
Why Hiring the Right React Developer Matters for SaaS Success
The frontend is the product for SaaS companies, not a supporting layer. The frontend mediates all user interactions with your platform, including dashboards, settings panels, and onboarding processes. Research consistently shows that performance, usability, and stability directly affect user retention and conversion. A slow or unstable interface erodes trust quickly, leading to increased churn and reduced lifetime value.
React is widely adopted because it enables teams to build dynamic, responsive interfaces efficiently. However, React intentionally provides flexibility rather than rigid conventions. This flexibility is a double-edged sword: strong developers create scalable, maintainable systems, while weak architectural decisions silently accumulate technical debt.
Over time, this debt slows feature development, increases bug frequency, and raises the cost of change, problems that compound in SaaS products that evolve continuously.
Hiring the right React developer is therefore not about checking off a list of technologies. It is about selecting someone whose decisions will shape your product’s velocity, stability, and scalability for years.
Overview of What This Checklist Covers
This guide is designed to help SaaS founders, technical and non-technical alike, evaluate React developers holistically. It covers:
How to align frontend hiring with your SaaS product stage
Core React and JavaScript capabilities that matter in real products
SaaS-specific concerns like scalability, performance, and security
Problem-solving ability, communication, and long-term ownership
Rather than focusing on buzzwords, this checklist emphasizes decision quality, judgment, and long-term impact.
Define SaaS Requirements Before Hiring a React Developer
Define Your Product Vision
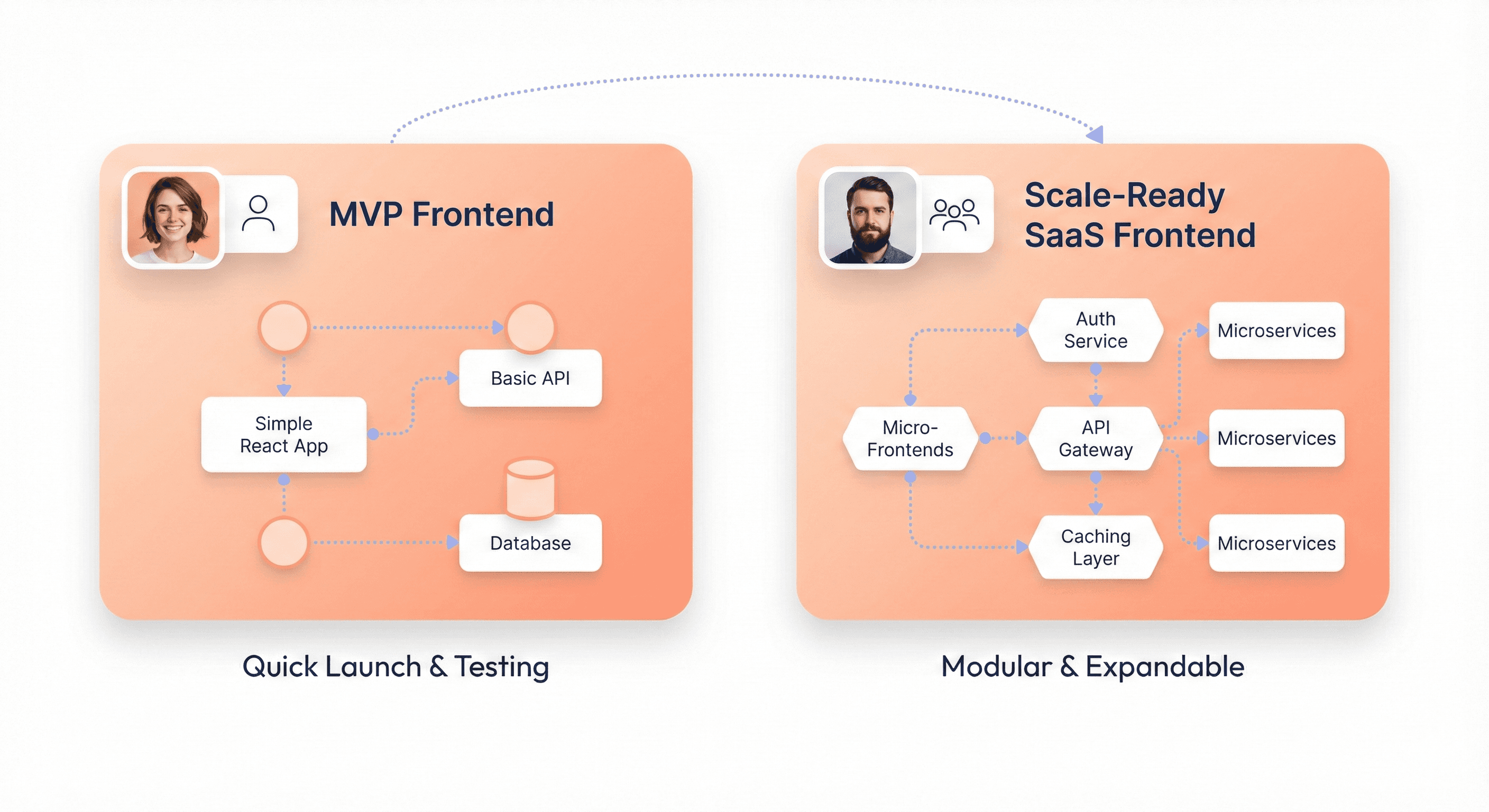
Before evaluating any candidate, founders must be clear about what they are building now and what the product must become.
An MVP exists to validate assumptions quickly. At this stage, speed of learning is more important than perfect architecture. Overengineering too early delays feedback and increases cost without delivering proportional value. However, this does not mean ignoring structure entirely. Early decisions still influence how difficult future changes will be.
SaaS offerings are dynamic. They constantly change, adding new features, user segments, and integrations, in contrast to one-time websites. Frontend choices made during the MVP stage have the potential to either facilitate this evolution or increase the cost of each change. A strong React developer understands how to move fast without painting the product into a corner.
Identify Technical Requirements
Front-End Complexity Assessment

Not all SaaS frontends are equal. A simple landing page with authentication differs vastly from a multi-tenant dashboard with real-time updates, role-based access, and complex data visualization.
React encourages a component-driven architecture, where interfaces are broken down into reusable pieces. This approach improves clarity and consistency, especially in complex UIs. However, as component trees grow deeper, performance issues can emerge if rendering is not managed carefully. Unnecessary re-renders reduce responsiveness and degrade user experience.
Founders should assess whether their product involves:
Data-heavy dashboards
Highly interactive workflows
Conditional UI based on roles or permissions
These factors increase frontend complexity and raise the bar for architectural competence.
Integration Needs
Most SaaS products are API-driven. The frontend is responsible for fetching data, handling partial responses, managing loading states, and gracefully dealing with failures. Real users experience network latency, dropped connections, and backend errors—conditions that are often invisible during development.
Poor handling of these scenarios results in broken flows and confusing interfaces. Conversely, thoughtful API integration improves resilience and user trust. A React developer must understand how to synchronize UI state with asynchronous data while keeping components readable and maintainable.
Core React Developer Skills for SaaS Frontends
Core React Knowledge
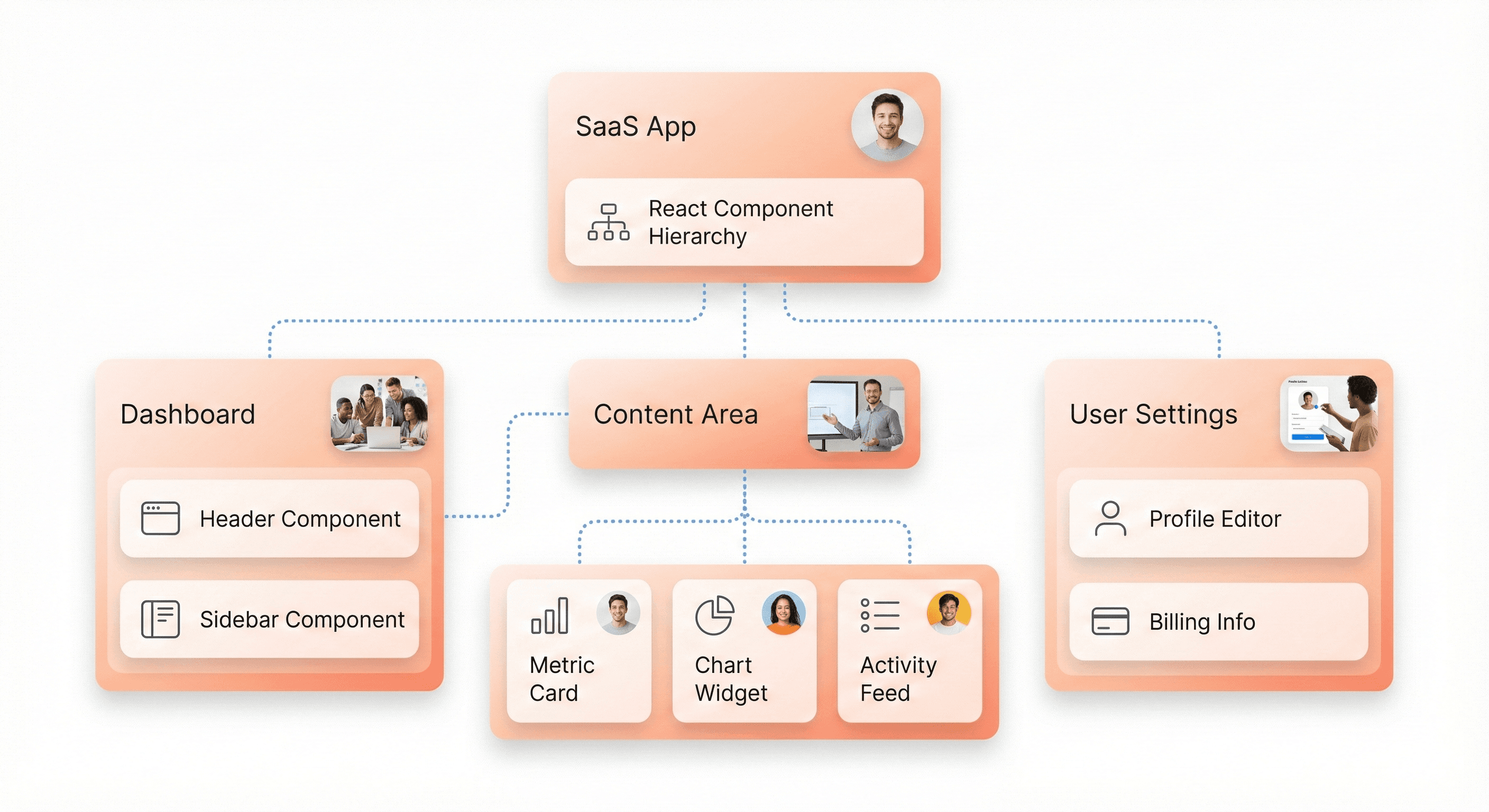
React is built on declarative UI principles and component composition. Strong developers understand how to break interfaces into logical components that encapsulate responsibility clearly.
Modern React relies on hooks to manage state and side effects. Hooks are not merely a syntactic change; they fundamentally influence how logic is structured and reused. Developers should know how to separate concerns using hooks without introducing hidden dependencies or unclear data flow.
Good component design improves maintainability. As SaaS products grow, well-structured components make it easier to add features, refactor logic, and onboard new developers without destabilizing the system.
JavaScript and TypeScript Proficiency
React does not replace JavaScript, it amplifies it. Proficiency in modern JavaScript is essential for writing predictable, readable code.
TypeScript has become common in large React codebases because it introduces static typing. Static types act as documentation and guardrails, catching errors before they reach production. In long-lived SaaS products, this reduces regressions and improves collaboration, especially as teams scale.
A React developer’s comfort with TypeScript often correlates with their ability to reason about complex systems and long-term maintainability.
State Management Expertise
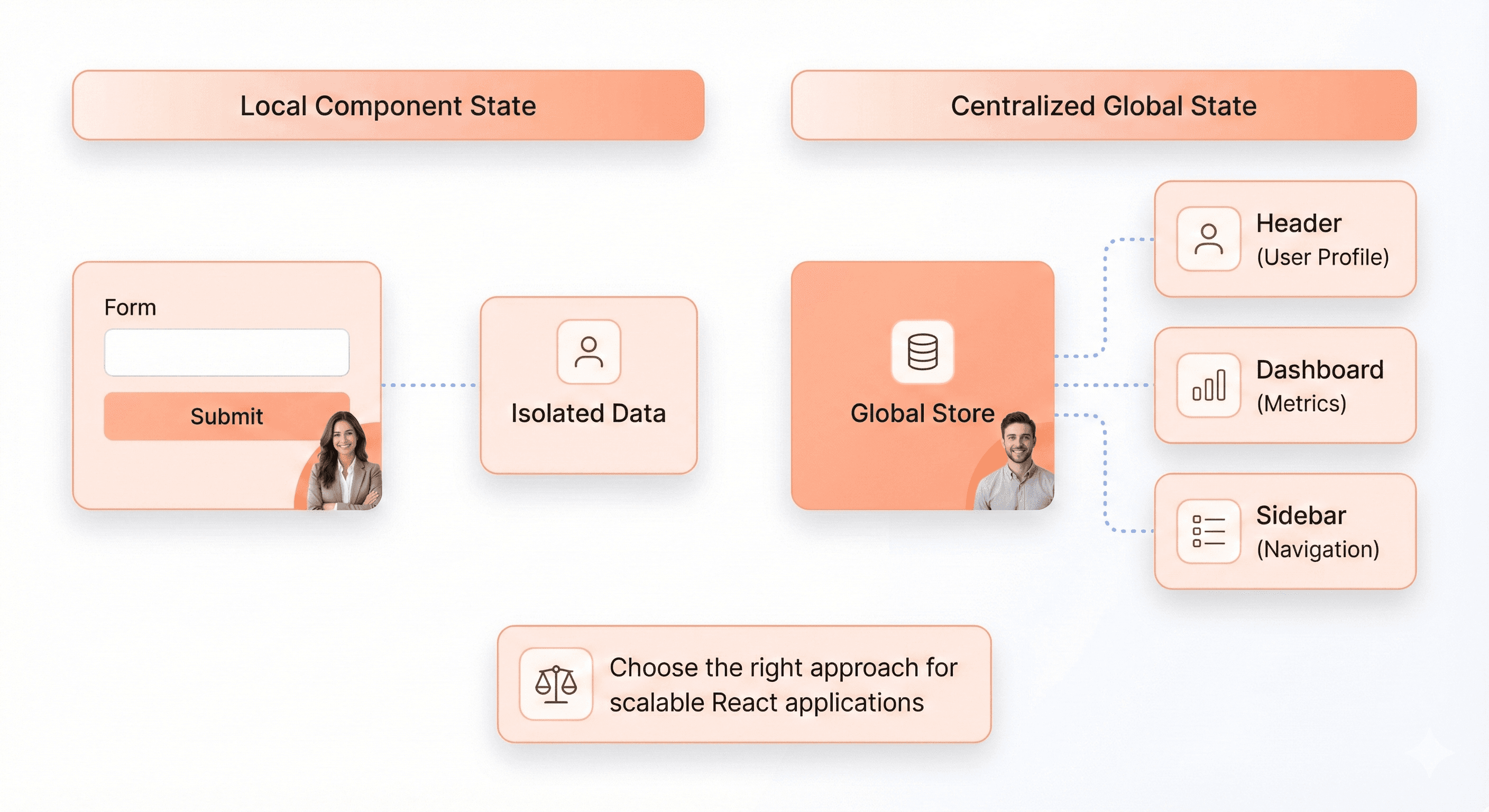
State management is one of the most common sources of frontend complexity. React encourages keeping state local whenever possible. Local state is easier to reason about, test, and refactor.
Global state introduces coupling across features. While sometimes necessary, it should be introduced deliberately. Overusing global state often leads to brittle architectures where small changes have unintended consequences elsewhere.
Strong developers understand that state management is not about choosing a popular library, it is about minimizing complexity and preserving clarity as the product evolves.
API Integration Experience
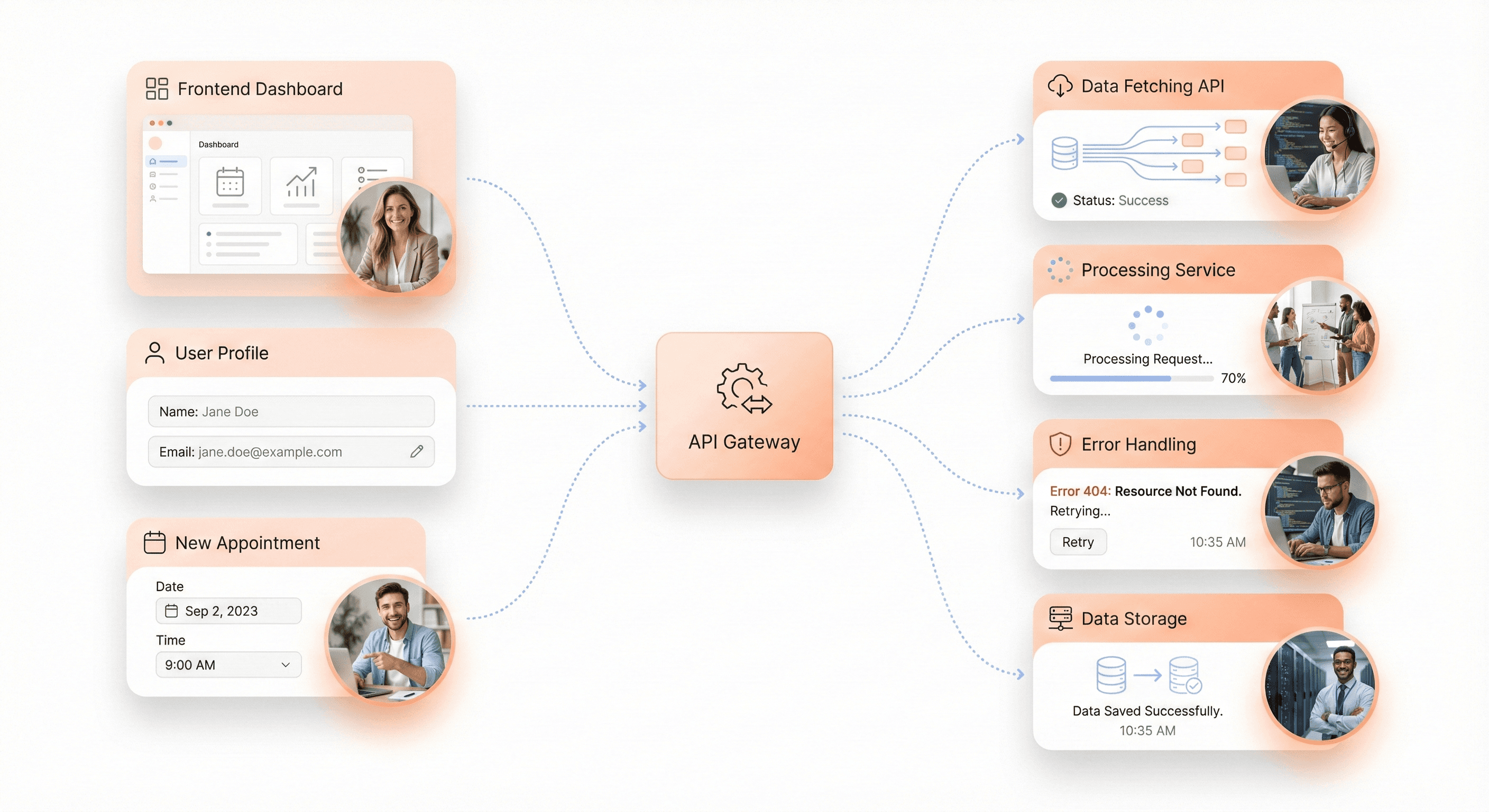
API integration is not just about fetching data. It involves handling partial failures, validating responses, and ensuring the UI remains consistent under unpredictable conditions.
Network requests fail. APIs change. Data arrives later than expected. A mature React developer designs interfaces that degrade gracefully rather than break outright. This resilience is essential for SaaS products operating at scale.
How to Test React Problem-Solving in Interviews
Coding Challenges
Research shows that realistic coding tasks are better predictors of job performance than abstract algorithm tests. For SaaS roles, the goal is not to assess how well someone memorizes patterns, but how they reason through real problems.
Good coding challenges reveal how developers:
Structure logic
Name variables and functions
Balance correctness, readability, and performance
Readable code is especially important in SaaS environments, where code is maintained and extended over years by multiple contributors.
System Design Questions
Frontend system design includes component hierarchy, data flow, and separation of concerns. These decisions determine how well a codebase scales as features and teams grow.
Poor early design increases rework later. SaaS founders should probe how candidates think about organizing UI systems, not just implementing isolated features. The ability to explain architectural trade-offs clearly is a strong signal of depth.
Assessing SaaS-Specific Experience
Scalability Understanding
Scalability in SaaS is not limited to handling more users. It also includes supporting more features, more use cases, and more developers.
Component isolation and clear boundaries enable parallel work without constant conflicts. Developers who understand this build systems that grow with the company rather than slow it down.
Technical debt compounds over time. SaaS products that ignore this reality often face painful rewrites that disrupt momentum.
Performance Optimization Skills
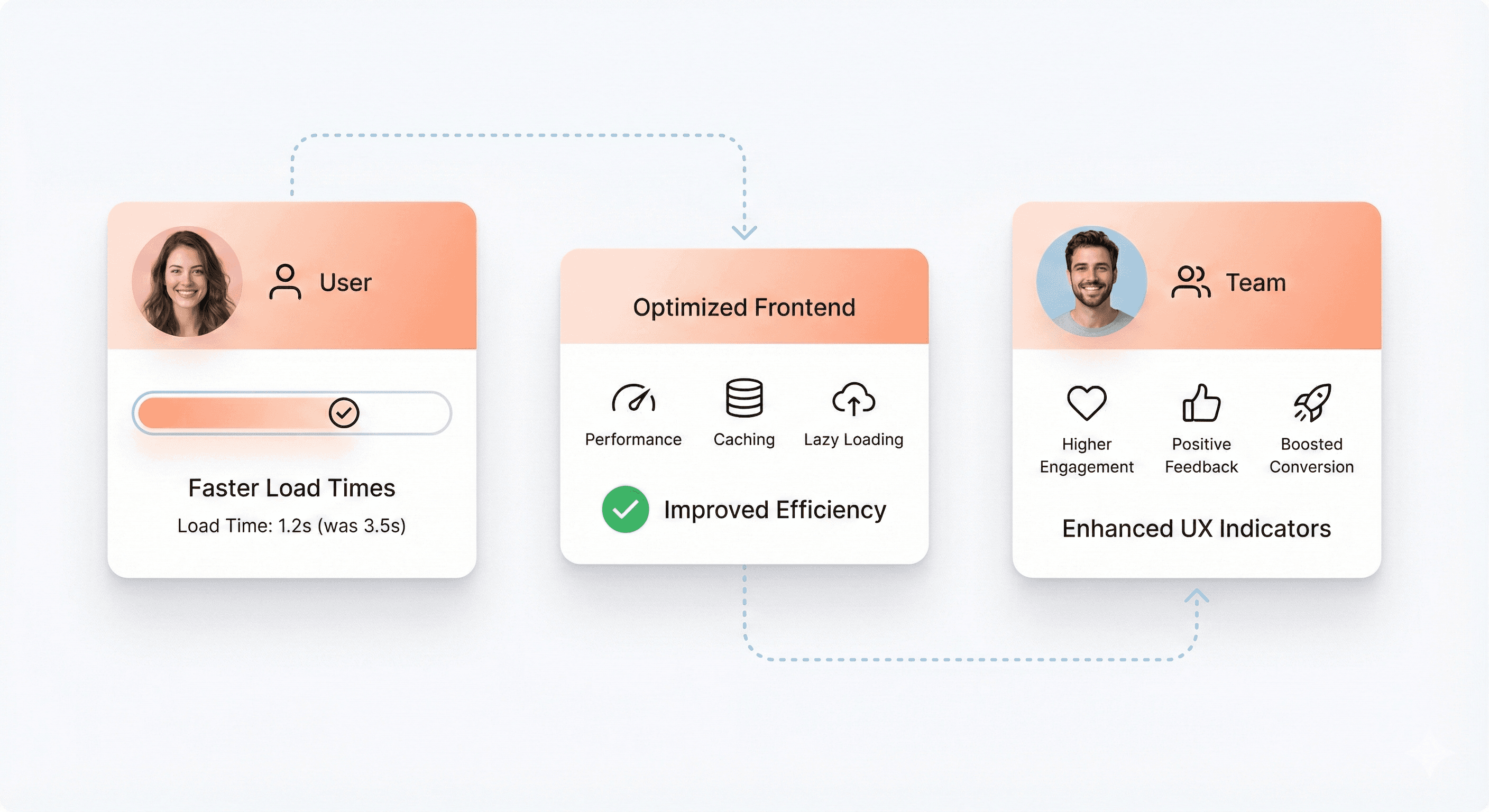
Performance is a business concern, not just a technical one. Faster interfaces retain users better and convert more effectively.
Techniques like code splitting reduce initial load times by delivering only what users need upfront. However, optimization must be guided by measurement. Production metrics reveal real-world performance issues that lab tests cannot fully capture.
A strong React developer understands both how to optimize and when optimization is justified.
Security Awareness
Frontend code runs in the user’s browser and is inherently visible. Secrets must never be stored client-side. Authentication and authorization must be handled carefully to prevent abuse.
Cross-site scripting remains a common vulnerability. While React mitigates some risks by default, developers must still understand safe data handling practices. Security awareness is essential in SaaS products that manage user data and permissions.
Soft Skills That Matter
Communication Skills
React developers frequently collaborate with non-technical stakeholders. The ability to explain trade-offs clearly reduces misunderstandings and rework.
Clear communication improves execution speed. It ensures that technical decisions align with business priorities rather than working at cross-purposes.
Collaboration and Teamwork
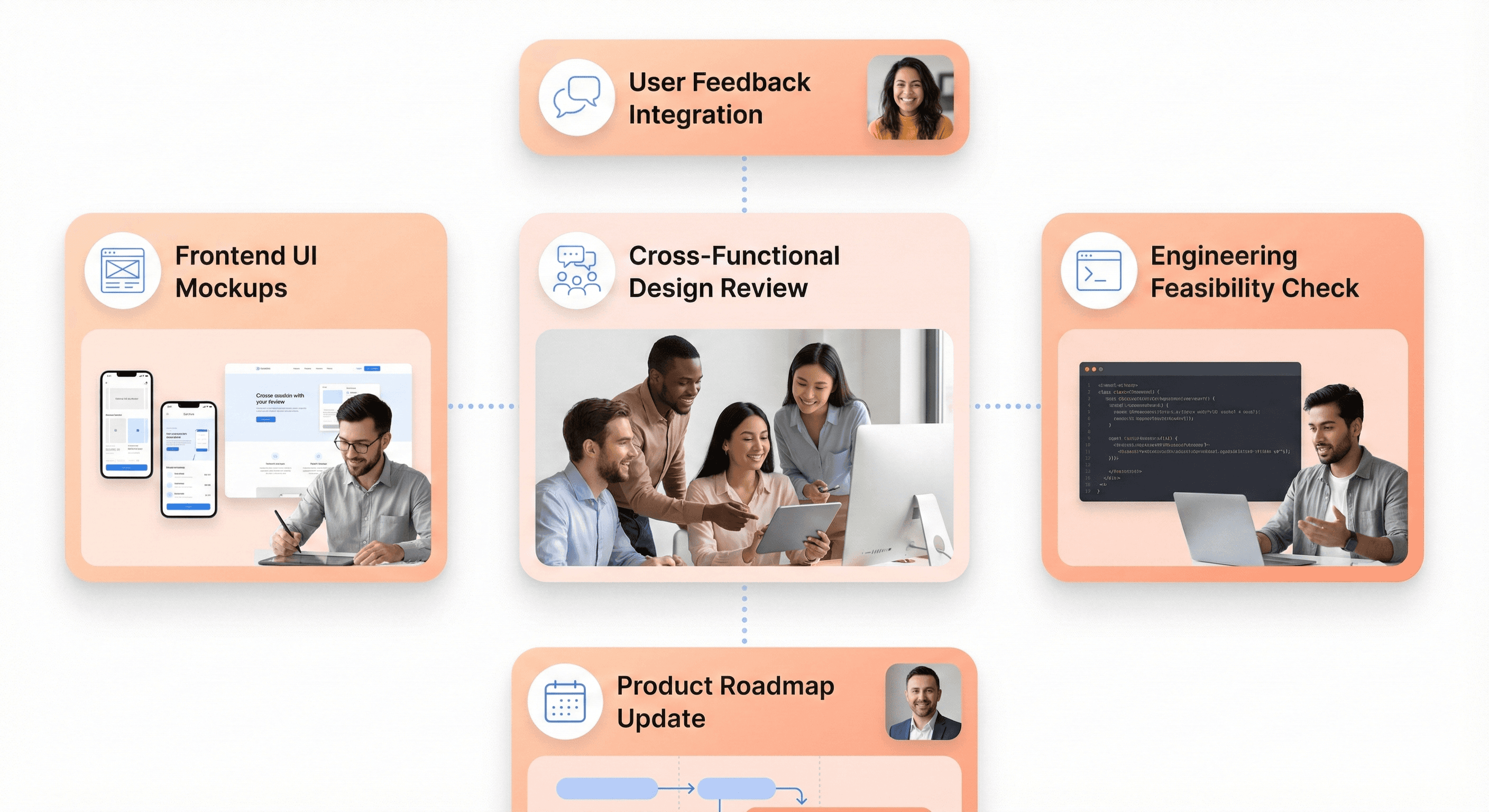
SaaS development is cross-functional by nature. Frontend developers must work closely with designers, backend engineers, and product managers.
Healthy collaboration practices, such as constructive code reviews, improve code quality and reduce defects. Developers who value teamwork contribute more than isolated individual contributors.
Adaptability
The React ecosystem evolves rapidly. New APIs, patterns, and best practices emerge regularly. Developers must evaluate changes critically rather than adopting trends blindly.
Continuous learning is essential to remain effective over time. SaaS products benefit from developers who can adapt without destabilizing the codebase.
How to Evaluate a React Developer Portfolio
What to Look for in a Portfolio
Real product work provides stronger signals than toy projects. Live demos reveal performance characteristics, UX quality, and attention to detail.
A portfolio should demonstrate problem-solving in context—how constraints were handled and decisions justified.
Questions to Ask About Previous Projects
Understanding why decisions were made is more valuable than knowing what tools were used. Developers who can articulate trade-offs and lessons learned tend to take ownership seriously.
This insight helps founders assess how candidates will behave when facing new challenges.
Cultural Fit and Company Values
Alignment with Startup Culture
Startups operate under ambiguity. Requirements change, priorities shift, and constraints are constant.
Developers who are comfortable navigating uncertainty adapt more effectively. This resilience is crucial in early-stage SaaS environments where clarity emerges through iteration.
Long-Term Vision
Retention reduces hiring and onboarding costs. Developers who align with the company’s long-term vision contribute to stability and sustained momentum.
Ownership mindset matters. SaaS products benefit from developers who care about long-term quality, not just immediate output.
The Interview Process
Structuring Your Technical Interview
Structured interviews reduce bias and improve hiring outcomes. Consistency allows fair comparison between candidates and leads to better decisions.
A clear interview structure signals professionalism and respect for candidates’ time.
Behavioral Interview Components
Past behavior is a strong predictor of future performance. Behavioral questions reveal how candidates handle feedback, conflict, and failure.
These traits directly affect team health and execution quality.
Red Flags to Watch Out For
Lack of curiosity, poor code quality, and inability to explain decisions clearly are common warning signs. These issues often surface later as collaboration problems or technical debt.
Identifying red flags early saves significant cost and disruption.
Compensation and Benefits Strategy
Market Rate Research
Developer compensation varies widely by geography. Founders should benchmark offers realistically to avoid misalignment.
Underpaying increases churn; overpaying without clarity strains resources.
Equity Considerations
Equity is commonly used in early-stage SaaS to offset cash constraints. Clear communication around equity prevents misunderstandings and builds trust.
Onboarding Your React Developer
First Week Essentials
Effective onboarding improves productivity and retention. Clear access, documentation, and expectations help new hires contribute sooner.
Setting Clear Expectations
Clear goals improve performance. Developers should understand ownership areas and success metrics early to avoid ambiguity.
Conclusion
Hiring a React developer for your SaaS is a strategic decision with long-term consequences. The right hire compounds value through better architecture, faster delivery, and fewer costly mistakes. The wrong hire silently accumulates debt that slows growth.
This checklist helps founders move beyond surface-level skills and evaluate what truly matters: judgment, clarity, and the ability to build a frontend that scales with the business.

About the author
Author Name:
Parth G
|
Founder of
Hashbyt
I’m the founder of Hashbyt, an AI-first frontend and UI/UX SaaS partner helping 200+ SaaS companies scale faster through intelligent, growth-driven design. My work focuses on building modern frontend systems, design frameworks, and product modernization strategies that boost revenue, improve user adoption, and help SaaS founders turn their UI into a true growth engine.
Is a clunky UI holding back your growth?
Is a clunky UI holding back your growth?
▶︎
Transform slow, frustrating dashboards into intuitive interfaces that ensure effortless user adoption.
▶︎
Transform slow, frustrating dashboards into intuitive interfaces that ensure effortless user adoption.






