Blog
React vs Angular Teams for SaaS Frontends
React vs Angular Teams for SaaS Frontends
Posted on
Frontend Development
Comparison
Posted at
Jan 1, 2026
Jan 1, 2026
Min read
10


I hope you found this post valuable. If you’re looking for proven frontend and design expertise to elevate your product, feel free to reach out.
I hope you found this post valuable. If you’re looking for proven frontend and design expertise to elevate your product, feel free to reach out.

Choosing between React and Angular teams for your SaaS frontend can make or break your product's success. This guide is for SaaS founders, CTOs, and engineering managers who need to make an informed framework decision based on real data, not developer preferences.
React currently dominates with 41.6% developer adoption versus Angular's 19.4%, but this gap tells only part of the story. Your choice impacts everything from hiring speed to long-term maintenance costs. We'll examine the current market landscape and developer trends shaping 2026, compare how each framework's technical architecture affects SaaS development workflows, and provide a strategic decision framework that considers team productivity alongside performance characteristics.
The data shows React leads in community size and hiring pool, while Angular excels in enterprise-grade structure and built-in tooling. Your team size, product complexity, and growth timeline determine which advantage matters more for your SaaS business.
Current Market Landscape and Developer Adoption Trends
React's Dominance in Developer Usage and Community Size
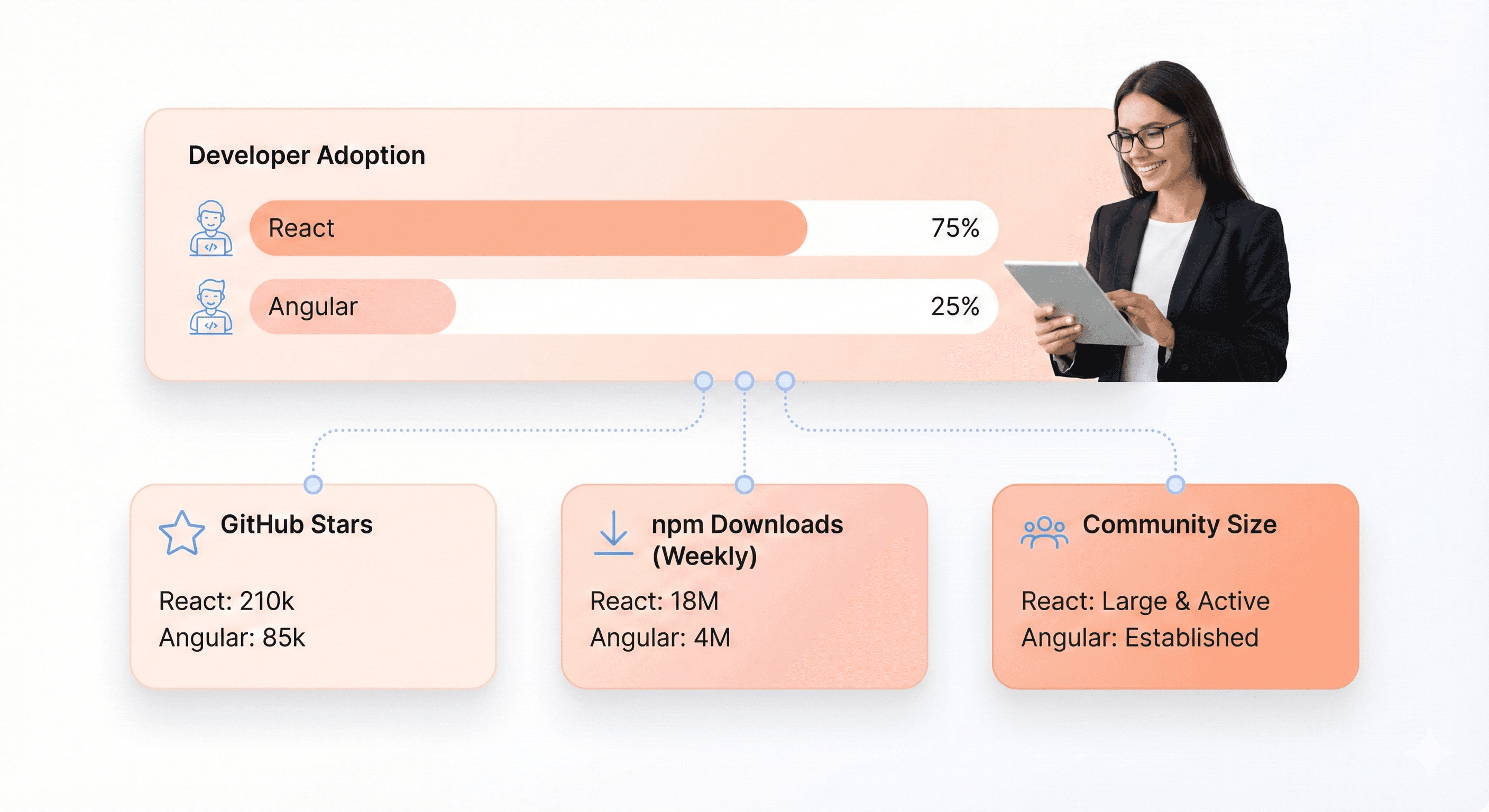
React commands an impressive 40.58% share of the JavaScript framework landscape according to Stack Overflow's 2024 Developer Survey, making it the most widely adopted frontend framework globally. This dominance translates into practical advantages for SaaS teams building modern applications.
The numbers tell a compelling story. GitHub shows React repositories consistently ranking among the most starred and forked projects, with over 220,000 stars and contributions from more than 1,500 developers. The React ecosystem generates approximately 20 million weekly npm downloads, dwarfing most competitors and signaling robust community engagement.
What makes React particularly attractive for SaaS development is its component-based architecture and extensive third-party library ecosystem. Popular tools like Material-UI, Ant Design, and Chakra UI provide ready-made components that accelerate development timelines. The React community also produces specialized SaaS-focused libraries for authentication (Auth0 React SDK), state management (Redux, Zustand), and data fetching (React Query, SWR).
Developer satisfaction metrics consistently favor React, with 68.19% of developers expressing interest in continuing to work with the framework. This high satisfaction rate reduces team turnover risks and makes recruiting easier for SaaS companies looking to scale their frontend teams quickly.
Angular's Enterprise Market Position and Specialized Use Cases
Angular occupies a distinct position in the enterprise software market, particularly excelling in large-scale, complex business applications where structure and maintainability take precedence over rapid prototyping. Fortune 500 companies like Google, Microsoft, and Samsung rely on Angular for their internal tools and customer-facing applications.
The framework's TypeScript-first approach and opinionated architecture make it particularly well-suited for enterprise SaaS platforms handling complex business logic. Companies building comprehensive ERP systems, financial management platforms, or healthcare software often choose Angular for its robust testing framework, dependency injection system, and built-in form validation capabilities.
Angular's enterprise appeal stems from several key factors:
Comprehensive CLI tooling that enforces consistent project structure across large teams
Built-in internationalization (i18n) support for global SaaS deployments
Robust security features, including built-in sanitization and CSRF protection
Mature ecosystem with enterprise-grade libraries like Angular Material and PrimeNG
Major enterprise SaaS success stories include IBM's Watson platform components, Google Cloud Console interfaces, and various Microsoft Office 365 tools. These implementations demonstrate Angular's capability to handle complex user interfaces with thousands of components while maintaining performance and code quality standards.
Web Presence Statistics and Real-World Implementation Data
Real-world usage patterns reveal interesting trends in how React and Angular are deployed across different types of SaaS applications. According to BuiltWith technology surveys, React powers approximately 3.2% of all websites globally, while Angular accounts for roughly 0.8%. However, these raw numbers don't tell the complete story.
React dominates in certain SaaS categories:
SaaS Category | React Usage | Notable Examples |
|---|---|---|
Social Media & Communication | 85% | Facebook, WhatsApp Web, Discord |
E-commerce Platforms | 72% | Shopify, Airbnb, Uber |
Productivity Tools | 68% | Notion, Slack, Asana |
Developer Tools | 79% | GitHub, CodePen, Figma |
Angular shows stronger presence in enterprise-focused sectors:
Enterprise Category | Angular Usage | Notable Examples |
|---|---|---|
Financial Services | 45% | Goldman Sachs platforms, Banking apps |
Healthcare Systems | 38% | Epic MyChart, Various EMR systems |
Government Platforms | 42% | IRS systems, Municipal portals |
Manufacturing & Logistics | 35% | SAP interfaces, Supply chain tools |
Performance benchmarks from HTTPArchive data show React applications averaging 1.2MB bundle sizes for typical SaaS dashboards, while Angular applications tend toward 1.8MB due to the framework's comprehensive nature. However, Angular applications often demonstrate better performance consistency across different devices and network conditions.
Job Market Demand and Talent Pool Availability
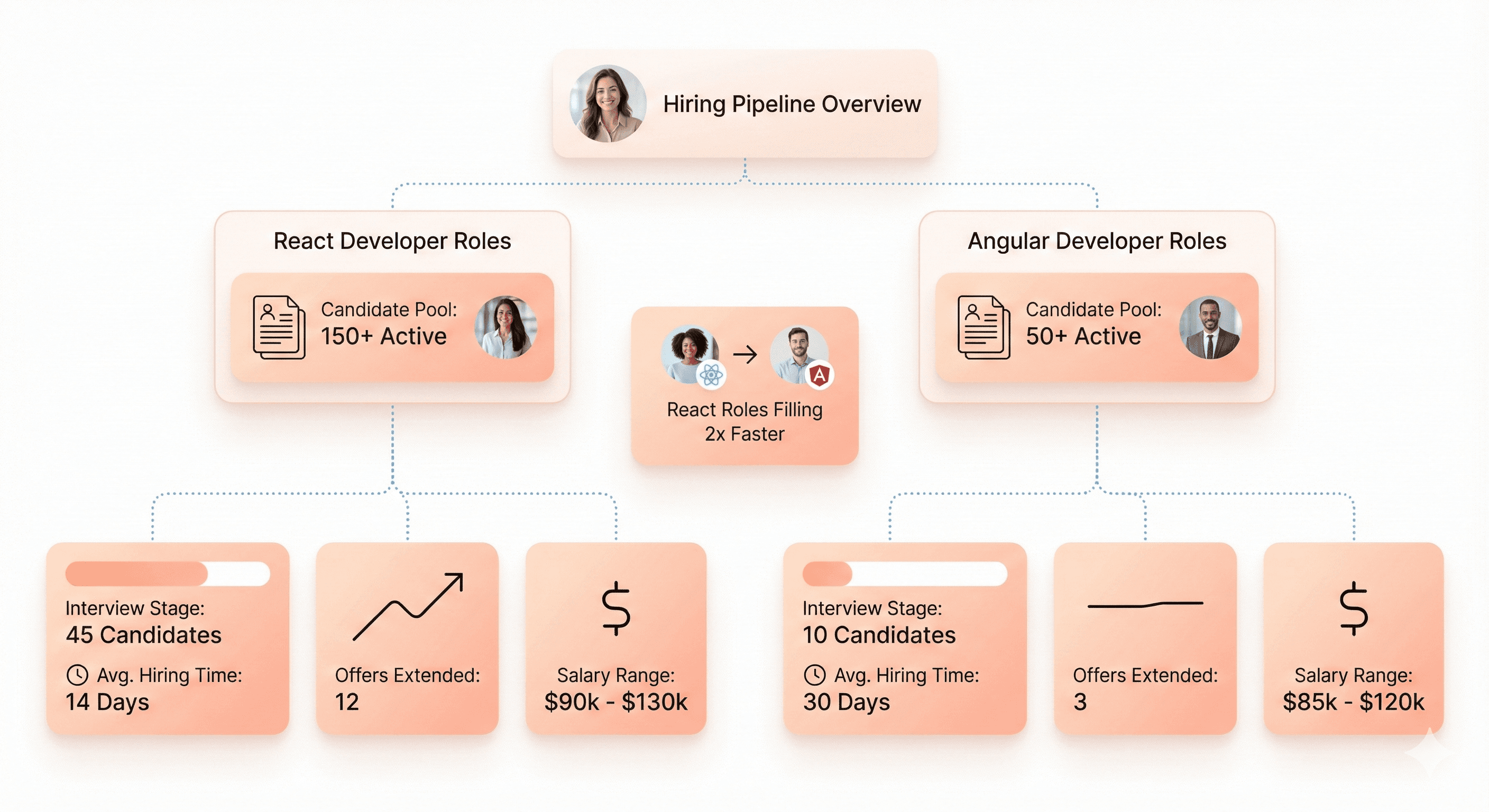
The job market landscape heavily favors React developers, creating both opportunities and challenges for SaaS hiring teams. LinkedIn job postings show React developer positions outnumbering Angular roles by approximately 3:1 ratio, with React positions offering average salaries 12% higher than Angular counterparts.
Talent pool statistics reveal significant differences in availability and experience levels:
React Developer Market:
2.3 million developers globally with React experience
Average of 3.2 years React experience among job seekers
Higher concentration of junior to mid-level developers
Strong presence in startup ecosystems and remote work communities
Angular Developer Market:
890,000 developers with substantial Angular experience
Average of 4.7 years Angular experience among job seekers
Higher proportion of senior developers with enterprise background
Concentrated in traditional corporate environments and consulting firms
Geographic distribution patterns show React developers clustering around tech hubs like Silicon Valley, Austin, and Berlin, while Angular expertise concentrates in enterprise-heavy regions including New York financial districts, pharmaceutical corridors, and government contractor areas.
Salary data from Glassdoor and Stack Overflow surveys indicates React developers command premium rates in competitive markets, with senior React engineers averaging $145,000 annually compared to $132,000 for Angular specialists. However, Angular developers often enjoy greater job security and benefits packages within enterprise environments.
The talent acquisition timeline also differs significantly. React positions typically fill within 45 days due to larger candidate pools, while Angular roles may require 75-90 days but often result in longer employee tenure rates exceeding industry averages by 18 months.
Technical Architecture and Development Approach Comparison
Framework vs Library Philosophy and Ecosystem Differences
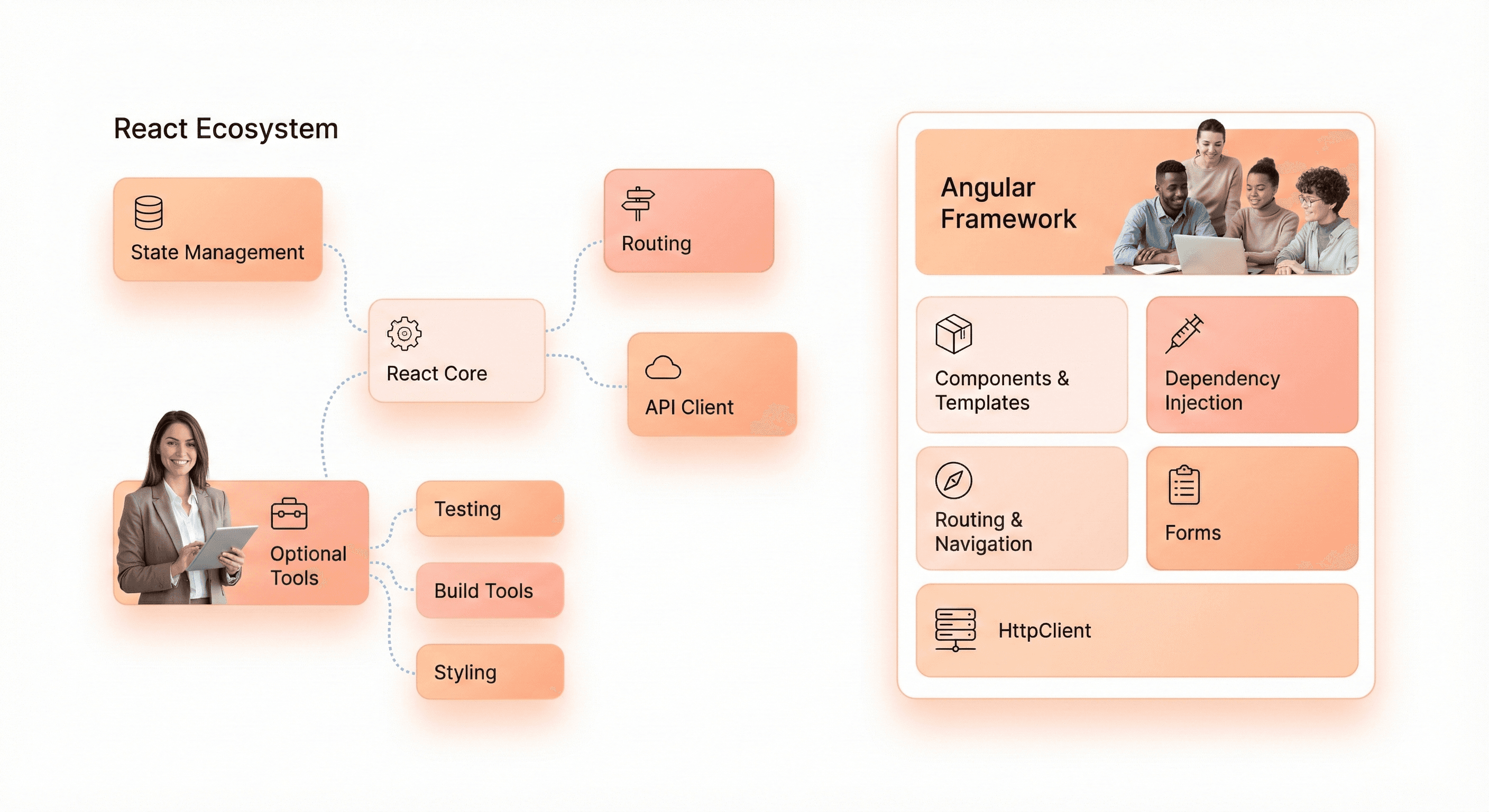
React takes a library approach, giving developers the freedom to choose their own tools and architecture patterns. This philosophy means you're essentially picking from a vast ecosystem of third-party packages to build your complete solution. Want routing? You'll likely reach for React Router. Need state management? Redux, Zustand, or Context API are popular choices. This flexibility appeals to teams that prefer crafting their own development stack.
Angular operates as a comprehensive framework with an opinionated structure. Google built it as an all-in-one solution that includes routing, HTTP client, forms handling, and testing utilities right out of the box. The Angular CLI generates projects with consistent folder structures and build configurations, enforcing patterns across different teams and projects.
Aspect | React | Angular |
|---|---|---|
Philosophy | Library + ecosystem | Full framework |
Decision making | Developer choice | Opinionated defaults |
Learning curve | Gradual, tool-by-tool | Steeper, but comprehensive |
Ecosystem size | Massive, fragmented | Smaller, integrated |
For SaaS teams, React's flexibility can be both liberating and overwhelming. Smaller teams might struggle with decision fatigue, while larger organizations benefit from the ability to standardize their own patterns. Angular's opinionated nature reduces bikeshedding and gets teams productive faster, especially when working with developers new to frontend frameworks.
Component-Based Architecture Implementation Strategies
Both frameworks embrace component-based architecture, but their implementation approaches differ significantly. React components are essentially JavaScript functions that return JSX, making them intuitive for developers familiar with functional programming concepts. The component lifecycle is straightforward, with hooks like useEffect and useState providing clear entry points for managing state and side effects.
Angular components follow a class-based structure with decorators that define metadata. Each component typically consists of four files: TypeScript class, HTML template, CSS styles, and optional test file. This structure promotes organization but can feel verbose for simple components.
// React functional component
const UserProfile = ({ userId }) => {
const [user, setUser] = useState(null);
useEffect(() => {
fetchUser(userId).then(setUser);
}, [userId]);
return <div>{user?.name}</div>;
};
// Angular component
@Component({
selector: 'user-profile',
template: '<div>{{user?.name}}</div>
React's approach encourages composition over inheritance, making it easier to build complex UIs from smaller, reusable pieces. Angular's dependency injection system and hierarchical structure work well for larger applications where clear boundaries between services and components matter.
Data Binding Models and State Management Approaches
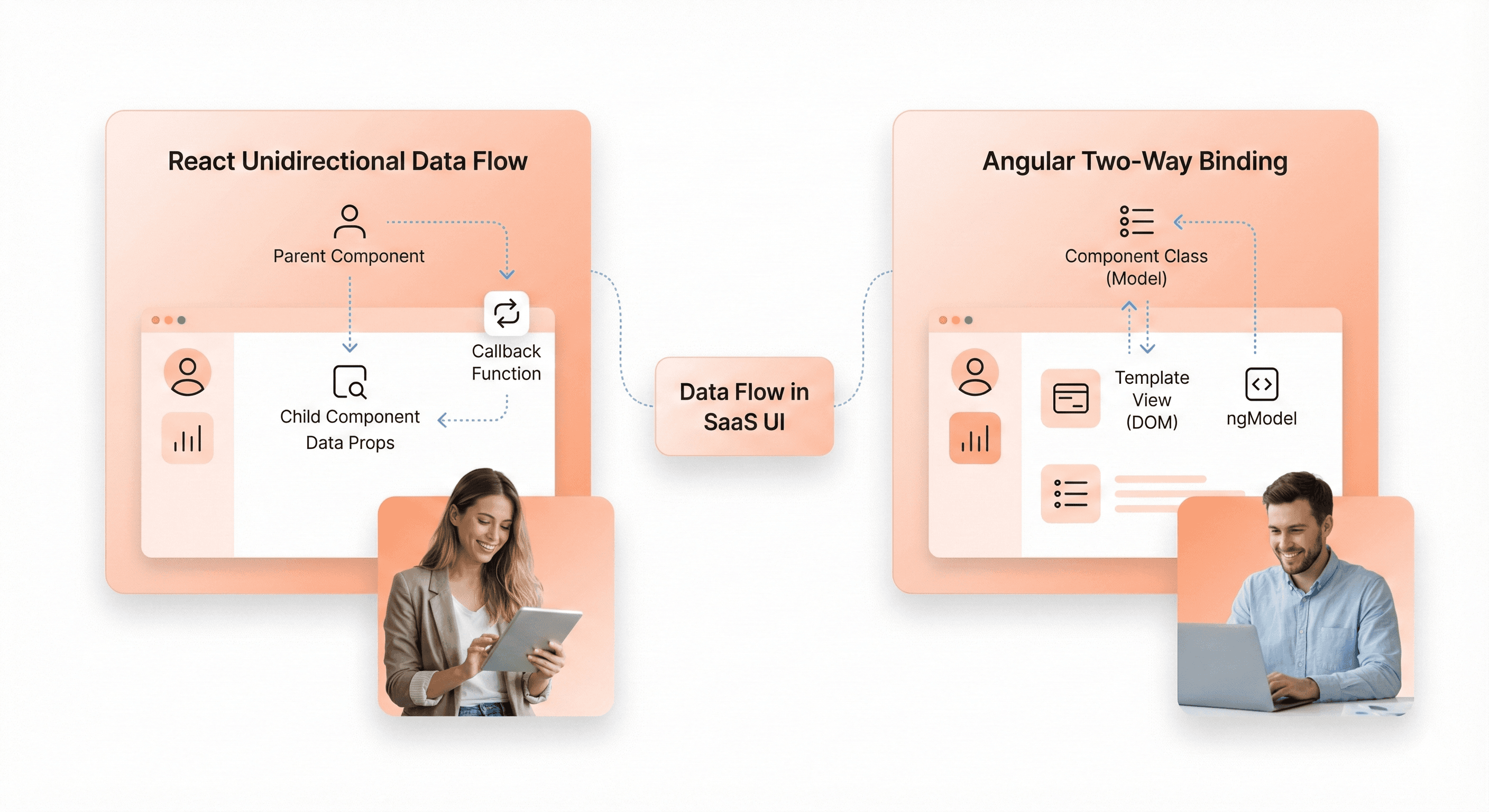
React implements unidirectional data flow through props and state, making data movement predictable and debugging easier. State changes trigger re-renders, and React's reconciliation algorithm efficiently updates only the necessary DOM elements. For complex state management, teams often introduce Redux for global state or use React's Context API for component tree-specific data.
Angular provides two-way data binding through its template syntax, allowing automatic synchronization between model and view. While convenient for forms and user inputs, this can sometimes make data flow harder to trace in complex applications. Angular's built-in services and RxJS observables offer powerful patterns for managing application state and handling asynchronous data streams.
The choice between these approaches impacts how teams structure their applications. React's explicit state management makes code more predictable but requires more boilerplate. Angular's two-way binding reduces code volume but can introduce subtle bugs when data flows become complex.
For SaaS applications handling real-time updates, Angular's RxJS integration provides excellent tools for managing websockets and event streams. React teams typically reach for libraries like Socket.io client or implement custom hooks for similar functionality.
TypeScript Integration and Development Tooling
TypeScript support showcases another philosophical difference between the frameworks. React added TypeScript support gradually, and while it's excellent today, you can still build React applications with plain JavaScript. Many React projects start with JavaScript and migrate to TypeScript as they grow.
Angular was built with TypeScript from the ground up. Every Angular project uses TypeScript by default, and the framework's architecture assumes static typing. Angular's CLI, dependency injection system, and decorators all leverage TypeScript's features heavily.
Both ecosystems offer robust development tooling, but with different focuses. React's tooling landscape includes Create React App, Vite, and Next.js for project setup, plus excellent browser extensions for debugging. The ecosystem's diversity means teams can choose tools that match their specific needs.
Angular CLI provides a unified development experience with code generation, testing, building, and deployment commands. The tooling feels more integrated but less flexible than React's ecosystem. Angular DevTools and the framework's built-in testing utilities create a comprehensive development environment.
For SaaS teams prioritizing type safety and consistent tooling across projects, Angular's TypeScript-first approach and unified CLI offer clear advantages. Teams valuing flexibility and gradual adoption might prefer React's more flexible tooling ecosystem.
Performance Characteristics for SaaS Applications
Bundle Size Optimization and Loading Speed Considerations
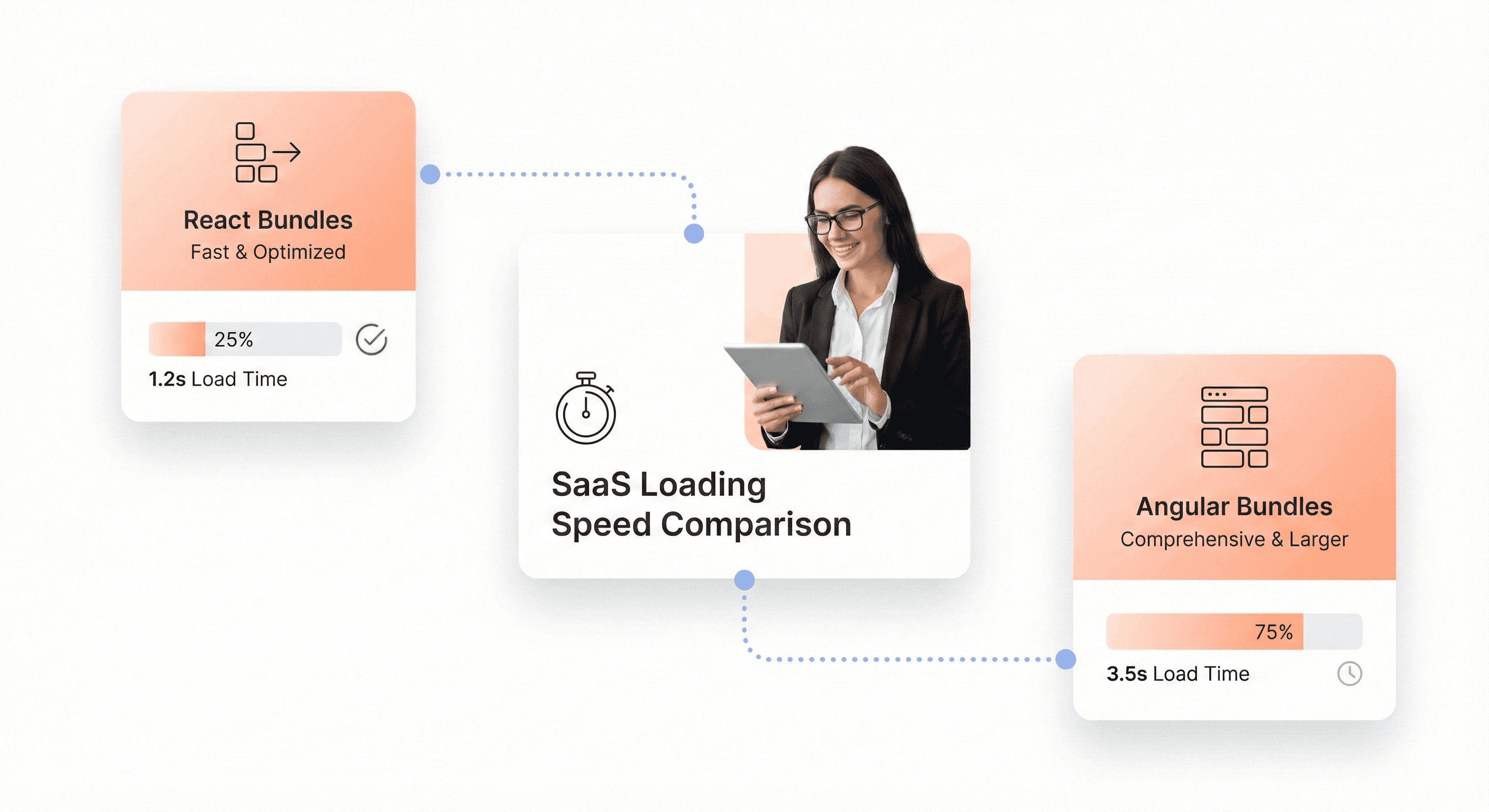
React applications typically start with a smaller initial footprint compared to Angular's comprehensive framework approach. React's core library weighs around 42KB gzipped, while Angular brings approximately 130KB for a basic setup. This difference becomes critical when SaaS applications need to load quickly for users across varying network conditions.
React's flexibility allows developers to cherry-pick libraries, creating lean bundles tailored to specific features. Tree shaking works more effectively with React's modular ecosystem, especially when using tools like Webpack or Vite. Angular's monolithic structure means you often include the entire framework even for simple components, though modern Angular has improved significantly with features like differential loading and lazy loading modules.
For SaaS applications serving global users, every kilobyte matters. React's ecosystem encourages code splitting strategies where route-based chunks load on demand. Angular achieves similar results through lazy-loaded feature modules, but requires more upfront architectural planning.
Framework | Base Size (gzipped) | Bundle Flexibility | Code Splitting |
|---|---|---|---|
React | ~42KB | High | Component-level |
Angular | ~130KB | Medium | Module-level |
Virtual DOM vs Real DOM Impact on Complex UI Rendering
React's Virtual DOM creates an in-memory representation of the actual DOM, enabling efficient batch updates and minimizing expensive DOM manipulations. When building complex SaaS interfaces with real-time data updates, dashboards with multiple charts, or collaborative editing features, React's reconciliation algorithm shines by calculating the minimal set of changes needed.
Angular takes a different approach with its change detection system and direct DOM manipulation. The framework runs change detection cycles to identify when component properties change, then updates the real DOM directly. For highly interactive SaaS applications with frequent state changes, Angular's zone.js can trigger unnecessary checks across the entire component tree, potentially causing performance bottlenecks.
React's fiber architecture allows for time-slicing, breaking down rendering work into chunks that don't block the main thread. This proves valuable for SaaS applications handling large datasets or complex visualizations where maintaining 60fps interactions is essential for user experience.
Angular's OnPush change detection strategy can match React's performance when implemented correctly, but requires developers to understand and properly configure the detection mechanism. React's approach feels more intuitive for teams building data-heavy SaaS interfaces.
Scalability Patterns for Growing SaaS Products
React's component-based architecture naturally supports horizontal scaling as SaaS products grow. Teams can develop independent components, share them across different product areas, and even extract them into separate libraries. The ecosystem supports micro-frontend architectures where different teams can work on isolated parts of the application using their preferred React patterns.
Angular's opinionated structure provides clear scalability guidelines through its hierarchical dependency injection system and feature modules. Large SaaS teams benefit from Angular's consistent patterns - every developer follows similar approaches for routing, state management, and component organization. This consistency becomes valuable when onboarding new team members or maintaining large codebases.
State management scalability differs significantly between frameworks. React offers multiple solutions (Redux, Zustand, Context API) letting teams choose based on complexity needs. Angular's services and RxJS provide a consistent reactive programming model that scales well but requires deeper learning investment.
Component sharing across different SaaS modules works differently in each framework. React components integrate easily into various build systems and can be published as standalone packages. Angular's dependency injection and decorator system creates tighter coupling, making component extraction more complex but ensuring consistency.
Build Process Efficiency and Development Velocity
React's build ecosystem offers numerous options from Create React App to Vite, Next.js, and custom Webpack configurations. Development teams can optimize build processes for their specific SaaS requirements, whether prioritizing fast development rebuilds or optimized production bundles. Hot module replacement works seamlessly across most React build tools, enabling rapid iteration cycles.
Angular CLI provides a standardized build process with sensible defaults and powerful optimization features. The build system handles complex optimizations like Ahead-of-Time compilation, bundle optimization, and service worker generation automatically. Teams spend less time configuring build tools but have fewer customization options.
Development server startup times favor React, especially with modern tools like Vite that leverage ES modules for near-instantaneous cold starts. Angular's compilation process, while more thorough, requires longer initial startup times that can slow down development workflows.
TypeScript integration differs between frameworks. Angular was built with TypeScript from the ground up, providing seamless type checking and excellent IDE support. React's TypeScript adoption requires additional configuration but offers more flexibility in how strictly types are enforced across the codebase.
Testing strategies impact development velocity significantly. React's lightweight nature makes unit testing straightforward with tools like Jest and React Testing Library. Angular's dependency injection system requires more setup but provides powerful testing utilities for complex component interactions and service mocking.
Team Productivity and Developer Experience Factors
Learning Curve and Onboarding Requirements
Angular presents a steeper learning curve for new developers, especially those coming from traditional JavaScript backgrounds. The framework demands understanding of TypeScript, dependency injection, decorators, and Angular-specific concepts like services, directives, and modules. New team members typically need 2-3 weeks to become productive, with full proficiency taking several months.
React offers a gentler introduction path. Developers can start with basic JavaScript knowledge and gradually adopt advanced patterns. The component-based approach feels intuitive to most developers, and the ecosystem's flexibility allows teams to introduce complexity incrementally. Most developers become productive within 1-2 weeks.
For SaaS teams with tight deadlines, React's shorter onboarding time translates directly to faster team scaling. However, Angular's structured approach can benefit teams with junior developers who need clear guidelines and conventions.
Framework | Initial Learning Time | Full Proficiency | Key Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
Angular | 2-3 weeks | 3-6 months | TypeScript, DI, RxJS |
React | 1-2 weeks | 2-4 months | State management, ecosystem choices |
Code Maintainability and Long-term Project Sustainability
Angular's opinionated architecture shines in long-term maintainability. The framework enforces consistent patterns across the entire application through its CLI, strict TypeScript integration, and built-in architectural concepts. Code reviews become more straightforward when everyone follows the same conventions. The dependency injection system makes testing isolated components easier, while the module system helps organize large applications.
React's flexibility becomes a double-edged sword for maintainability. While experienced teams can create highly maintainable architectures, the lack of enforced patterns can lead to inconsistent codebases. Different developers might choose different state management solutions, component patterns, or file structures. This freedom requires strong technical leadership and clear coding standards.
SaaS applications often evolve rapidly with changing business requirements. Angular's structured approach helps teams refactor confidently, knowing that breaking changes will surface at compile time. React applications require more discipline to maintain consistency as they grow, but offer greater flexibility to adapt to unique requirements.
Testing Frameworks and Quality Assurance Capabilities
Angular comes with a comprehensive testing story out of the box. Jasmine and Karma are pre-configured for unit testing, while Protractor (now deprecated, replaced by Cypress or Playwright) handles end-to-end testing. The framework's dependency injection makes mocking services straightforward, and TestBed provides excellent utilities for component testing.
React's testing ecosystem centers around Jest and React Testing Library, with additional tools like Enzyme still in use. The component-focused approach makes unit testing intuitive, but teams often need to make decisions about additional testing utilities and patterns.
Both frameworks support similar quality assurance practices:
Unit Testing: Angular's TestBed vs React Testing Library
Integration Testing: Both support component integration testing well
E2E Testing: Cypress, Playwright, and similar tools work with both
Visual Regression: Storybook integration available for both
Angular's built-in testing setup reduces decision fatigue, while React's ecosystem offers more specialized testing tools for specific needs.
Component Reusability and Development Speed
Angular's component system promotes reusability through clear interfaces and dependency injection. The CLI generates boilerplate quickly, and the module system helps organize reusable components. However, Angular components tend to be more heavyweight due to the framework's comprehensive feature set.
React's lightweight component model excels at creating reusable UI elements. The props-based approach makes components highly composable, and the rich ecosystem provides countless pre-built components. Tools like Storybook integrate seamlessly for component development and documentation.
Development speed varies significantly between teams. Angular teams often move faster on enterprise features that benefit from the framework's built-in capabilities like forms, HTTP interceptors, and routing guards. React teams typically move faster on custom UI requirements and when leveraging the extensive third-party ecosystem.
Angular Advantages for Development Speed:
Built-in form validation and handling
Comprehensive HTTP client with interceptors
Integrated routing with guards
CLI code generation
React Advantages for Development Speed:
Faster iteration on UI components
Rich ecosystem of specialized libraries
Simpler component composition
Hot reloading and development tools
Strategic Decision Framework for SaaS Teams
Rapid Prototyping and MVP Development Scenarios
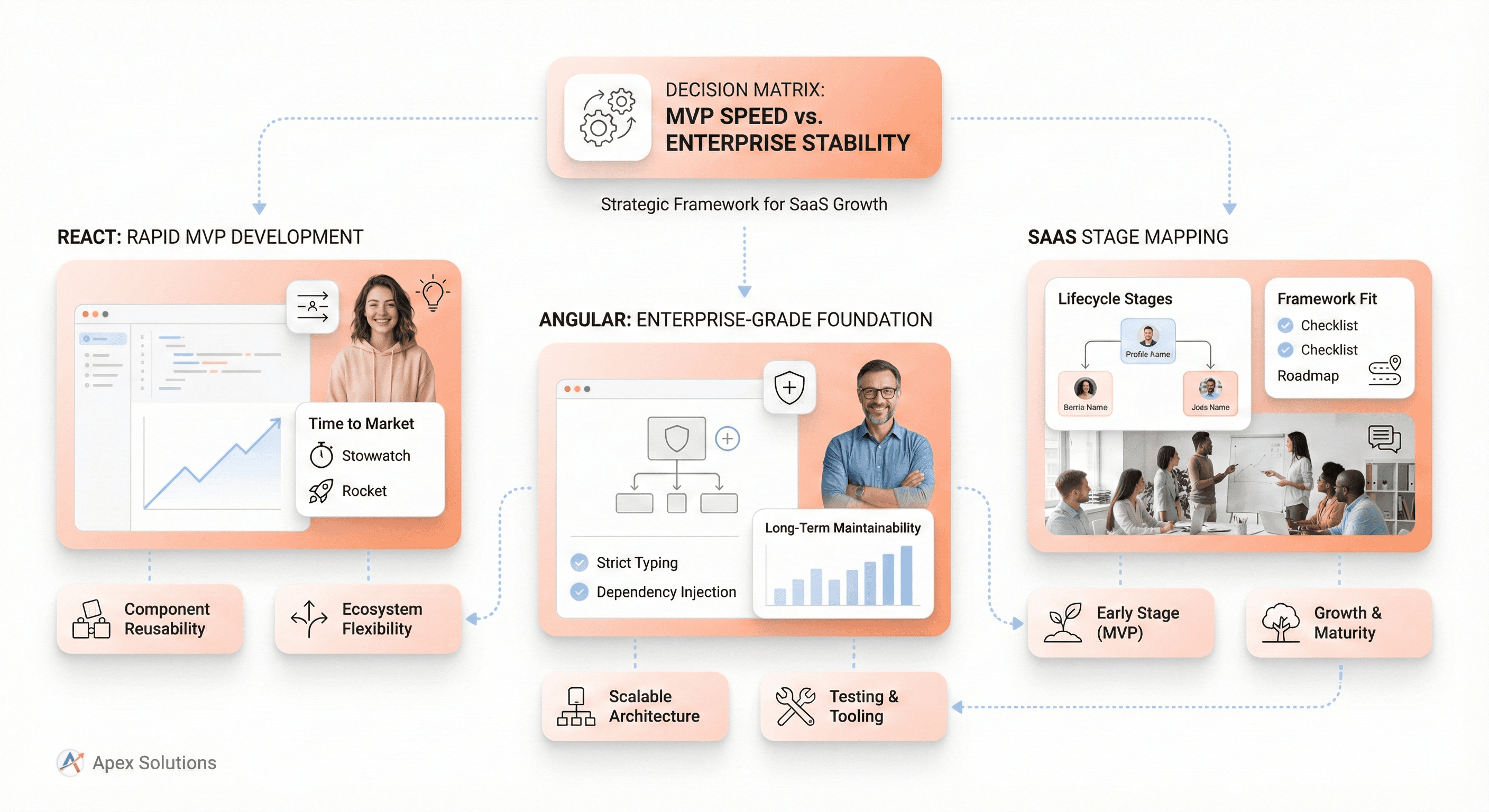
When you're racing against time to validate a product idea or secure your next funding round, React typically emerges as the clear winner for rapid prototyping scenarios. The component-based architecture allows teams to quickly cobble together functional interfaces using pre-built libraries like Material-UI or Ant Design. You can have a working prototype up and running in days rather than weeks.
React's massive ecosystem means you'll find ready-made solutions for almost every common SaaS feature - from authentication flows to payment integrations. The learning curve is gentler for junior developers, and you can often pull in freelancers or contractors who can contribute immediately without extensive onboarding.
Angular, while powerful, introduces complexity that can slow down MVP development. The opinionated structure and TypeScript requirements mean more upfront decisions and boilerplate code. However, if your team already has strong Angular expertise, this framework can actually accelerate development by providing clear patterns and reducing decision fatigue.
Framework | Prototyping Speed | Library Ecosystem | Learning Curve |
|---|---|---|---|
React | Fast | Extensive | Moderate |
Angular | Moderate | Comprehensive | Steep |
The sweet spot for React in MVP scenarios lies in consumer-facing SaaS products where speed to market trumps long-term architectural concerns.
Enterprise-Grade Applications with Complex Requirements
Enterprise SaaS applications demand a different calculus entirely. These systems often involve intricate business logic, complex data flows, and stringent security requirements that can span hundreds of components and multiple development teams.
Angular shines in these scenarios through its opinionated architecture and built-in enterprise features. The framework's dependency injection system, robust routing capabilities, and comprehensive testing utilities provide the scaffolding needed for large-scale applications. TypeScript isn't just recommended - it becomes essential for maintaining code quality across large teams.
The CLI tooling in Angular creates consistent project structures, making it easier for new team members to navigate codebases and understand established patterns. When you're managing multiple feature teams working on different parts of the application, this consistency becomes invaluable.
React can certainly handle enterprise complexity, but it requires more architectural decisions upfront. Teams need to establish conventions for state management, routing, testing, and project structure. While this flexibility can be powerful, it also introduces potential points of friction as teams scale.
Consider these factors for enterprise applications:
Team size and structure: Angular's conventions work better with larger, distributed teams
Long-term maintenance: Both frameworks are viable, but Angular provides more guardrails
Integration complexity: Angular's comprehensive approach often simplifies complex integrations
Performance at scale: Both can handle enterprise loads with proper optimization
Public-Facing vs Internal Tool Development Considerations
The intended audience for your SaaS application significantly influences the React vs Angular decision. Public-facing products prioritize different concerns than internal tools, and each framework has distinct advantages depending on your target users.
For public-facing SaaS products, React often provides better outcomes. The framework's flexibility allows for highly customized user experiences and easier integration with marketing tools, analytics platforms, and A/B testing frameworks. Bundle size optimization is typically more straightforward with React, leading to faster initial load times - a critical factor for user acquisition and retention.
React's server-side rendering capabilities through Next.js also give public products better SEO performance, which can be crucial for organic growth strategies. The vast ecosystem of UI libraries means you can create unique, branded experiences that differentiate your product in competitive markets.
Internal tools operate under different constraints. Users are typically more forgiving of longer load times, and the focus shifts toward productivity, consistency, and ease of maintenance. Angular's comprehensive approach often proves more valuable here:
Internal Tool Advantages (Angular):
Consistent UI patterns across different internal applications
Built-in form handling and validation for complex data entry
Comprehensive testing framework for business-critical workflows
Better long-term maintainability with less architectural drift
Public Product Advantages (React):
Faster time-to-interactive for better user experience
More flexibility for marketing integrations and conversion optimization
Easier customization for unique brand experiences
Better performance optimization options for diverse user environments
Hybrid Approaches and Technology Migration Strategies
Many successful SaaS companies don't commit exclusively to one framework. Instead, they adopt hybrid approaches that leverage the strengths of both technologies across different parts of their application ecosystem.
A common pattern involves using React for customer-facing interfaces and marketing sites while building internal admin panels and dashboards with Angular. This separation allows teams to optimize each tool for its specific use case and user requirements.
Micro-frontend architectures enable this hybrid approach by treating different sections of your application as independent deployments. You can gradually migrate from one framework to another without the risk and expense of a complete rewrite. Teams can experiment with new technologies in low-risk areas before making broader commitments.
Migration Strategies That Work:
Edge-first migration: Start with new features or less critical components
Service-by-service: Replace individual microservices with different frontend technologies
User-segment based: Different frameworks for different user types (customers vs admins)
Feature flagging: Gradual rollout of new framework implementations
When planning migrations, consider the total cost of ownership beyond just development time. Factor in team training, tooling changes, deployment pipeline modifications, and ongoing maintenance overhead. Sometimes the best technical choice isn't the best business choice, especially for stable, profitable products.
The most successful SaaS teams treat framework choice as an ongoing strategic decision rather than a one-time commitment. They maintain flexibility to adapt as their product, team, and market requirements evolve while avoiding the constant churn that can derail development productivity.
Conclusion
The data consistently shows React's dominance in 2026, with 41.6% developer adoption compared to Angular's 19.4%, and a commanding 6.0% web presence versus Angular's 0.2%. React's flexibility, extensive ecosystem, and lower barrier to entry make it the optimal choice for most SaaS teams seeking rapid development, easier hiring, and faster time-to-market. The framework's component-based architecture and virtual DOM deliver superior performance for dynamic, user-heavy applications that define modern SaaS products.
However, Angular remains the strategic choice for enterprise SaaS applications requiring strict architectural patterns, long-term maintainability, and integrated tooling out of the box. Teams building complex admin dashboards, regulated systems, or large-scale applications with multiple development teams will benefit from Angular's opinionated structure and TypeScript-first approach. The decision ultimately depends on your team's experience, project complexity, and business timeline – choose React for speed and flexibility, or Angular for enterprise-grade structure and consistency.
Choosing between React and Angular teams for your SaaS frontend can make or break your product's success. This guide is for SaaS founders, CTOs, and engineering managers who need to make an informed framework decision based on real data, not developer preferences.
React currently dominates with 41.6% developer adoption versus Angular's 19.4%, but this gap tells only part of the story. Your choice impacts everything from hiring speed to long-term maintenance costs. We'll examine the current market landscape and developer trends shaping 2026, compare how each framework's technical architecture affects SaaS development workflows, and provide a strategic decision framework that considers team productivity alongside performance characteristics.
The data shows React leads in community size and hiring pool, while Angular excels in enterprise-grade structure and built-in tooling. Your team size, product complexity, and growth timeline determine which advantage matters more for your SaaS business.
Current Market Landscape and Developer Adoption Trends
React's Dominance in Developer Usage and Community Size

React commands an impressive 40.58% share of the JavaScript framework landscape according to Stack Overflow's 2024 Developer Survey, making it the most widely adopted frontend framework globally. This dominance translates into practical advantages for SaaS teams building modern applications.
The numbers tell a compelling story. GitHub shows React repositories consistently ranking among the most starred and forked projects, with over 220,000 stars and contributions from more than 1,500 developers. The React ecosystem generates approximately 20 million weekly npm downloads, dwarfing most competitors and signaling robust community engagement.
What makes React particularly attractive for SaaS development is its component-based architecture and extensive third-party library ecosystem. Popular tools like Material-UI, Ant Design, and Chakra UI provide ready-made components that accelerate development timelines. The React community also produces specialized SaaS-focused libraries for authentication (Auth0 React SDK), state management (Redux, Zustand), and data fetching (React Query, SWR).
Developer satisfaction metrics consistently favor React, with 68.19% of developers expressing interest in continuing to work with the framework. This high satisfaction rate reduces team turnover risks and makes recruiting easier for SaaS companies looking to scale their frontend teams quickly.
Angular's Enterprise Market Position and Specialized Use Cases

Angular occupies a distinct position in the enterprise software market, particularly excelling in large-scale, complex business applications where structure and maintainability take precedence over rapid prototyping. Fortune 500 companies like Google, Microsoft, and Samsung rely on Angular for their internal tools and customer-facing applications.
The framework's TypeScript-first approach and opinionated architecture make it particularly well-suited for enterprise SaaS platforms handling complex business logic. Companies building comprehensive ERP systems, financial management platforms, or healthcare software often choose Angular for its robust testing framework, dependency injection system, and built-in form validation capabilities.
Angular's enterprise appeal stems from several key factors:
Comprehensive CLI tooling that enforces consistent project structure across large teams
Built-in internationalization (i18n) support for global SaaS deployments
Robust security features, including built-in sanitization and CSRF protection
Mature ecosystem with enterprise-grade libraries like Angular Material and PrimeNG
Major enterprise SaaS success stories include IBM's Watson platform components, Google Cloud Console interfaces, and various Microsoft Office 365 tools. These implementations demonstrate Angular's capability to handle complex user interfaces with thousands of components while maintaining performance and code quality standards.
Web Presence Statistics and Real-World Implementation Data
Real-world usage patterns reveal interesting trends in how React and Angular are deployed across different types of SaaS applications. According to BuiltWith technology surveys, React powers approximately 3.2% of all websites globally, while Angular accounts for roughly 0.8%. However, these raw numbers don't tell the complete story.
React dominates in certain SaaS categories:
SaaS Category | React Usage | Notable Examples |
|---|---|---|
Social Media & Communication | 85% | Facebook, WhatsApp Web, Discord |
E-commerce Platforms | 72% | Shopify, Airbnb, Uber |
Productivity Tools | 68% | Notion, Slack, Asana |
Developer Tools | 79% | GitHub, CodePen, Figma |
Angular shows stronger presence in enterprise-focused sectors:
Enterprise Category | Angular Usage | Notable Examples |
|---|---|---|
Financial Services | 45% | Goldman Sachs platforms, Banking apps |
Healthcare Systems | 38% | Epic MyChart, Various EMR systems |
Government Platforms | 42% | IRS systems, Municipal portals |
Manufacturing & Logistics | 35% | SAP interfaces, Supply chain tools |
Performance benchmarks from HTTPArchive data show React applications averaging 1.2MB bundle sizes for typical SaaS dashboards, while Angular applications tend toward 1.8MB due to the framework's comprehensive nature. However, Angular applications often demonstrate better performance consistency across different devices and network conditions.
Job Market Demand and Talent Pool Availability

The job market landscape heavily favors React developers, creating both opportunities and challenges for SaaS hiring teams. LinkedIn job postings show React developer positions outnumbering Angular roles by approximately 3:1 ratio, with React positions offering average salaries 12% higher than Angular counterparts.
Talent pool statistics reveal significant differences in availability and experience levels:
React Developer Market:
2.3 million developers globally with React experience
Average of 3.2 years React experience among job seekers
Higher concentration of junior to mid-level developers
Strong presence in startup ecosystems and remote work communities
Angular Developer Market:
890,000 developers with substantial Angular experience
Average of 4.7 years Angular experience among job seekers
Higher proportion of senior developers with enterprise background
Concentrated in traditional corporate environments and consulting firms
Geographic distribution patterns show React developers clustering around tech hubs like Silicon Valley, Austin, and Berlin, while Angular expertise concentrates in enterprise-heavy regions including New York financial districts, pharmaceutical corridors, and government contractor areas.
Salary data from Glassdoor and Stack Overflow surveys indicates React developers command premium rates in competitive markets, with senior React engineers averaging $145,000 annually compared to $132,000 for Angular specialists. However, Angular developers often enjoy greater job security and benefits packages within enterprise environments.
The talent acquisition timeline also differs significantly. React positions typically fill within 45 days due to larger candidate pools, while Angular roles may require 75-90 days but often result in longer employee tenure rates exceeding industry averages by 18 months.
Technical Architecture and Development Approach Comparison
Framework vs Library Philosophy and Ecosystem Differences

React takes a library approach, giving developers the freedom to choose their own tools and architecture patterns. This philosophy means you're essentially picking from a vast ecosystem of third-party packages to build your complete solution. Want routing? You'll likely reach for React Router. Need state management? Redux, Zustand, or Context API are popular choices. This flexibility appeals to teams that prefer crafting their own development stack.
Angular operates as a comprehensive framework with an opinionated structure. Google built it as an all-in-one solution that includes routing, HTTP client, forms handling, and testing utilities right out of the box. The Angular CLI generates projects with consistent folder structures and build configurations, enforcing patterns across different teams and projects.
Aspect | React | Angular |
|---|---|---|
Philosophy | Library + ecosystem | Full framework |
Decision making | Developer choice | Opinionated defaults |
Learning curve | Gradual, tool-by-tool | Steeper, but comprehensive |
Ecosystem size | Massive, fragmented | Smaller, integrated |
For SaaS teams, React's flexibility can be both liberating and overwhelming. Smaller teams might struggle with decision fatigue, while larger organizations benefit from the ability to standardize their own patterns. Angular's opinionated nature reduces bikeshedding and gets teams productive faster, especially when working with developers new to frontend frameworks.
Component-Based Architecture Implementation Strategies
Both frameworks embrace component-based architecture, but their implementation approaches differ significantly. React components are essentially JavaScript functions that return JSX, making them intuitive for developers familiar with functional programming concepts. The component lifecycle is straightforward, with hooks like useEffect and useState providing clear entry points for managing state and side effects.
Angular components follow a class-based structure with decorators that define metadata. Each component typically consists of four files: TypeScript class, HTML template, CSS styles, and optional test file. This structure promotes organization but can feel verbose for simple components.
// React functional component
const UserProfile = ({ userId }) => {
const [user, setUser] = useState(null);
useEffect(() => {
fetchUser(userId).then(setUser);
}, [userId]);
return <div>{user?.name}</div>;
};
// Angular component
@Component({
selector: 'user-profile',
template: '<div>{{user?.name}}</div>
React's approach encourages composition over inheritance, making it easier to build complex UIs from smaller, reusable pieces. Angular's dependency injection system and hierarchical structure work well for larger applications where clear boundaries between services and components matter.
Data Binding Models and State Management Approaches

React implements unidirectional data flow through props and state, making data movement predictable and debugging easier. State changes trigger re-renders, and React's reconciliation algorithm efficiently updates only the necessary DOM elements. For complex state management, teams often introduce Redux for global state or use React's Context API for component tree-specific data.
Angular provides two-way data binding through its template syntax, allowing automatic synchronization between model and view. While convenient for forms and user inputs, this can sometimes make data flow harder to trace in complex applications. Angular's built-in services and RxJS observables offer powerful patterns for managing application state and handling asynchronous data streams.
The choice between these approaches impacts how teams structure their applications. React's explicit state management makes code more predictable but requires more boilerplate. Angular's two-way binding reduces code volume but can introduce subtle bugs when data flows become complex.
For SaaS applications handling real-time updates, Angular's RxJS integration provides excellent tools for managing websockets and event streams. React teams typically reach for libraries like Socket.io client or implement custom hooks for similar functionality.
TypeScript Integration and Development Tooling
TypeScript support showcases another philosophical difference between the frameworks. React added TypeScript support gradually, and while it's excellent today, you can still build React applications with plain JavaScript. Many React projects start with JavaScript and migrate to TypeScript as they grow.
Angular was built with TypeScript from the ground up. Every Angular project uses TypeScript by default, and the framework's architecture assumes static typing. Angular's CLI, dependency injection system, and decorators all leverage TypeScript's features heavily.
Both ecosystems offer robust development tooling, but with different focuses. React's tooling landscape includes Create React App, Vite, and Next.js for project setup, plus excellent browser extensions for debugging. The ecosystem's diversity means teams can choose tools that match their specific needs.
Angular CLI provides a unified development experience with code generation, testing, building, and deployment commands. The tooling feels more integrated but less flexible than React's ecosystem. Angular DevTools and the framework's built-in testing utilities create a comprehensive development environment.
For SaaS teams prioritizing type safety and consistent tooling across projects, Angular's TypeScript-first approach and unified CLI offer clear advantages. Teams valuing flexibility and gradual adoption might prefer React's more flexible tooling ecosystem.
Performance Characteristics for SaaS Applications
Bundle Size Optimization and Loading Speed Considerations

React applications typically start with a smaller initial footprint compared to Angular's comprehensive framework approach. React's core library weighs around 42KB gzipped, while Angular brings approximately 130KB for a basic setup. This difference becomes critical when SaaS applications need to load quickly for users across varying network conditions.
React's flexibility allows developers to cherry-pick libraries, creating lean bundles tailored to specific features. Tree shaking works more effectively with React's modular ecosystem, especially when using tools like Webpack or Vite. Angular's monolithic structure means you often include the entire framework even for simple components, though modern Angular has improved significantly with features like differential loading and lazy loading modules.
For SaaS applications serving global users, every kilobyte matters. React's ecosystem encourages code splitting strategies where route-based chunks load on demand. Angular achieves similar results through lazy-loaded feature modules, but requires more upfront architectural planning.
Framework | Base Size (gzipped) | Bundle Flexibility | Code Splitting |
|---|---|---|---|
React | ~42KB | High | Component-level |
Angular | ~130KB | Medium | Module-level |
Virtual DOM vs Real DOM Impact on Complex UI Rendering
React's Virtual DOM creates an in-memory representation of the actual DOM, enabling efficient batch updates and minimizing expensive DOM manipulations. When building complex SaaS interfaces with real-time data updates, dashboards with multiple charts, or collaborative editing features, React's reconciliation algorithm shines by calculating the minimal set of changes needed.
Angular takes a different approach with its change detection system and direct DOM manipulation. The framework runs change detection cycles to identify when component properties change, then updates the real DOM directly. For highly interactive SaaS applications with frequent state changes, Angular's zone.js can trigger unnecessary checks across the entire component tree, potentially causing performance bottlenecks.
React's fiber architecture allows for time-slicing, breaking down rendering work into chunks that don't block the main thread. This proves valuable for SaaS applications handling large datasets or complex visualizations where maintaining 60fps interactions is essential for user experience.
Angular's OnPush change detection strategy can match React's performance when implemented correctly, but requires developers to understand and properly configure the detection mechanism. React's approach feels more intuitive for teams building data-heavy SaaS interfaces.
Scalability Patterns for Growing SaaS Products

React's component-based architecture naturally supports horizontal scaling as SaaS products grow. Teams can develop independent components, share them across different product areas, and even extract them into separate libraries. The ecosystem supports micro-frontend architectures where different teams can work on isolated parts of the application using their preferred React patterns.
Angular's opinionated structure provides clear scalability guidelines through its hierarchical dependency injection system and feature modules. Large SaaS teams benefit from Angular's consistent patterns - every developer follows similar approaches for routing, state management, and component organization. This consistency becomes valuable when onboarding new team members or maintaining large codebases.
State management scalability differs significantly between frameworks. React offers multiple solutions (Redux, Zustand, Context API) letting teams choose based on complexity needs. Angular's services and RxJS provide a consistent reactive programming model that scales well but requires deeper learning investment.
Component sharing across different SaaS modules works differently in each framework. React components integrate easily into various build systems and can be published as standalone packages. Angular's dependency injection and decorator system creates tighter coupling, making component extraction more complex but ensuring consistency.
Build Process Efficiency and Development Velocity
React's build ecosystem offers numerous options from Create React App to Vite, Next.js, and custom Webpack configurations. Development teams can optimize build processes for their specific SaaS requirements, whether prioritizing fast development rebuilds or optimized production bundles. Hot module replacement works seamlessly across most React build tools, enabling rapid iteration cycles.
Angular CLI provides a standardized build process with sensible defaults and powerful optimization features. The build system handles complex optimizations like Ahead-of-Time compilation, bundle optimization, and service worker generation automatically. Teams spend less time configuring build tools but have fewer customization options.
Development server startup times favor React, especially with modern tools like Vite that leverage ES modules for near-instantaneous cold starts. Angular's compilation process, while more thorough, requires longer initial startup times that can slow down development workflows.
TypeScript integration differs between frameworks. Angular was built with TypeScript from the ground up, providing seamless type checking and excellent IDE support. React's TypeScript adoption requires additional configuration but offers more flexibility in how strictly types are enforced across the codebase.
Testing strategies impact development velocity significantly. React's lightweight nature makes unit testing straightforward with tools like Jest and React Testing Library. Angular's dependency injection system requires more setup but provides powerful testing utilities for complex component interactions and service mocking.
Team Productivity and Developer Experience Factors
Learning Curve and Onboarding Requirements
Angular presents a steeper learning curve for new developers, especially those coming from traditional JavaScript backgrounds. The framework demands understanding of TypeScript, dependency injection, decorators, and Angular-specific concepts like services, directives, and modules. New team members typically need 2-3 weeks to become productive, with full proficiency taking several months.
React offers a gentler introduction path. Developers can start with basic JavaScript knowledge and gradually adopt advanced patterns. The component-based approach feels intuitive to most developers, and the ecosystem's flexibility allows teams to introduce complexity incrementally. Most developers become productive within 1-2 weeks.
For SaaS teams with tight deadlines, React's shorter onboarding time translates directly to faster team scaling. However, Angular's structured approach can benefit teams with junior developers who need clear guidelines and conventions.
Framework | Initial Learning Time | Full Proficiency | Key Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
Angular | 2-3 weeks | 3-6 months | TypeScript, DI, RxJS |
React | 1-2 weeks | 2-4 months | State management, ecosystem choices |
Code Maintainability and Long-term Project Sustainability
Angular's opinionated architecture shines in long-term maintainability. The framework enforces consistent patterns across the entire application through its CLI, strict TypeScript integration, and built-in architectural concepts. Code reviews become more straightforward when everyone follows the same conventions. The dependency injection system makes testing isolated components easier, while the module system helps organize large applications.
React's flexibility becomes a double-edged sword for maintainability. While experienced teams can create highly maintainable architectures, the lack of enforced patterns can lead to inconsistent codebases. Different developers might choose different state management solutions, component patterns, or file structures. This freedom requires strong technical leadership and clear coding standards.
SaaS applications often evolve rapidly with changing business requirements. Angular's structured approach helps teams refactor confidently, knowing that breaking changes will surface at compile time. React applications require more discipline to maintain consistency as they grow, but offer greater flexibility to adapt to unique requirements.
Testing Frameworks and Quality Assurance Capabilities
Angular comes with a comprehensive testing story out of the box. Jasmine and Karma are pre-configured for unit testing, while Protractor (now deprecated, replaced by Cypress or Playwright) handles end-to-end testing. The framework's dependency injection makes mocking services straightforward, and TestBed provides excellent utilities for component testing.
React's testing ecosystem centers around Jest and React Testing Library, with additional tools like Enzyme still in use. The component-focused approach makes unit testing intuitive, but teams often need to make decisions about additional testing utilities and patterns.
Both frameworks support similar quality assurance practices:
Unit Testing: Angular's TestBed vs React Testing Library
Integration Testing: Both support component integration testing well
E2E Testing: Cypress, Playwright, and similar tools work with both
Visual Regression: Storybook integration available for both
Angular's built-in testing setup reduces decision fatigue, while React's ecosystem offers more specialized testing tools for specific needs.
Component Reusability and Development Speed
Angular's component system promotes reusability through clear interfaces and dependency injection. The CLI generates boilerplate quickly, and the module system helps organize reusable components. However, Angular components tend to be more heavyweight due to the framework's comprehensive feature set.
React's lightweight component model excels at creating reusable UI elements. The props-based approach makes components highly composable, and the rich ecosystem provides countless pre-built components. Tools like Storybook integrate seamlessly for component development and documentation.
Development speed varies significantly between teams. Angular teams often move faster on enterprise features that benefit from the framework's built-in capabilities like forms, HTTP interceptors, and routing guards. React teams typically move faster on custom UI requirements and when leveraging the extensive third-party ecosystem.
Angular Advantages for Development Speed:
Built-in form validation and handling
Comprehensive HTTP client with interceptors
Integrated routing with guards
CLI code generation
React Advantages for Development Speed:
Faster iteration on UI components
Rich ecosystem of specialized libraries
Simpler component composition
Hot reloading and development tools
Strategic Decision Framework for SaaS Teams
Rapid Prototyping and MVP Development Scenarios

When you're racing against time to validate a product idea or secure your next funding round, React typically emerges as the clear winner for rapid prototyping scenarios. The component-based architecture allows teams to quickly cobble together functional interfaces using pre-built libraries like Material-UI or Ant Design. You can have a working prototype up and running in days rather than weeks.
React's massive ecosystem means you'll find ready-made solutions for almost every common SaaS feature - from authentication flows to payment integrations. The learning curve is gentler for junior developers, and you can often pull in freelancers or contractors who can contribute immediately without extensive onboarding.
Angular, while powerful, introduces complexity that can slow down MVP development. The opinionated structure and TypeScript requirements mean more upfront decisions and boilerplate code. However, if your team already has strong Angular expertise, this framework can actually accelerate development by providing clear patterns and reducing decision fatigue.
Framework | Prototyping Speed | Library Ecosystem | Learning Curve |
|---|---|---|---|
React | Fast | Extensive | Moderate |
Angular | Moderate | Comprehensive | Steep |
The sweet spot for React in MVP scenarios lies in consumer-facing SaaS products where speed to market trumps long-term architectural concerns.
Enterprise-Grade Applications with Complex Requirements
Enterprise SaaS applications demand a different calculus entirely. These systems often involve intricate business logic, complex data flows, and stringent security requirements that can span hundreds of components and multiple development teams.
Angular shines in these scenarios through its opinionated architecture and built-in enterprise features. The framework's dependency injection system, robust routing capabilities, and comprehensive testing utilities provide the scaffolding needed for large-scale applications. TypeScript isn't just recommended - it becomes essential for maintaining code quality across large teams.
The CLI tooling in Angular creates consistent project structures, making it easier for new team members to navigate codebases and understand established patterns. When you're managing multiple feature teams working on different parts of the application, this consistency becomes invaluable.
React can certainly handle enterprise complexity, but it requires more architectural decisions upfront. Teams need to establish conventions for state management, routing, testing, and project structure. While this flexibility can be powerful, it also introduces potential points of friction as teams scale.
Consider these factors for enterprise applications:
Team size and structure: Angular's conventions work better with larger, distributed teams
Long-term maintenance: Both frameworks are viable, but Angular provides more guardrails
Integration complexity: Angular's comprehensive approach often simplifies complex integrations
Performance at scale: Both can handle enterprise loads with proper optimization
Public-Facing vs Internal Tool Development Considerations
The intended audience for your SaaS application significantly influences the React vs Angular decision. Public-facing products prioritize different concerns than internal tools, and each framework has distinct advantages depending on your target users.
For public-facing SaaS products, React often provides better outcomes. The framework's flexibility allows for highly customized user experiences and easier integration with marketing tools, analytics platforms, and A/B testing frameworks. Bundle size optimization is typically more straightforward with React, leading to faster initial load times - a critical factor for user acquisition and retention.
React's server-side rendering capabilities through Next.js also give public products better SEO performance, which can be crucial for organic growth strategies. The vast ecosystem of UI libraries means you can create unique, branded experiences that differentiate your product in competitive markets.
Internal tools operate under different constraints. Users are typically more forgiving of longer load times, and the focus shifts toward productivity, consistency, and ease of maintenance. Angular's comprehensive approach often proves more valuable here:
Internal Tool Advantages (Angular):
Consistent UI patterns across different internal applications
Built-in form handling and validation for complex data entry
Comprehensive testing framework for business-critical workflows
Better long-term maintainability with less architectural drift
Public Product Advantages (React):
Faster time-to-interactive for better user experience
More flexibility for marketing integrations and conversion optimization
Easier customization for unique brand experiences
Better performance optimization options for diverse user environments
Hybrid Approaches and Technology Migration Strategies
Many successful SaaS companies don't commit exclusively to one framework. Instead, they adopt hybrid approaches that leverage the strengths of both technologies across different parts of their application ecosystem.
A common pattern involves using React for customer-facing interfaces and marketing sites while building internal admin panels and dashboards with Angular. This separation allows teams to optimize each tool for its specific use case and user requirements.
Micro-frontend architectures enable this hybrid approach by treating different sections of your application as independent deployments. You can gradually migrate from one framework to another without the risk and expense of a complete rewrite. Teams can experiment with new technologies in low-risk areas before making broader commitments.
Migration Strategies That Work:
Edge-first migration: Start with new features or less critical components
Service-by-service: Replace individual microservices with different frontend technologies
User-segment based: Different frameworks for different user types (customers vs admins)
Feature flagging: Gradual rollout of new framework implementations
When planning migrations, consider the total cost of ownership beyond just development time. Factor in team training, tooling changes, deployment pipeline modifications, and ongoing maintenance overhead. Sometimes the best technical choice isn't the best business choice, especially for stable, profitable products.
The most successful SaaS teams treat framework choice as an ongoing strategic decision rather than a one-time commitment. They maintain flexibility to adapt as their product, team, and market requirements evolve while avoiding the constant churn that can derail development productivity.
Conclusion

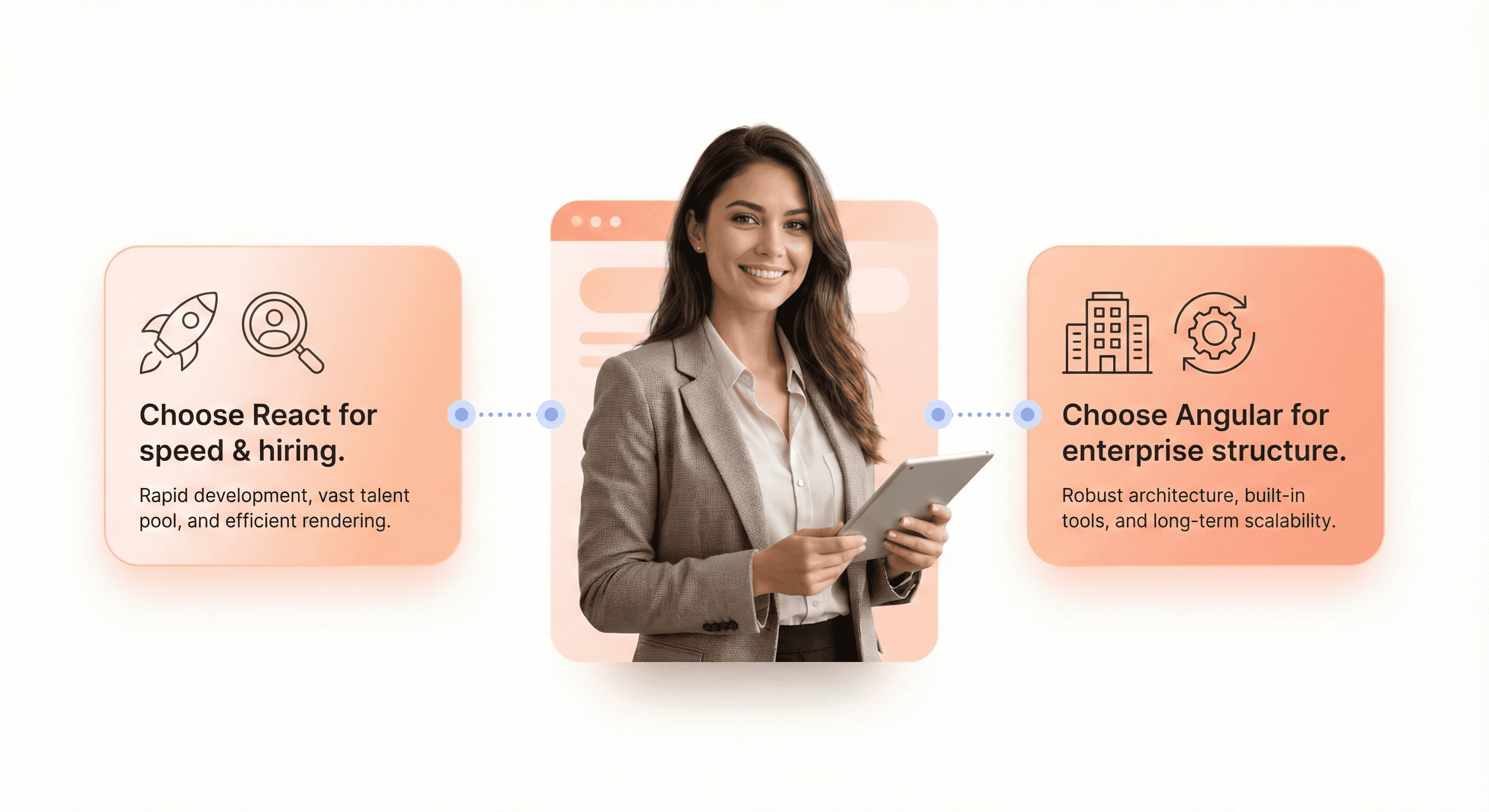
The data consistently shows React's dominance in 2026, with 41.6% developer adoption compared to Angular's 19.4%, and a commanding 6.0% web presence versus Angular's 0.2%. React's flexibility, extensive ecosystem, and lower barrier to entry make it the optimal choice for most SaaS teams seeking rapid development, easier hiring, and faster time-to-market. The framework's component-based architecture and virtual DOM deliver superior performance for dynamic, user-heavy applications that define modern SaaS products.
However, Angular remains the strategic choice for enterprise SaaS applications requiring strict architectural patterns, long-term maintainability, and integrated tooling out of the box. Teams building complex admin dashboards, regulated systems, or large-scale applications with multiple development teams will benefit from Angular's opinionated structure and TypeScript-first approach. The decision ultimately depends on your team's experience, project complexity, and business timeline – choose React for speed and flexibility, or Angular for enterprise-grade structure and consistency.
Hiring a React developer for your SaaS? This in-depth checklist helps founders assess frontend skills, scalability, performance, and product impact.

Stuck with slow releases and high IT costs?
▶︎
Launch 2.5x faster with our AI-driven frontend workflows, specialized for SaaS.
▶︎
Cut IT costs by up to 50% and boost user adoption by 2x with our proprietary frameworks.

Stuck with slow releases and high IT costs?
▶︎
Launch 2.5x faster with our AI-driven frontend workflows, specialized for SaaS.
▶︎
Cut IT costs by up to 50% and boost user adoption by 2x with our proprietary frameworks.

Stuck with slow releases and high IT costs?
▶︎
Launch 2.5x faster with our AI-driven frontend workflows, specialized for SaaS.
▶︎
Cut IT costs by up to 50% and boost user adoption by 2x with our proprietary frameworks.
Frequently Asked Questions
We're ready to answer your questions
Slow releases, clunky dashboards, and frustrated users? You've got questions about how to fix them. We have the Frontend-First answers that unlock growth. Let's talk solutions.
According to the 2024 Stack Overflow Developer Survey, React is used by a significantly higher proportion of professional developers than Angular — with React usage around ~41.6% compared to Angular at ~19.4%. Additionally, the State of JavaScript 2024 survey shows React continuing to lead usage and retention among front-end frameworks, while Angular remains commonly used but behind React in raw adoption among respondents.
Answer
What’s the difference in popularity between React and Angular among developers?
Question
The strong usage figures for React reflect its flexibility and widespread adoption in the developer ecosystem. React is a library focused on building user interfaces and supports incremental adoption, meaning teams can integrate it gradually or extend it with additional tools as needed. In contrast, Angular is a full framework that provides a comprehensive, opinionated structure but generally trails React in overall developer usage.
Answer
Why do many SaaS teams choose React over Angular?
Question
Yes. While Angular is less widely used than React overall, it remains a strong choice — particularly for structured, enterprise-scale applications — because it is a full framework built on TypeScript with a rich set of built-in patterns and tooling. The surveys show Angular continues to be adopted and remains a significant part of the front-end ecosystem.
Answer
Is Angular still relevant for modern SaaS applications?
Question
Ecosystem signals such as npm activity indicate that React-related packages receive far more weekly downloads than Angular’s core package, reflecting a larger volume of usage and dependency across projects. However, download counts alone don’t equal developer count — they include automated tooling, CI builds, and mirrors. Both ecosystems remain actively maintained.
Answer
How do React and Angular differ in ecosystem activity?
Question
Yes. Surveys and ecosystem analysis suggest that React’s popularity and flexibility make it easier to hire for and adopt incrementally across varying project sizes, while Angular’s comprehensive, structured nature can benefit larger teams building enterprise-scale SaaS applications with complex requirements.
Answer
Should team size and project scale influence framework choice?
Question
Frequently Asked Questions
We're ready to answer your questions
Slow releases, clunky dashboards, and frustrated users? You've got questions about how to fix them. We have the Frontend-First answers that unlock growth. Let's talk solutions.
According to the 2024 Stack Overflow Developer Survey, React is used by a significantly higher proportion of professional developers than Angular — with React usage around ~41.6% compared to Angular at ~19.4%. Additionally, the State of JavaScript 2024 survey shows React continuing to lead usage and retention among front-end frameworks, while Angular remains commonly used but behind React in raw adoption among respondents.
Answer
What’s the difference in popularity between React and Angular among developers?
Question
The strong usage figures for React reflect its flexibility and widespread adoption in the developer ecosystem. React is a library focused on building user interfaces and supports incremental adoption, meaning teams can integrate it gradually or extend it with additional tools as needed. In contrast, Angular is a full framework that provides a comprehensive, opinionated structure but generally trails React in overall developer usage.
Answer
Why do many SaaS teams choose React over Angular?
Question
Yes. While Angular is less widely used than React overall, it remains a strong choice — particularly for structured, enterprise-scale applications — because it is a full framework built on TypeScript with a rich set of built-in patterns and tooling. The surveys show Angular continues to be adopted and remains a significant part of the front-end ecosystem.
Answer
Is Angular still relevant for modern SaaS applications?
Question
Ecosystem signals such as npm activity indicate that React-related packages receive far more weekly downloads than Angular’s core package, reflecting a larger volume of usage and dependency across projects. However, download counts alone don’t equal developer count — they include automated tooling, CI builds, and mirrors. Both ecosystems remain actively maintained.
Answer
How do React and Angular differ in ecosystem activity?
Question
Yes. Surveys and ecosystem analysis suggest that React’s popularity and flexibility make it easier to hire for and adopt incrementally across varying project sizes, while Angular’s comprehensive, structured nature can benefit larger teams building enterprise-scale SaaS applications with complex requirements.
Answer
Should team size and project scale influence framework choice?
Question
Frequently Asked Questions
We're ready to answer your questions
Slow releases, clunky dashboards, and frustrated users? You've got questions about how to fix them. We have the Frontend-First answers that unlock growth. Let's talk solutions.
According to the 2024 Stack Overflow Developer Survey, React is used by a significantly higher proportion of professional developers than Angular — with React usage around ~41.6% compared to Angular at ~19.4%. Additionally, the State of JavaScript 2024 survey shows React continuing to lead usage and retention among front-end frameworks, while Angular remains commonly used but behind React in raw adoption among respondents.
Answer
What’s the difference in popularity between React and Angular among developers?
Question
The strong usage figures for React reflect its flexibility and widespread adoption in the developer ecosystem. React is a library focused on building user interfaces and supports incremental adoption, meaning teams can integrate it gradually or extend it with additional tools as needed. In contrast, Angular is a full framework that provides a comprehensive, opinionated structure but generally trails React in overall developer usage.
Answer
Why do many SaaS teams choose React over Angular?
Question
Yes. While Angular is less widely used than React overall, it remains a strong choice — particularly for structured, enterprise-scale applications — because it is a full framework built on TypeScript with a rich set of built-in patterns and tooling. The surveys show Angular continues to be adopted and remains a significant part of the front-end ecosystem.
Answer
Is Angular still relevant for modern SaaS applications?
Question
Ecosystem signals such as npm activity indicate that React-related packages receive far more weekly downloads than Angular’s core package, reflecting a larger volume of usage and dependency across projects. However, download counts alone don’t equal developer count — they include automated tooling, CI builds, and mirrors. Both ecosystems remain actively maintained.
Answer
How do React and Angular differ in ecosystem activity?
Question
Yes. Surveys and ecosystem analysis suggest that React’s popularity and flexibility make it easier to hire for and adopt incrementally across varying project sizes, while Angular’s comprehensive, structured nature can benefit larger teams building enterprise-scale SaaS applications with complex requirements.
Answer
Should team size and project scale influence framework choice?
Question


About the author
Author Name:
Parth G
|
Founder of
Hashbyt
I’m the founder of Hashbyt, an AI-first frontend and UI/UX SaaS partner helping 200+ SaaS companies scale faster through intelligent, growth-driven design. My work focuses on building modern frontend systems, design frameworks, and product modernization strategies that boost revenue, improve user adoption, and help SaaS founders turn their UI into a true growth engine.
Related Blogs
Related Blogs
Is a clunky UI holding back your growth?
Is a clunky UI holding back your growth?
▶︎
Transform slow, frustrating dashboards into intuitive interfaces that ensure effortless user adoption.
▶︎
Transform slow, frustrating dashboards into intuitive interfaces that ensure effortless user adoption.

Is a clunky UI holding back your growth?
Is a clunky UI holding back your growth?
▶︎
Transform slow, frustrating dashboards into intuitive interfaces that ensure effortless user adoption.
▶︎
Transform slow, frustrating dashboards into intuitive interfaces that ensure effortless user adoption.

Is a clunky UI holding back your growth?
Is a clunky UI holding back your growth?
▶︎
Transform slow, frustrating dashboards into intuitive interfaces that ensure effortless user adoption.
▶︎
Transform slow, frustrating dashboards into intuitive interfaces that ensure effortless user adoption.





