacy systems create what experts describe as "quiet cracks" beneath the surface that gradually restrict innovation capabilities. These monolithic architectures lack the flexibility to adapt to evolving market demands, forcing product teams to work within the confines of decades-old technical constraints. The result is a product roadmap that becomes increasingly disconnected from customer expectations and competitive pressures.
Companies operating under these constraints often find themselves unable to capitalize on emerging market opportunities because their systems simply cannot support new features or integrations. This creates a dangerous cycle where businesses become reactive rather than proactive, constantly playing catch-up while competitors with modern, flexible infrastructures move ahead with customer-centric innovations.
Small changes require disproportionate engineering effort and time
Legacy systems are notorious for creating scenarios where seemingly simple modifications demand extensive engineering resources and prolonged development cycles. What should be straightforward updates become complex, time-consuming projects that drain both technical talent and budget allocation.
The reference content highlights how legacy systems suffer from decreased productivity, characterized by slow performance, manual data entry requirements, and complex workflows with limited automation capabilities. These characteristics compound to create environments where routine changes require significant manual intervention and careful coordination across multiple system components.
The maintenance costs of these outdated systems escalate dramatically over time. Industry analysis shows that companies typically spend more on maintenance every five years than they originally invested in the software purchase. This cost escalation occurs because finding experts capable of maintaining and troubleshooting older systems becomes increasingly difficult and expensive as technology evolves.
Furthermore, the lack of modern development tools and practices in legacy environments means that engineers must work with outdated programming languages and frameworks. This not only slows down development but also makes it challenging to attract and retain top technical talent who prefer working with contemporary technologies.
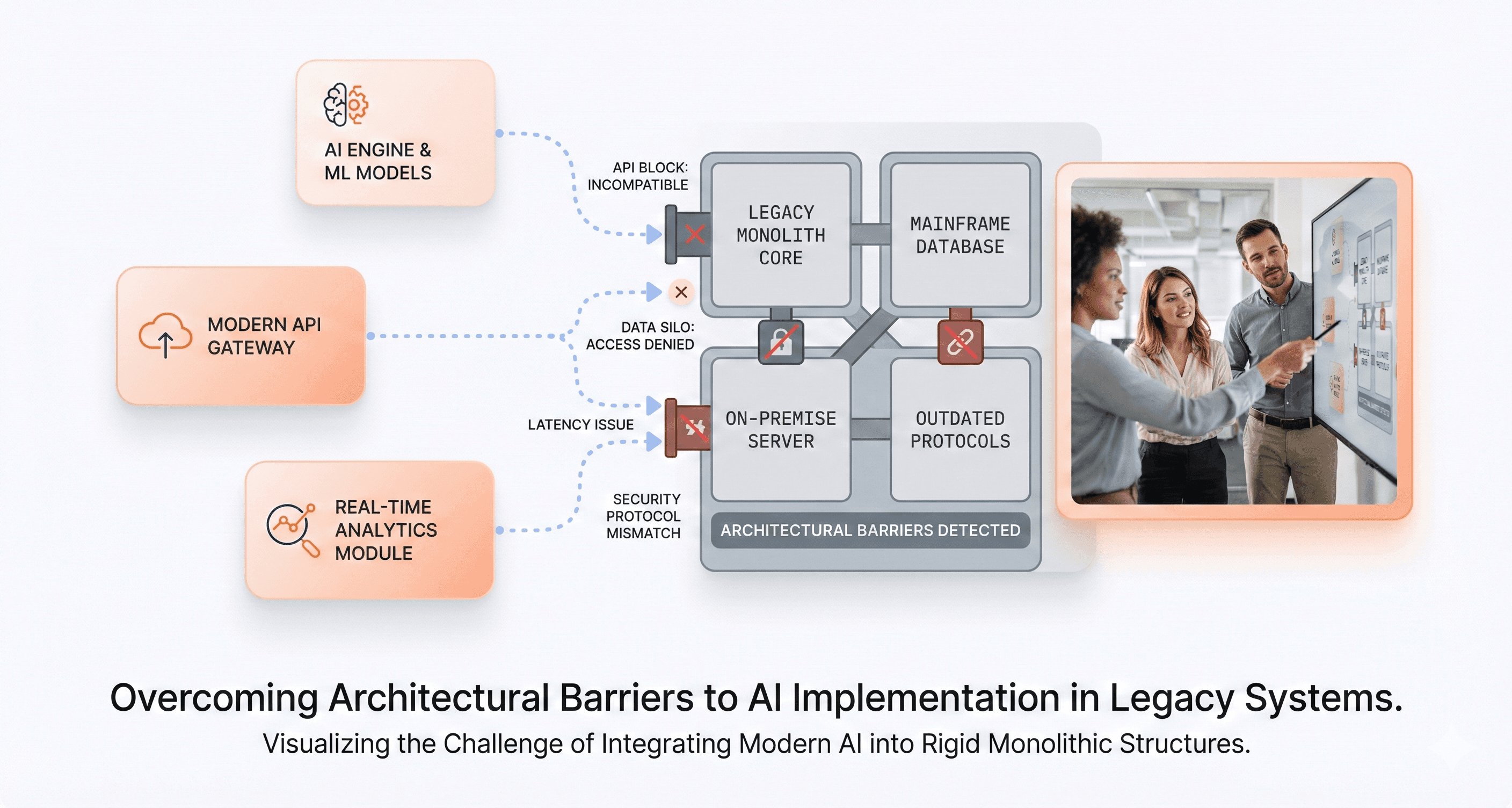
Modern AI and automation initiatives stall due to architectural constraints
Perhaps the most critical warning sign in today's business environment is when AI application modernization efforts fail to deliver expected business outcomes due to underlying architectural limitations. Legacy systems were designed in an era when AI, machine learning, and advanced automation were not considerations, making them fundamentally incompatible with modern AI-ready infrastructure requirements.
The rigid architecture of legacy systems prevents the seamless integration necessary for successful AI implementation. These monolithic structures cannot easily accommodate the API-first approaches that modern AI tools require, creating significant barriers to digital transformation initiatives. Without the ability to integrate with specialized applications and modern data processing capabilities, businesses find their AI transformation efforts stalled before they can demonstrate meaningful business value.
Data silos represent another major constraint, as legacy systems typically store information in isolated databases that cannot efficiently feed the real-time data analysis requirements of AI applications. This limitation prevents organizations from leveraging machine learning algorithms, predictive analytics, and automated decision-making processes that could drive competitive advantage.
The incompatibility extends to cloud integration challenges, as many AI services operate on cloud-native platforms that require flexible, scalable infrastructure. Legacy systems' inability to seamlessly connect with these modern platforms results in AI initiatives that fail to achieve the scalability and performance necessary for meaningful business impact, ultimately leading to disappointing ROI on modernization investments.
Essential Components of Effective Modernization Strategy
Gain complete system visibility through code analysis and dependency mapping
Now that we have covered the importance of focusing on business outcomes, the foundation of any effective application modernization strategy begins with understanding what you currently have. Without comprehensive visibility into your existing application landscape, modernization efforts often fail to deliver expected business value.
Conducting a thorough assessment of your existing application portfolio is critical before taking any modernization action. This detailed analysis should examine individual applications, their architecture, dependencies, code quality, and alignment with current business needs. Understanding your application's current state helps determine whether it needs modernization and identifies the best path forward for AI application modernization initiatives.
Automated analysis tools play a crucial role in this discovery process. These tools can map complex dependencies and identify separation boundaries that would otherwise require extensive manual effort to discover and document. By deeply analyzing an application's codebase, including its structure, dependencies, and underlying business logic, these tools provide essential insights that create a comprehensive understanding of the application landscape.
The assessment process should uncover the most pressing technical challenges, including accumulated technical debt, complex dependencies, and outdated programming practices that slow innovation. This visibility enables organizations to strategically prioritize modernization efforts and develop a clear roadmap toward their target state architecture.
Build durable knowledge bases that accelerate future changes and prevent technical debt
With complete system visibility established, the next essential component focuses on creating sustainable knowledge repositories that support long-term modernization success. Building durable knowledge bases becomes particularly important as applications undergo transformation, ensuring that critical architectural insights and business logic understanding persist throughout the modernization journey.
Technical debt accumulation represents one of the biggest obstacles to successful AI implementation best practices. Older systems often contain inefficient architectures, complex dependencies, and undocumented workarounds that make any change slow, expensive, and prone to unintended consequences. A robust knowledge management approach addresses these challenges by systematically documenting architectural decisions, dependency relationships, and business logic as modernization progresses.
Architectural observability plays a vital role in maintaining these knowledge bases. As application modernization projects get underway, monitoring and documenting every architectural change - such as adding classes or services - allows architects to observe the overall impacts of modifications and prevent architectural drift from the target state. This continuous documentation approach ensures that future development teams can understand not just what the system does, but why specific design decisions were made.
The knowledge base should capture both technical and business context. This includes understanding which components serve specific business functions, how data flows between systems, and which integrations are critical for operations. Documentation should also include lessons learned from modernization efforts, successful patterns that can be replicated, and potential pitfalls to avoid in future changes.
Choose the right modernization approach based on feasibility, cost, and business impact
Previously, I've outlined the importance of visibility and knowledge management. With this foundation established, selecting the appropriate modernization approach becomes a strategic decision that must align with business objectives, application characteristics, and available resources.
The established "Rs" of modernization framework provides a systematic approach to evaluating options. Not every legacy application requires transformation, sometimes the best path forward involves replacing with commercial solutions, retaining systems that function adequately, or retiring applications that no longer serve business needs. The key is matching each approach to the specific circumstances and business-driven modernization goals.
For applications requiring active modernization, several proven methodologies exist. Rehosting or "lift and shift" approaches work well for rapidly realizing cloud benefits without significant code changes. Replatforming adapts applications to new platforms with limited modifications while maintaining core functionality. More intensive approaches like refactoring focus on restructuring codebases to enhance maintainability and performance, while complete rewrites may be necessary when systems are no longer viable.
Incremental modernization using the "Strangler Fig" pattern offers particular value for complex enterprise applications. This approach systematically replaces monolithic components with modern implementations, allowing old and new systems to operate side-by-side during controlled transitions. This risk-managed migration approach reduces disruption while demonstrating value through early wins.
Technology choices should support long-term vision while addressing immediate needs. Cloud-native architectures, containerization, and microservices patterns enable improved agility and scalability, but the specific combination must align with organizational capabilities and business requirements. The goal is creating an AI-ready infrastructure that can adapt to future needs while solving current business challenges.
Success depends on realistic assessment of feasibility, cost implications, and expected business impact. Organizations should prioritize modernization efforts based on where they will yield the greatest results and align with overall strategic goals, ensuring that technology modernization ROI justifies the investment.
Implement Risk-Managed Migration Using Proven Methodologies
Execute Safe, Iterative Migrations That Avoid Disruptive Big-Bang Deployments
Previously discussed business outcome challenges often stem from migration approaches that create unnecessary risk and operational disruption. Phased migration strategies offer the most effective protection against extended outages that can derail AI application modernization initiatives. Instead of attempting a complete system cutover in one massive deployment, organizations should migrate applications and data in manageable stages while maintaining operational continuity.
The statistics reveal the severity of migration risks: over 80% of migration projects run over time or budget, with less than 70% considered successful according to industry analysis. These failures often result from big-bang approaches where promised maintenance windows stretch from hours into days of frantic troubleshooting while revenue operations remain idle.
Modern replication tools enable near-zero downtime migrations by continuously syncing data to new platforms while legacy systems remain operational. Database replication and change data capture technologies allow organizations to close gaps of minutes rather than transferring entire datasets during cutover periods. This approach transforms potential disasters into managed transitions, supporting AI-ready infrastructure development without business interruption.
Migration teams must also consider global operational schedules when planning deployment windows. What appears to be quiet Sunday morning maintenance in one region could impact Monday business hours elsewhere. Having backup operational processes ready ensures critical transactions can continue during transitions, turning potential catastrophes into controlled inconveniences.
Expand Automated Testing Coverage to Catch Regressions and Edge Cases Early
Now that we understand phased migration approaches, comprehensive automated testing becomes the cornerstone of risk-managed application modernization strategy. Testing strategies must extend beyond basic functionality to validate data integrity, performance characteristics, and integration dependencies that support AI implementation requirements.
Automated data reconciliation forms the foundation of effective testing coverage. Organizations should implement tools and scripts that verify row counts, checksums, and data distributions between source and target environments. SQL queries must confirm that critical aggregations like revenue totals, customer counts, and transaction sums remain consistent throughout the migration process. When these fundamental checks fail, teams can immediately identify investigation areas before issues propagate.
Schema and constraint validation prevents compatibility errors that commonly derail modernization projects. Automated checks should verify that target platforms contain all expected tables and columns, ensuring no constraints are violated during migration. Teams must profile data to detect schema drift and confirm data types meet expectations for downstream AI processing requirements.
Performance testing during migration reveals bottlenecks that could impact AI application modernization objectives. Organizations should monitor query response times, system throughput, and resource utilization patterns to ensure new platforms can handle production workloads effectively. This testing prevents scenarios where modernized applications perform worse than legacy systems, undermining business confidence in transformation initiatives.
Establish Clear Architectural Destinations Aligned with AI and Growth Objectives
With comprehensive testing frameworks in place, establishing architectural clarity becomes essential for successful AI application modernization outcomes. Migration efforts must target specific, well-defined architectural patterns that support both immediate operational needs and future AI capabilities, rather than simply replicating existing system designs in new environments.
Architectural planning requires thorough inventory of all data assets, dependency mapping, and complexity assessment before initiating any migration activities. This process should involve database administrators, engineers, and business users to capture requirements and constraints that technical teams might otherwise overlook. Detailed migration plans with clear timelines and responsibilities prevent schema issues and missing data problems that commonly plague modernization projects.
The target architecture must accommodate AI-ready infrastructure requirements including scalable data processing capabilities, real-time analytics support, and flexible integration patterns. Organizations should select migration tools that handle large data volumes, validate data integrity throughout transfer processes, and maintain security protocols during transitions. Cloud provider migration services and established ETL platforms typically reduce risk compared to custom-built solutions.
Dependency mapping becomes particularly crucial for AI application modernization since machine learning workflows often require complex data lineage and real-time processing capabilities. Teams must understand field-level dependencies to prevent integration failures where downstream AI processes break due to missing or incorrectly mapped data sources. This comprehensive planning ensures that modernized applications can support advanced analytics and machine learning workloads from day one.
Unlock Data and Scale Operations for AI-Ready Infrastructure
Break down legacy data silos to enable AI-driven insights and automation
Legacy data infrastructure represents one of the most significant obstacles to successful AI implementation. Organizations struggle with data silos where critical information remains trapped across different departments, systems, and databases. According to industry research, 70% of professionals still need to invest substantial resources in fixing data quality issues, despite 87% of businesses viewing their data ecosystem as ready for AI platform development.
Outdated data architectures create fundamental barriers to AI readiness. These legacy systems were designed for siloed operations and lack the scale, flexibility, and integrations necessary for modern AI and automation. The inability to aggregate data from various internal and external sources creates operationally isolated insights, wasting valuable time during critical decision-making processes. Organizations often find themselves without the infrastructure to act on real-time opportunities or mitigate emerging risks.
Data quality and consistency emerge as critical factors in breaking down these silos. Poor data quality leads to unreliable AI outcomes, the classic "garbage in, garbage out" scenario. Companies must establish comprehensive frameworks that ensure high data standards, making insights meaningful and automation reliable. This requires implementing robust data governance programs that define data storage, accessibility, and management protocols across the organization.
Modern data modernization strategies focus on eliminating data fragmentation through centralized approaches. By implementing centralized data lakes, organizations can compile information from various business services into unified platforms, providing consistency and regulatory compliance. This transformation enables seamless data sharing between departments, hospitals, patients, insurance companies, and diagnostic labs through interoperability standards like FHIR in healthcare environments.
Create scalable, cloud-native platforms that support future growth requirements
Scalability and flexibility form the cornerstone of AI-ready infrastructure modernization. Modern organizations require systems that can seamlessly adapt to growing business demands and evolving technological requirements. The infrastructure must handle increasing data volumes and support complex AI models while maintaining cost-effectiveness and operational efficiency.
Cloud-native platforms provide the foundation for this scalable approach. Hybrid data centers balance performance, cost, and compliance by combining on-premises and cloud solutions effectively. For on-premises deployments, organizations must focus on AI-critical fundamentals: storage throughput, elastic computing, intelligent networking, and deep observability. Hybrid architectures allow fine-tuning for latency requirements, data sovereignty concerns, and economic optimization per workload.
Resource and cost management become essential components of scalable infrastructure. Cloud environments need demand-based scaling capabilities with robust controls to manage consumption costs. These controls should include comprehensive workload monitoring, query validation, and operational efficiencies to prevent cost overruns from poorly optimized pipelines or unpredictable usage patterns.
The infrastructure must support diverse AI applications, from small-scale departmental solutions to enterprise-level deployments. This requires implementing real-time data processing capabilities that provide immediate data analysis as information arrives in the system. Companies need infrastructure that supports low-latency operations to ensure AI application effectiveness and enable prompt actions based on real-time insights.
Interoperability and integration capabilities ensure seamless connections between different data sources and business operational systems. The infrastructure should support various data formats and sources, integrating both structured and unstructured data from internal and external origins. This creates a cohesive data ecosystem where all tools and systems work harmoniously together.
Reduce energy consumption and operational overhead through modern architecture
Modern architecture design directly impacts operational efficiency and environmental sustainability. Legacy systems typically consume significantly more energy due to outdated hardware, inefficient processing methods, and redundant operational overhead. AI-ready infrastructure modernization addresses these concerns through strategic architectural improvements.
Cloud-native platforms inherently provide better energy efficiency compared to traditional on-premises solutions. Modern cloud providers implement advanced cooling systems, energy-efficient hardware, and optimized resource utilization that dramatically reduces per-workload energy consumption. Organizations can achieve substantial operational cost reductions while improving their environmental footprint through strategic migration to modern architectures.
Automated compliance monitoring reduces manual operational overhead while ensuring regulatory adherence. Data lineage tracking maintains transparency for fraud investigations and annual audits, eliminating time-intensive manual processes. Real-time transaction processing frameworks like Apache Kafka transform legacy financial systems, resulting in faster settlements and reduced operational complexity.
Modern infrastructure enables predictive maintenance capabilities that prevent costly downtime and reduce operational overhead. By analyzing real-time data from IoT sensors and connected equipment, organizations can identify potential failures before they occur, ensuring continuous productivity while minimizing maintenance costs and production shutdowns.
The integration of digital twin technology and IoT data platforms provides comprehensive operational visibility while reducing manual monitoring requirements. Manufacturing firms can connect factory equipment with cloud-based data platforms, providing real-time production information and insightful monitoring capabilities that optimize operational efficiency and reduce energy waste through intelligent automation systems.
Conclusion
The path to AI-driven transformation isn't about adding artificial intelligence to broken systems, it's about building the foundation that allows AI to multiply your business impact. Organizations that focus on business outcomes rather than technical features consistently achieve measurable results: cutting feature delivery from months to weeks, reducing costs by 30-80%, and unlocking data from legacy silos to power new AI initiatives. The warning signs are clear when technology becomes the bottleneck: roadmaps dictated by system constraints, small changes requiring outsized effort, and AI capabilities hitting architectural walls.
Effective modernization requires a strategic approach that combines proper foundation-setting with risk-managed migration methodologies. By revealing how systems actually behave, code, data, integrations, and dependencies, organizations can make informed decisions and avoid costly rework. The goal isn't just to modernize technology, but to create AI-ready infrastructure that scales operations and drives long-term business value. Ready to break free from legacy paralysis and unlock your organization's true potential? The time to modernize is now.

About the author
Author Name:
Parth G
|
Founder of
Hashbyt
I’m the founder of Hashbyt, an AI-first frontend and UI/UX SaaS partner helping 200+ SaaS companies scale faster through intelligent, growth-driven design. My work focuses on building modern frontend systems, design frameworks, and product modernization strategies that boost revenue, improve user adoption, and help SaaS founders turn their UI into a true growth engine.
Is a clunky UI holding back your growth?
Is a clunky UI holding back your growth?
▶︎
Transform slow, frustrating dashboards into intuitive interfaces that ensure effortless user adoption.
▶︎
Transform slow, frustrating dashboards into intuitive interfaces that ensure effortless user adoption.






