
Finding the right web app developers can make or break your project. A wrong hire often leads to missed deadlines, budget overruns, poor performance, and products that fail to scale with business growth.
This guide is designed for startup founders, CTOs, project managers, and business owners who want to build reliable, scalable web applications but are unsure how to approach hiring. It covers everything from identifying the right developer roles and technical skills to choosing between freelancers, in-house teams, and development agencies.
You’ll learn how to evaluate developer portfolios, assess real-world experience, structure project requirements, and negotiate contracts that protect your investment, so you can confidently hire web app developers who deliver long-term value.
Types of Web App Developers and Their Roles
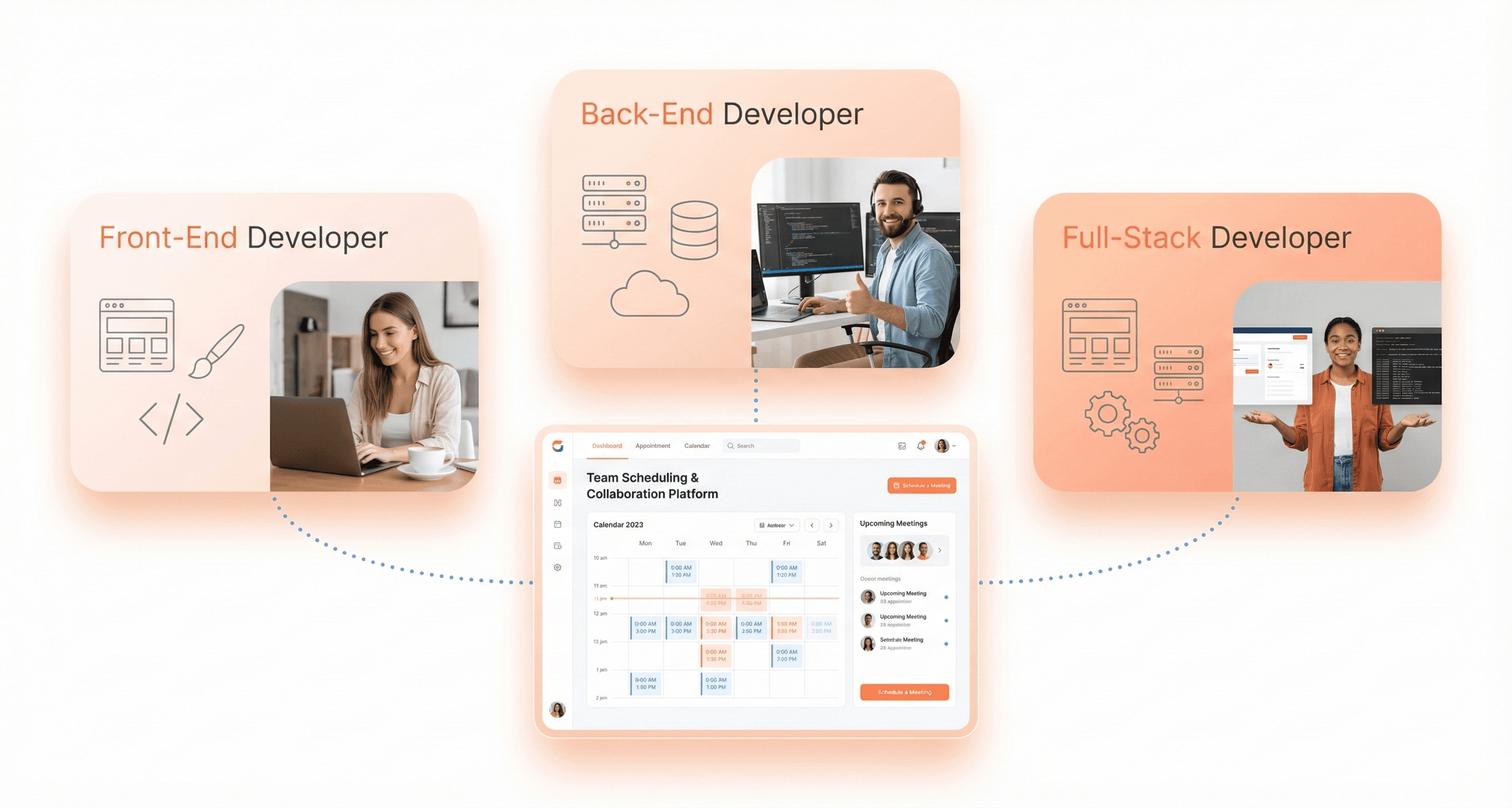
Front-End Web Developers: UI, UX, and Client-Side Development
Front-end web developers are coders who focus on the website's structural layout and user-facing elements. They achieve an appropriate mix of web design's graphical, functional, and aesthetic components to guarantee maximum efficiency across all devices. These professionals specialize in creating everything users see and interact with directly on a website.
Front-end developers must be proficient in several core programming languages. HTML5 is the most recent version of the HTML standard, which is a markup language used to bring structure to online content. Web developers use HTML5 to determine how to structure text like paragraphs, headers, lists, links, and other element categories. Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) allows developers to manage the overall appearance of site components across many pages, affecting font faces, colors, element spacing, and element sizes.
JavaScript serves as the primary programming language for interactive web pages and is utilized on most current websites. Front-end developers use JavaScript to bring websites to "life" by controlling actions such as dynamic loading and specifying an element's reaction to a user's click, enabling infinite interactive options.
Back-End Web Developers: Servers, APIs, and Databases
Back-end web developers provide code for server-side systems and services, which, when combined with front-end technologies, contribute to producing a smooth, personalized response to an end user's request for a website. These professionals specialize in server-side scripting languages and work behind the scenes to ensure websites function properly.
Back-end developers commonly work with PHP, a server-side scripting language used in online CMSs, HTML code, web template structures, and web frameworks. They use PHP in server scripting to define how a website responds to user activities. Database management is essential in their role because almost all software manipulates large amounts of data. Data synchronization between internal memory and remote databases is required when using software offline, making database knowledge crucial for these developers.
Back-end developers are responsible for connecting databases and maintaining integrations that power the website's functionality. They ensure all security protocols are in place and promptly detect anomalies that could affect website performance.
If your project involves modernizing or integrating with older systems, you’ll find our Ultimate Guide to Enterprise App Modernization extremely useful for understanding the backend challenges involved.
Full-Stack Developers: End-to-End Web App Development
A full-stack web developer is an expert in both back-end and front-end programming. Due to their knowledge of both technologies, full-stack engineers are the highest-paid experts in the web development business. These versatile professionals can handle projects from end to end, making them particularly valuable for comprehensive web development projects.
Full-stack developers possess proficiency in frameworks such as ASP.NET and Angular.js. ASP.NET is an open-source framework that offers web developers the tools and resources necessary to create dynamic websites, apps, and services. Angular.js is a fully accessible, industry-standard application framework managed by Google and its user community. Due to its JavaScript base, developers often use Angular.js to modify a site's entire front end.
Online development experts with extensive experience typically design, create, and optimize web apps and websites from end to end. They have extensive knowledge of SEO best practices, web development programming languages, and comprehensive experience managing complex projects.
Core Responsibilities of Web App Developers
Regardless of specialization, all web developers share certain core responsibilities that are fundamental to successful web development projects. The primary professional objective is creating websites through programming, employing various programming techniques and tools to deliver high-quality results while conforming to contemporary web development standards and ethics.
Testing and debugging represent another universal responsibility. Developers must routinely examine their websites to dessseetect flaws early and review code for potential bugs before publishing programs. Thorough testing prevents future issues and ensures continuous functionality.
All developers must focus on website maintenance and support. To keep customers satisfied, websites must respond as quickly as possible, requiring developers to guarantee all functions remain operational. This involves spreading updates to maintain website functionality and implementing security protocols.
Collaboration with designers is essential across all developer types to extract intended visual outcomes for websites. Developers must work with creative specialists to effectively implement key features and functionalities, developing consistent themes throughout all web pages.
Additional universal responsibilities include ensuring responsive design that seamlessly adapts to various screen sizes, maintaining documentation for software, retaining current understanding of technology trends, and implementing backup procedures if sites crash. Web developers must also demonstrate proficiency in version control systems like Git to track, manage, and modify code changes effectively.
To dive deeper into how skilled developers enhance performance, check out 7 Myths About Front-End Performance, which reveals optimization techniques top engineers rely on.
Web Developer Skills to Evaluate Before Hiring
Technical Skills for Front-End Development
When evaluating front-end developers, focus on their mastery of core programming languages essential for web development. JavaScript stands out as the most critical language, serving as the backbone of interactive web applications. Candidates should demonstrate proficiency in modern JavaScript frameworks, particularly React, which has become the industry standard for front-end development.
Beyond JavaScript proficiency, assess their understanding of HTML and CSS fundamentals, as these form the structural foundation of web interfaces. Look for developers who can create responsive, user-friendly designs that work seamlessly across different devices and browsers.
Algorithm knowledge plays a crucial role in front-end development, as developers must efficiently solve problems related to user interface optimization, data manipulation, and performance enhancement. Strong algorithmic thinking enables developers to translate complex user requirements into streamlined, functional code that delivers optimal user experiences.
For teams deciding between popular JavaScript frameworks, this detailed comparison of React vs Angular can help clarify which technology aligns better with your project goals.
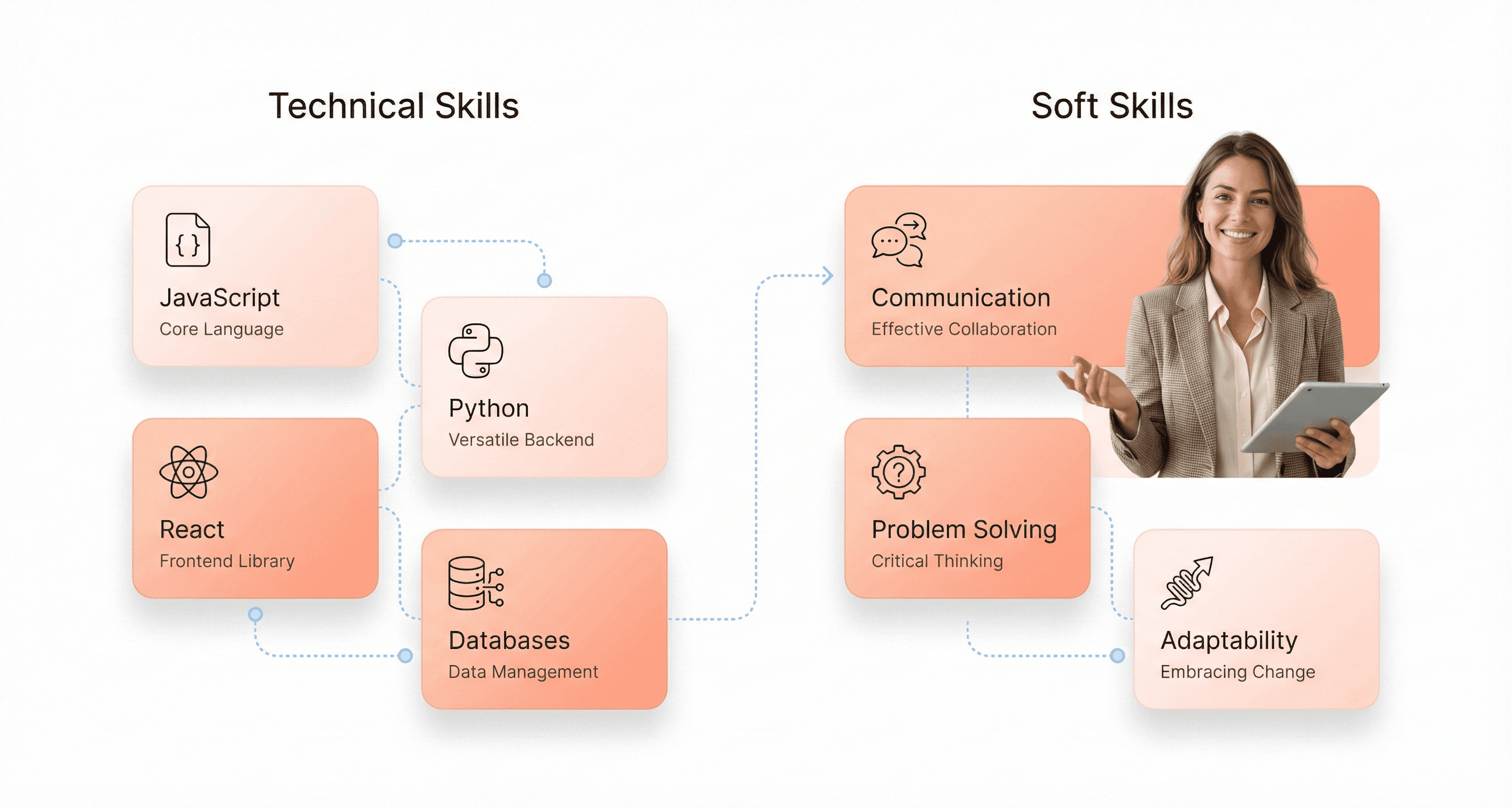
Back-End Programming and Database Management Skills
Back-end developers require expertise in server-side programming languages, with Python and Java being highly desirable due to their versatility and strong performance capabilities. Python's flexibility makes it excellent for rapid development and complex data processing, while Java provides robust performance for enterprise-level applications.
Framework knowledge is equally important for back-end operations. Django for Python development represents a critical skill, enabling developers to build scalable, secure web applications efficiently. These frameworks provide structured approaches to common back-end challenges like database management, user authentication, and API development.
Database management skills encompass an understanding of both relational and non-relational databases, query optimization, and data structure design. Developers should demonstrate the ability to design efficient database schemas and write optimized queries that support application performance and scalability requirements.
Critical Soft Skills for Effective Collaboration
Effective communication skills are fundamental for web developers, enabling them to articulate complex technical concepts to non-technical stakeholders and collaborate seamlessly with cross-functional teams. Developers must translate technical jargon into understandable terms, ensuring all team members can contribute meaningfully to project discussions.
Problem-solving capabilities require a combination of creative and analytical thinking. Web developers encounter unexpected challenges daily, from debugging complex code to optimizing application performance. The ability to approach problems systematically while thinking creatively about solutions distinguishes exceptional developers from average ones.
Adaptability and continuous learning dedication are essential in the rapidly evolving web development landscape. Technology stacks, frameworks, and best practices change frequently, requiring developers to stay current with industry trends and continuously update their skill sets to remain effective and relevant.
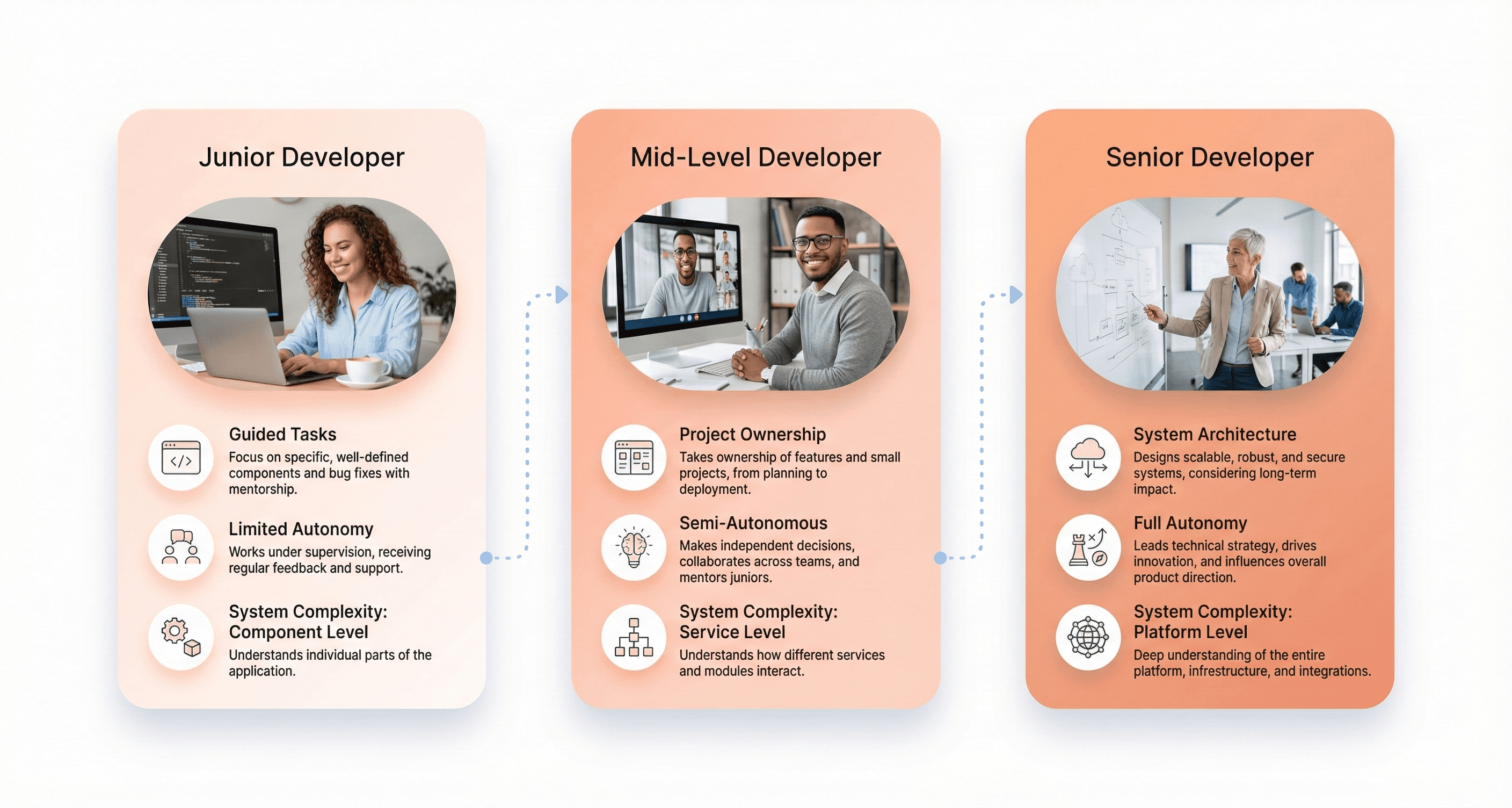
Experience Levels: Junior vs Mid-Level vs Senior Developers
Junior developers typically possess foundational technical skills in programming languages and frameworks, but require guidance on complex problem-solving and system architecture decisions. They bring enthusiasm for learning and fresh perspectives, but need mentorship to develop advanced technical judgment and collaborative skills.
Mid-level developers demonstrate solid technical competency across multiple technologies and can work independently on most tasks. They possess enough experience to make informed technical decisions, contribute to code reviews, and mentor junior team members while continuing to develop their expertise in specialized areas.
Senior developers bring comprehensive technical expertise combined with strong leadership and communication abilities. They can architect complex systems, make strategic technical decisions, and effectively guide development teams. Their experience enables them to anticipate potential issues, optimize performance, and ensure code quality while mentoring other team members and driving project success.
How to Define Your Web App Project Requirements
Defining Website Requirements and Deliverables
The foundation of any successful web development project begins with clearly defining what your website needs to accomplish and what specific deliverables you expect from your development team. This process involves creating a comprehensive information architecture that outlines both the structure and content strategy for your site.
Start by developing a detailed site map that displays the hierarchical structure of your website's pages in a 'tree' chart format. This visual representation helps developers understand the scope and complexity of your project while providing a clear roadmap for navigation flow. Consider your target audience and analyze any existing quantitative data that demonstrates limitations in your current site structure to inform improvements in the user journey.
Next, establish a taxonomic structure for your website content. This classification system makes your site easier to navigate for both users and search engines while improving overall performance. When creating your taxonomy, focus on what users want from your website, the purpose of your content, and how visitors typically search for information on your site.
Include detailed page template wireframes and mock-ups for key page types such as homepage, product/service pages, blog pages, and contact pages. These visual guides help developers understand your vision for specific page layouts and functionality requirements.
Document all functional requirements including e-commerce capabilities, multi-lingual options, social media integration, contact forms, SSL certification, and mobile responsiveness. Be specific about third-party integrations needed, such as payment gateways, shopping carts, or live social media feeds that align with your business objectives.
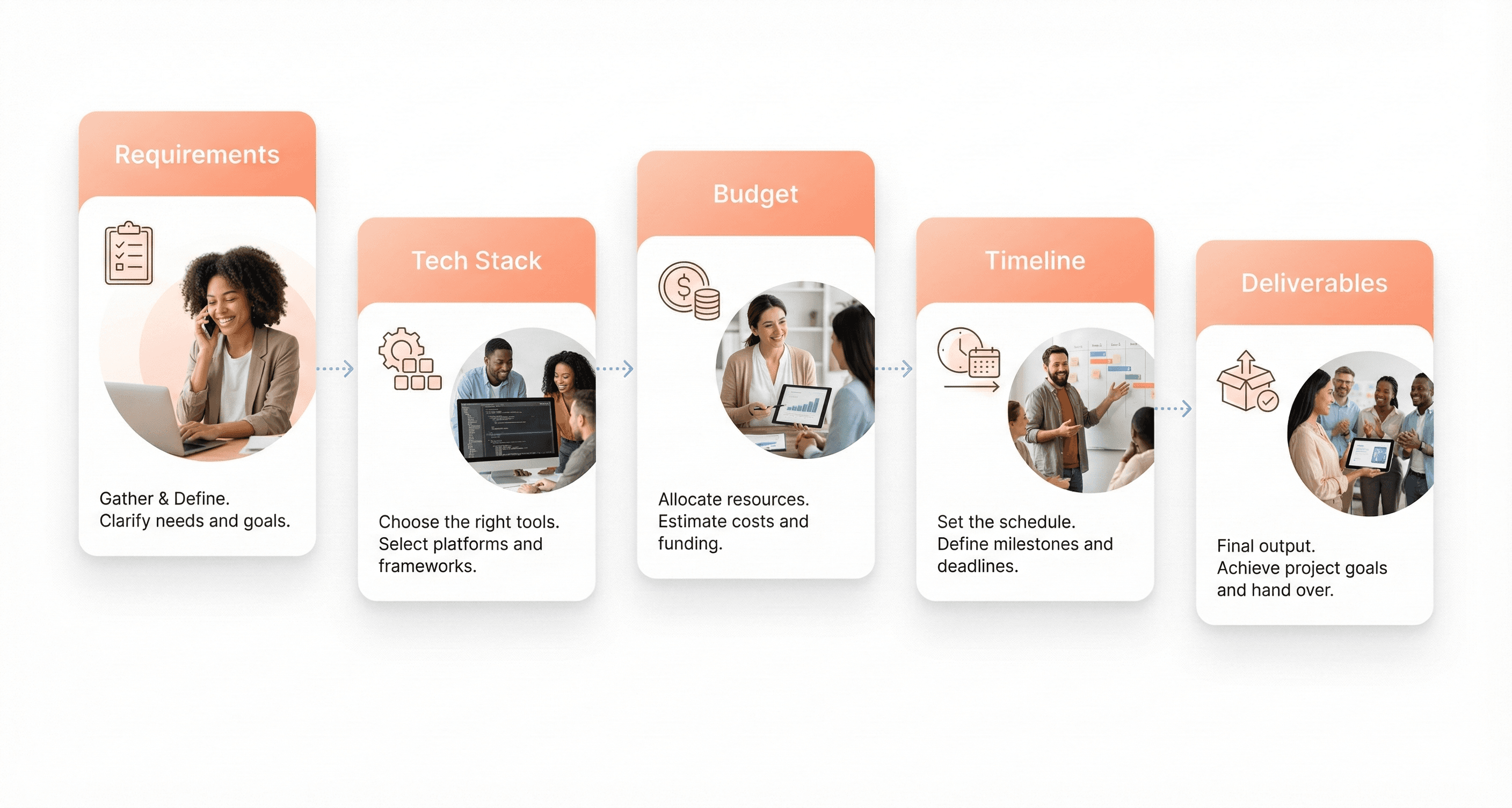
Setting Technology Stack and Development Approach
With your requirements defined, the next critical step involves establishing the technical foundation and development methodology for your project. This includes specifying the technology stack, development frameworks, and architectural approach that will best serve your website's functionality and performance requirements.
Consider non-functional elements that impact your technology choices, including accessibility requirements based on WCAG guidelines, especially if your site serves specific user groups such as children or elderly users. Security specifications are crucial if your site must comply with regulations like PCI Standards for payment processing or specific legal requirements for age-gated content.
Page load speed requirements should be emphasized as a top priority, particularly for e-commerce sites where performance directly impacts conversion rates and search engine rankings. Specify your hosting preferences and outline which browsers and devices your site must support based on your current visitor analytics and target market research.
Address ongoing maintenance and support needs early in the planning process. Determine whether your website will require regular security updates, content management capabilities, and technical maintenance to ensure optimal performance over time. Consider your internal team's technical limitations and communicate any constraints that might affect long-term site management.
Establishing Budget Parameters and Cost Expectations
Now that we have covered the technical requirements, establishing clear budget parameters becomes essential for project success. Your budget framework should align with the complexity of your requirements while providing realistic cost expectations for all stakeholders involved in the decision-making process.
Break down your budget into distinct categories, including design work, development costs, third-party integrations, hosting and maintenance, and ongoing support requirements. If design work already exists for your project, budget considerations will focus primarily on development implementation. However, if design is part of the project scope, allocate additional resources for brand guidelines development, competitive analysis, and design iteration phases.
Consider the total cost of ownership beyond initial development, including hosting platform expenses, SSL certification costs, third-party service subscriptions, and ongoing maintenance requirements. E-commerce functionality, multi-lingual capabilities, and complex integrations typically require larger budget allocations due to their technical complexity and ongoing operational needs.
Factor in potential scope changes and revision costs by including contingency allowances in your budget planning. Clear budget communication helps prevent scope creep and ensures all parties understand the financial boundaries of the project from the outset.
Clarifying Timeline and Milestone Requirements
Previously, we've established requirements, technology approaches, and budget parameters. With this foundation in place, creating a realistic timeline with clear milestones becomes crucial for project management and stakeholder alignment.
Develop a phased approach that breaks the project into manageable deliverable segments. Typical phases include discovery and planning, design development, technical implementation, content integration, testing and quality assurance, and launch preparation. Each phase should have specific deliverables, approval requirements, and timeline expectations clearly defined.
Consider dependencies between different project elements when establishing your timeline. For example, content creation may need to precede certain development phases, while design approval must happen before technical implementation can begin. Third-party integrations often require additional time for testing and refinement, which should be reflected in your project schedule.
Build buffer time into your timeline for revisions, stakeholder feedback incorporation, and unforeseen technical challenges. Quality assurance and testing phases are particularly critical for sites with complex functionality, security requirements, or accessibility compliance needs.
Establish clear communication protocols and approval processes for each milestone to maintain project momentum. Define who needs to approve deliverables at each stage and how feedback will be collected and incorporated into the development process. Regular check-ins and progress reviews help ensure the project stays on track while maintaining quality standards throughout the development lifecycle.
Choosing the Right Hiring Model for Your Project
Freelance Web Developers: Benefits and Limitations
Freelance web developers offer unparalleled flexibility and access to specialized skills without the commitment of full-time hiring. According to industry experts, freelancers allow companies to "get more things done without taking on the risk of increasing fixed costs." This model enables businesses to experiment with projects before making substantial investments in permanent staff.
The primary advantage of hiring freelancers lies in accessing highly specialized skill sets without enduring lengthy recruitment processes or expensive consultant fees. Companies can scale their development capacity up or down based on project demands, making it an ideal solution for businesses with fluctuating workloads or specific technical requirements.
However, freelance hiring comes with certain limitations. The assessment and interview process typically takes about a month, which can delay project timelines. Additionally, managing multiple freelancers across different time zones and ensuring consistent communication standards can present coordination challenges for project managers.
In-House Developers: Advantages and Considerations
In-house developers provide stability and deep integration within your company culture and processes. This model ensures better alignment with long-term business objectives and facilitates seamless collaboration with other departments. Full-time developers develop a comprehensive understanding of your product ecosystem and can contribute to strategic decision-making beyond immediate technical requirements.
The consideration with in-house hiring centers on the significant talent shortage affecting the tech industry globally. By 2030, the global talent shortage is expected to reach 85.2 million, potentially causing companies worldwide to lose $8.4 trillion in revenue due to a lack of skilled talent. This scarcity makes attracting and retaining top-tier developers increasingly challenging and expensive.
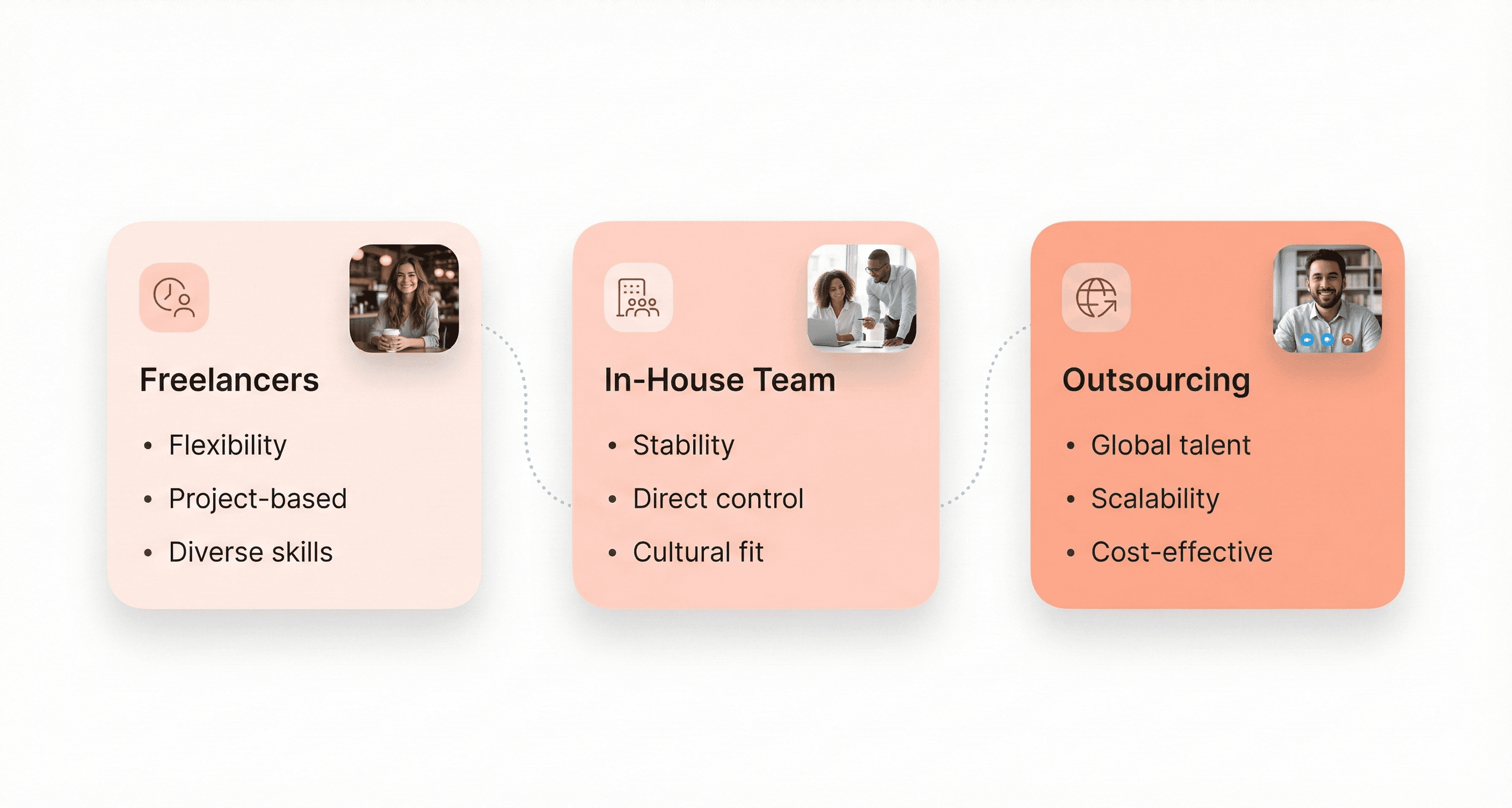
Outsourcing Options: Onshore, Offshore, and Nearshore Development
The digital revolution has fundamentally transformed how companies approach web development projects, with remote work becoming the norm rather than the exception. Pre-COVID-19, many companies viewed remote work suspiciously, but post-pandemic, it has become standard practice with seamless team integration.
US companies are increasingly looking worldwide for talent, driven not only by talent shortages but also by financial costs and time constraints associated with finding quality developers locally. This trend is particularly pronounced among small businesses seeking cost-effective solutions without compromising on quality.
Outsourcing provides access to global talent pools while offering various geographical advantages depending on your specific needs, time zone preferences, and budget constraints.
Selecting the Best Model for Your Business Needs
Industry leaders emphasize that successful companies require a strategic mix of employment models rather than relying on a single approach. As one expert notes, "More and more companies today are moving towards having a more flexible and agile organization where you have a mix of full-time, part-time, and freelance workers."
This hybrid approach allows businesses to maintain core competencies through in-house teams while leveraging freelancers and outsourcing partners for specialized projects or capacity scaling. The key lies in strategically aligning each hiring model with specific business objectives, project timelines, and budget constraints.
Consider your project's complexity, duration, required expertise level, and long-term strategic importance when selecting the optimal hiring model. Companies seeking sustained competitive advantage often benefit from combining stable in-house capabilities with flexible freelance resources to create an agile, responsive development organization.
How to Evaluate Web Developer Portfolios and Experience
Assessing Relevant Project Experience
Now that we have covered the essential skills to evaluate, let's examine how to thoroughly assess a developer's portfolio and past work. Every developer, from junior to senior professionals, should maintain an up-to-date portfolio that offers a window into their career path, showcasing professional experiences and coding prowess through various projects.
When reviewing portfolios, it's crucial to keep the specific requirements of the role in mind. For instance, a candidate might have an extensive portfolio in web development, but if the role demands an iOS developer, their suitability may be questionable. Focus on projects that mirror the complexity, scope, and technology relevant to the position you're filling.
Assess the diversity of technologies they've handled, the user base size their projects catered to, and the nature of problems they've tackled. A well-curated portfolio demonstrates not only technical competence but also the developer's ability to adapt to different project requirements and technological challenges.
Key areas to evaluate include:
Project complexity and scope alignment with your requirements
Technology stack relevance to your current needs
Problem-solving approaches demonstrated across different projects
Evolution of skills shown through project progression over time
Checking Client Testimonials and Reviews
With this evaluation framework in mind, next, we'll examine the importance of external validation through client feedback. References are ideal for gaining an external perspective on a developer's performance. Speaking with previous employers or colleagues can provide invaluable insights into a candidate's collaborative skills and contributions to team projects.
When contacting references, ask about the candidate's role in past projects, their ability to meet deadlines, how they handled feedback, and their contributions to team successes or failures. This information provides a more holistic picture of how the candidate collaborates in a team setting and communicates with others.
Client testimonials and reviews offer authentic perspectives on:
Work quality and consistency across different engagements
Communication effectiveness with both technical and non-technical stakeholders
Reliability in meeting project deadlines and deliverables
Problem-solving capabilities when facing unexpected challenges
Professional conduct and team integration skills
Verifying Technical Competency Through Past Projects
Previously, we've discussed the importance of portfolio review, but verifying technical competency requires deeper analysis of actual project outcomes. This strategy is particularly useful for senior-level roles, as analyzing performance metrics of past projects can give you a deeper understanding of whether a developer is a good fit for your team.
Start by discussing the candidate's project outcomes, assessing whether they have a history of meeting project deadlines and how they handled any delays. Look into the goals set for their past projects and the extent to which they were achieved. This can include technical goals, such as performance improvements or bug reduction, as well as broader project goals, like user engagement or revenue generation.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) allow you to have a clearer picture of how success was defined in their past roles and how their performance aligned with these metrics. KPIs can also help you understand if candidates used these for self-evaluation and continuous improvement.
Consider evaluating:
Code quality metrics from previous projects
Performance optimization achievements and measurable improvements
Bug resolution rates and debugging effectiveness
Project delivery timelines and adherence to specifications
Technical decision-making and architecture choices
Understanding Developer Specializations and Expertise
Now that we have covered project assessment methods, let's explore how to identify and evaluate developer specializations. Understanding a developer's area of expertise is crucial for determining project fit and future growth potential within your organization.
Developers often specialize in specific technologies, frameworks, or problem domains. A comprehensive evaluation should identify these specializations and assess their depth of knowledge in these areas. This involves examining not just what technologies they've used, but how effectively they've applied them to solve real-world problems.
Specialization assessment should include:
Domain expertise depth in specific technical areas
Framework and tool proficiency relevant to your project needs
Industry-specific knowledge and understanding of business contexts
Emerging technology adoption and learning agility
Cross-functional capabilities and versatility
Ask specific questions about their code and design choices. Focus on understanding their decision-making process, why they made certain trade-offs, and their thought process behind alternative designs. This reveals not only their technical knowledge but also their ability to make thoughtful design decisions and understand the implications of their choices.
By thoroughly analyzing project outcomes, discussing KPIs, and understanding specializations, you can gain a deeper understanding of a candidate's past performance and their potential to contribute to future projects.
Web Developer Contracts, Pricing, and Legal Considerations
Setting Clear Deliverables and Success Metrics
Now that we have covered the evaluation process, establishing precise deliverables and success metrics forms the foundation of any successful web development contract. The scope of services provided, including deliverables, milestones and customer requirements must be carefully defined in an agreement because those definitions will be the measuring stick for the parties' performance.
When negotiating deliverables, consider whether your company wants a custom website or one that uses a standard template. This decision will dictate your approach to the website development agreement and influence the specific deliverables required. Each deliverable should be clearly defined with measurable outcomes that both parties can evaluate objectively.
One effective approach is to divide a project into phases, each with their own deliverables and milestones. This phased approach allows for better project management and provides clear checkpoints for evaluating progress. Include timeframes for testing to occur and the consequences for failure to meet agreed specifications, including monetary penalties or termination for delay.
Success metrics should encompass both technical and business objectives. Technical metrics might include website loading speed, mobile responsiveness, and functionality across different browsers. Business metrics could involve user engagement rates, conversion goals, or specific performance benchmarks relevant to your industry.
Establishing Payment Structure and Budget Limits
With deliverables clearly defined, the next critical aspect involves structuring payment terms that protect both parties while ensuring project continuity. Website development agreements typically use either time and materials contracts based on agreed billing rates plus out-of-pocket expenses, or fixed fee contracts.
Regardless of the fee structure chosen, condition payments on reaching certain milestones and include a hold-back of a portion of the fee until final acceptance. This approach ensures that developers remain motivated to complete work satisfactorily while providing you with leverage should issues arise.
For milestone-based payments, align payment schedules with the delivery of specific project phases. This creates natural checkpoints where both parties can assess progress and address any concerns before proceeding. Consider requiring a deposit to secure the developer's commitment to the project, which also demonstrates your serious intent to move forward.
Budget limits should be clearly established upfront, including provisions for handling scope changes. Institute a clear change order process in the agreement to maintain control over contract performance and prevent cost overruns. This process should outline how additional work will be priced, approved, and documented.
Defining Timeline and Delivery Schedules
Previously established deliverables and payment structures must be supported by realistic and enforceable timelines. Carefully review provisions for testing and completion, ensuring that timeframes for testing are included along with consequences for delays.
When setting delivery schedules, consider the complexity of your project and the developer's capacity. Large developers may have more resources but could be less flexible with timelines, while smaller developers might offer more personalized attention but could face challenges if key employees leave the project.
Build buffer time into your schedule to account for potential revisions, testing phases, and unexpected challenges. Each phase should have specific deadlines with clear consequences for missing them. This approach helps maintain project momentum while providing recourse if delays occur.
Timeline negotiations should also address the client's responsibilities, such as providing content, feedback, or approvals within specified timeframes. Delays on the client side can significantly impact project completion, so establishing mutual accountability ensures smoother project execution.
Creating Written Agreements and Legal Protection
With project terms negotiated, creating comprehensive written agreements provides essential legal protection for both parties. A legally binding contract should include an offer, an intent to create legal relations, acceptance, and consideration.
Use clear, straightforward language to avoid ambiguity and reduce the risk of disputes. Your contract should identify all parties involved, specify the scope of work, and contain terms related to payments, deadlines, and deliverables. Include confidentiality provisions to protect any confidential information the developer receives during the project.
Ensure that you own your website's intellectual property. While developers may properly retain ownership of some software code used to create your website, insist on broad licenses to use all such software as necessary for your website's operation. Demand ownership of the unique viewable aspects of the website and any custom software code developed uniquely for your project.
Carefully review the representations and warranties section. The developer should promise to deliver a website meeting contract specifications and warrant that they will correct defects found after completion. Developers should also warrant that the website doesn't infringe third-party intellectual property rights and agree to indemnify you for any intellectual property claims.
Make sure to obtain all documentation created for the website, including technical specifications, functionality descriptions, and system architecture information. This documentation becomes crucial if you need to work with different developers in the future or require internal maintenance capabilities.
Conclusion
Finding the right web app developer for your project doesn't have to be overwhelming when you follow a structured approach. By understanding the different types of developers and their specializations, evaluating essential technical and soft skills, and creating comprehensive project descriptions, you set the foundation for successful hiring. Whether you choose freelancers, in-house developers, or outsource to a nearshore development agency, the key lies in matching your specific project needs with the right expertise and hiring model.
Remember that successful web development projects go beyond just technical capabilities. Take time to thoroughly review portfolios, negotiate clear contracts with defined deliverables and timelines, and establish open communication channels from the start. When you invest effort in the hiring process upfront, you're much more likely to find developers who will deliver high-quality results within your budget and timeline, ultimately bringing your web application vision to life.

About the author
Author Name:
Parth G
|
Founder of
Hashbyt
I’m the founder of Hashbyt, an AI-first frontend and UI/UX SaaS partner helping 200+ SaaS companies scale faster through intelligent, growth-driven design. My work focuses on building modern frontend systems, design frameworks, and product modernization strategies that boost revenue, improve user adoption, and help SaaS founders turn their UI into a true growth engine.
Is a clunky UI holding back your growth?
Is a clunky UI holding back your growth?
▶︎
Transform slow, frustrating dashboards into intuitive interfaces that ensure effortless user adoption.
▶︎
Transform slow, frustrating dashboards into intuitive interfaces that ensure effortless user adoption.






