
Choosing between React, Vue, and Angular is one of the most important technical decisions for modern front-end development. The framework you select influences not only how fast your product is built, but also how it performs, scales, and stays maintainable over time, especially for growing SaaS teams and long-term products.
React is widely adopted for its flexible, component-driven architecture and extensive ecosystem, making it a strong fit for highly interactive user interfaces. Angular takes a more opinionated, enterprise-ready approach with built-in tooling and strict structure, ideal for large and complex applications. Vue sits in between, offering a lightweight, progressive framework that’s easy to learn while still powerful enough for production-grade apps.
This in-depth React vs Vue vs Angular comparison focuses on the factors that matter most when choosing a JavaScript framework in 2025 and beyond. We’ll examine real-world performance and rendering behavior, compare learning curves and developer experience, and analyze scalability, ecosystem maturity, and market demand to help you make a confident, future-proof decision.
React vs Vue vs Angular: Core Differences Explained (Architecture, Ecosystem & Use Cases)
React: Component-Based JavaScript Library for Dynamic UIs
React Key Highlights:
Developed by Facebook (now Meta) and released in 2013
Component-based architecture promotes reusability and modularity
Utilizes a Virtual DOM for fast UI rendering and efficient updates
Follows one-way data binding, ensuring predictable data flow
Backed by a massive ecosystem and active developer community
Ideal for dynamic, interactive user interfaces and single-page applications (SPAs
React stands as a component-based JavaScript library developed by Facebook (now Meta), with its initial development beginning in 2011 and public release in 2013. This powerful library focuses specifically on the view layer of applications, making it an excellent choice for building fast and interactive user interfaces.
The core strength of React lies in its component-based architecture, which allows developers to create reusable UI components that serve as building blocks for complex applications. This approach significantly reduces development time and complexity by promoting code reusability and maintainability. Each component encapsulates its own logic and state, making applications more modular and easier to debug.
React implements one-way (unidirectional) data binding, which contributes to more predictable and maintainable code. This data flow pattern ensures that data moves in a single direction through the component hierarchy, making it easier to understand how data changes affect the application state and reducing potential bugs.
Angular: Full-Featured TypeScript Framework for Enterprise Applications
Angular Key Highlights:
Developed and maintained by Google, rewritten in TypeScript in 2016
A full-featured MVC framework designed for enterprise-grade web apps
Implements two-way data binding for automatic synchronization between model and view
Offers built-in tools for routing, HTTP requests, and dependency injection
Enforces strict structure and coding standards for scalable team development
Best suited for large, complex applications requiring long-term maintenance
Angular represents a comprehensive, full-fledged TypeScript-based framework developed by Google. While its predecessor AngularJS was released in 2010, the current Angular framework was launched in 2016 as a complete rewrite. This open-source framework offers a complete solution for building scalable web applications, particularly excelling in Single Page Application (SPA) development.
The framework provides a comprehensive set of tools and libraries specifically designed for complex enterprise applications. Angular follows an MVC (Model-View-Controller) architecture while maintaining a component-based structure, offering developers a robust foundation for large-scale projects.
One of Angular's distinctive features is its implementation of two-way data binding, where changes in the model are automatically reflected in the view and vice versa. This bidirectional data flow simplifies form handling and user interactions but requires careful consideration to maintain performance in complex applications.
Vue: Progressive JavaScript Framework for Flexible Development
Vue Key Highlights:
Created by Evan You in 2014 as a progressive JavaScript framework
Designed for simplicity, flexibility, and gradual adoption
Uses Single File Components (SFCs) for cleaner, modular code organization
Features a reactive data binding system for seamless DOM updates
Lightweight, fast-loading, and ideal for small to medium-sized projects
Balances ease of learning with powerful features for advanced use cases
Vue emerges as a progressive frontend JavaScript framework released in 2014, distinguished by its straightforward interface, ease of integration, and exceptional flexibility. This open-source framework proves suitable for both small projects and large-scale applications, making it an attractive choice for diverse development scenarios.
Vue provides a sophisticated reactivity system that automatically updates the DOM when underlying data changes, eliminating the need for manual DOM manipulation. This reactive nature ensures that user interfaces remain synchronized with application state efficiently.
A standout feature of Vue is its support for Single File Components (SFCs), allowing developers to define components in a single file that encapsulates template, script, and styles. This approach promotes better organization and maintainability of component code.
Vue generally follows the MVVM (Model View ViewModel) pattern and employs bidirectional data binding, though there can be varying interpretations of its exact data binding implementation. This flexibility in architectural approach makes Vue adaptable to different project requirements and developer preferences.
Performance Comparison: React vs Vue vs Angular (Rendering Speed, Bundle Size & Optimization)
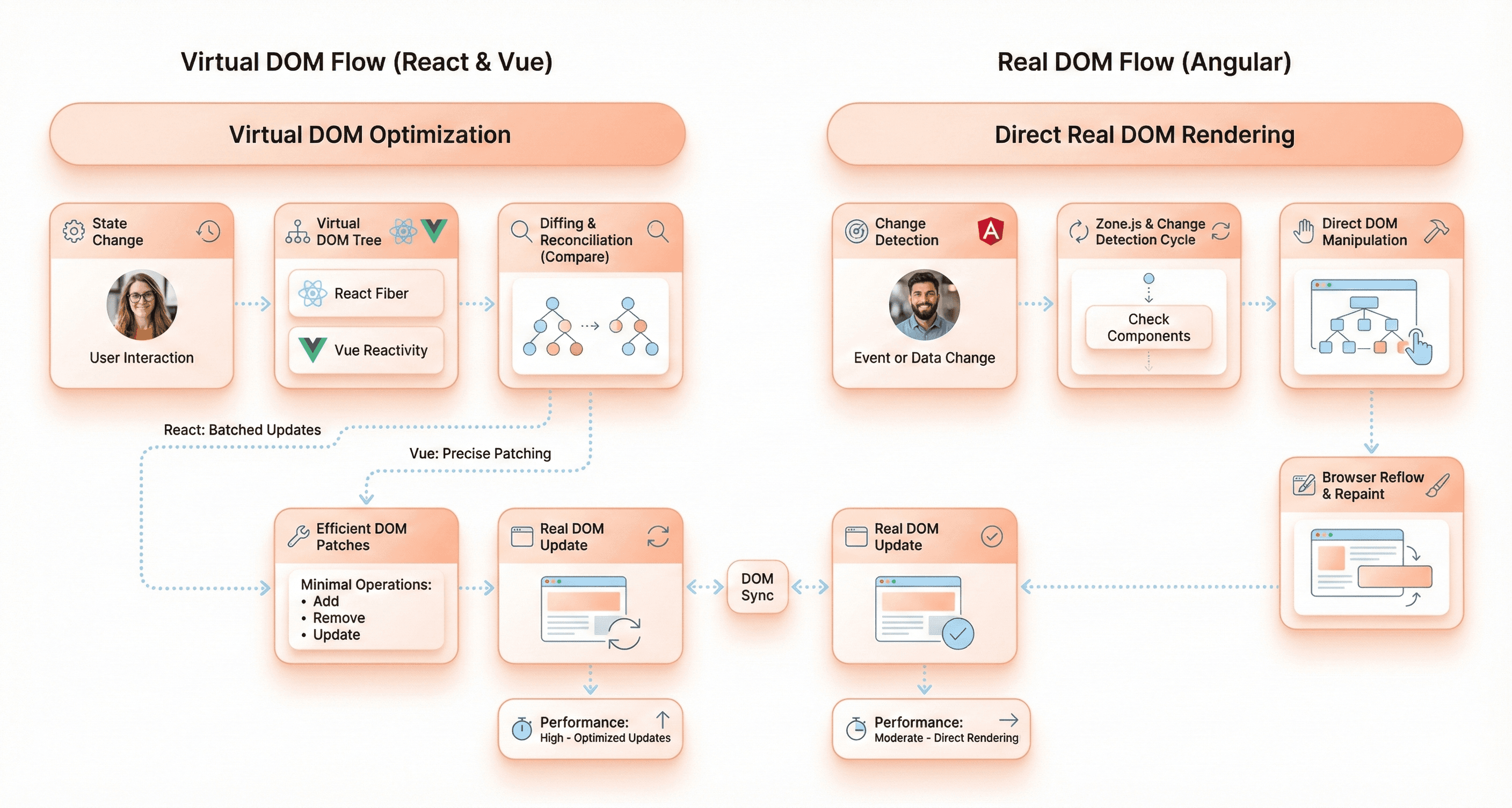
Virtual DOM vs Real DOM: How Each Framework Handles Updates
React and Vue both leverage the Virtual DOM approach, which creates a JavaScript representation of the actual DOM in memory. This architecture enables these frameworks to optimize rendering by calculating the differences between the current and new Virtual DOM states, then applying only the necessary changes to the real DOM. This selective updating mechanism makes both React and Vue highly efficient for complex applications that require frequent UI updates, as they minimize expensive DOM manipulations.
Angular takes a fundamentally different approach by working directly with the Real DOM. In this architecture, changes typically trigger a full page re-render unless developers implement specific optimization techniques. Angular offers the OnPush change detection strategy as one such optimization, but without careful implementation, this direct DOM manipulation can result in slower performance, particularly in large and complex applications where numerous components require updates simultaneously.
Speed and Optimization Features Across Frameworks
React excels in performance optimization through its Virtual DOM implementation and comprehensive suite of performance features. The framework provides developers with memoization capabilities, lazy loading functionality, and concurrent rendering features that offer granular control over the rendering process. These tools make React particularly effective for dynamic and highly interactive user interfaces where performance is critical.
Vue delivers solid performance characteristics, especially for small to mid-sized projects, thanks to its lightweight architecture and efficient reactivity system. The framework often demonstrates faster rendering speeds compared to Angular in many scenarios. However, as applications scale to enterprise levels, Vue may require additional performance tuning and optimization strategies to maintain optimal speed.
Angular demonstrates strong performance capabilities in large-scale applications through advanced optimization features like Ahead-of-Time (AOT) compilation and tree shaking. These techniques help eliminate unused code and pre-compile templates for better runtime performance. Despite these optimizations, Angular's comprehensive framework architecture can contribute to higher initial load times, which may impact the user experience during application startup.
Bundle Size Impact on Application Load Times
Framework | Core Size | Performance Impact |
|---|---|---|
Vue | 23KB | Fastest load time |
React | 31.8KB | Balanced performance |
Angular | 143KB | Slower initial load |
Bundle size plays a crucial role in application performance and SEO, as lighter websites typically load faster and provide better user experiences. Vue maintains the smallest footprint among the three frameworks with a core size of just 23KB, making it particularly beneficial for projects where fast loading times are essential for search engine optimization and user retention.
React offers a competitive bundle size with its 31.8KB core, striking a balance between functionality and performance. This moderate size allows React applications to load quickly while still providing the robust features developers expect from a modern JavaScript framework.
Angular presents the largest bundle size at 143KB for its core framework. While this larger size reflects the comprehensive feature set and enterprise-ready capabilities that Angular provides out of the box, it can impact initial load times, particularly on slower network connections or less powerful devices. Developers working with Angular must carefully consider bundle optimization strategies to mitigate these performance implications.
Learning Curve and Developer Experience: React vs Vue vs Angular
Beginner-Friendly Options vs Advanced Requirements
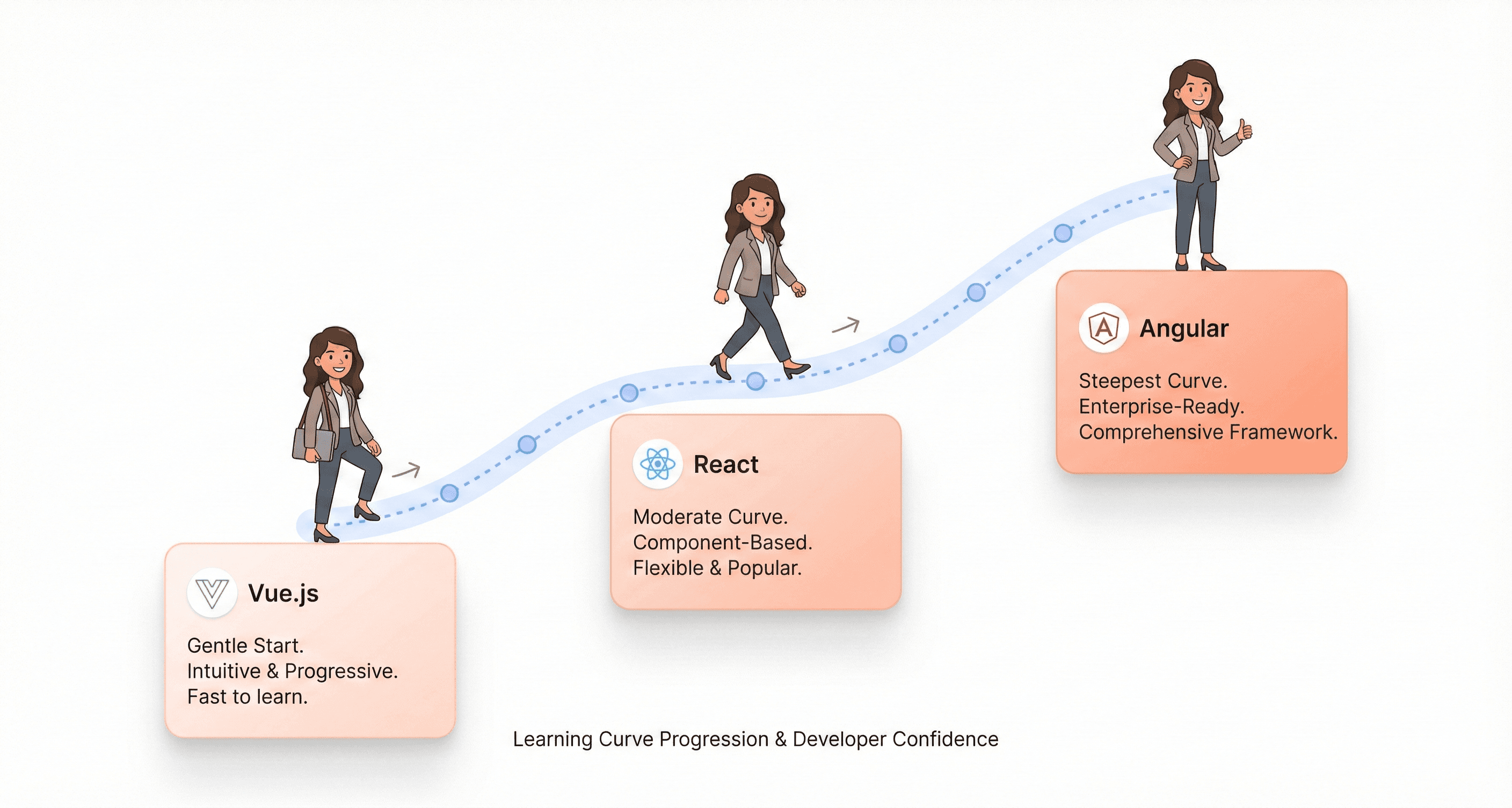
When examining the learning curve for JavaScript frameworks comparison, Vue.js emerges as the most beginner-friendly option among the three. Vue's approachability stems from its straightforward learning curve, allowing developers to create dynamic web applications without requiring prior specific skills. This makes it an ideal choice for those new to front-end development framework selection.
React occupies a middle ground in terms of learning difficulty. While it's considered relatively easy for web developers already familiar with HTML and JavaScript, the integration of JSX can present challenges for some developers. The JSX syntax, which blends JavaScript and HTML-like markup, sometimes proves tedious for developers transitioning from traditional web development approaches.
Angular presents the steepest learning curve among the three frameworks. This complexity arises from its requirement for TypeScript proficiency, demanding significantly greater effort compared to React and Vue. The comprehensive nature of Angular's architecture, while powerful, can overwhelm beginners entering the front-end development landscape.
Documentation Quality and Community Resources
Angular distinguishes itself with exceptionally detailed and well-explained documentation. The framework provides comprehensive examples written in accessible language, making it valuable even for beginners despite its steep learning curve. This thorough documentation helps offset some of the initial complexity developers encounter.
React benefits from robust community support and broad developer adoption across the industry. The large and active community surrounding React creates an extensive ecosystem of tutorials, third-party libraries, and problem-solving resources. This widespread adoption translates into abundant learning materials and community-driven solutions for common development challenges.
Also Read: Bootstrap vs Tailwind: The Framework Battle
Vue maintains active community support through dedicated forums and discussion platforms, which prove essential for both learning the technology and ongoing maintenance. Despite being maintained by a smaller core team compared to React's Facebook backing or Angular's Google support, Vue's community remains engaged and responsive to developer needs.
Required Skills and Prerequisites for Each Framework
The prerequisite requirements vary significantly across these frameworks, directly impacting the React vs Vue vs Angular learning curve. Angular enforces the most stringent requirements, mandating that developers possess solid TypeScript skills before attempting serious development work. This requirement creates a barrier to entry but ensures type safety and better code maintainability in larger applications.
React takes a more flexible approach to prerequisites, though familiarity with JSX becomes necessary for effective development. While React doesn't enforce strict requirements, developers must adapt to JSX syntax, which some find tedious initially. However, once mastered, JSX becomes a powerful tool for component development.
Vue stands out for its minimal prerequisite requirements, not mandating prior specific skills in JavaScript or TypeScript. This accessibility makes Vue an excellent choice for developers transitioning from traditional web development or those seeking their first JavaScript framework experience. The framework's design philosophy prioritizes ease of adoption while maintaining the flexibility to incorporate more advanced features as projects grow in complexity.
Architecture and Data Flow Comparison: Component-Based vs MVC vs MVVM
Component-Based vs MVC vs MVVM Patterns
The architectural patterns employed by React vs Vue vs Angular fundamentally shape how developers structure and organize their applications. React primarily adopts a component-based architecture that provides developers with significant flexibility in choosing design patterns. This approach starts with a single root component and allows the entire application to be built as a tree of reusable components, giving developers the freedom to implement their preferred architectural decisions.
Angular typically follows an MVC (Model-View-Controller) architecture while simultaneously being component-based. This framework incorporates a comprehensive structure that includes modules, templates, services, and components working together in a coordinated fashion. The MVC pattern in Angular ensures clear separation of concerns, making it easier for large development teams to maintain consistency across complex applications.
Vue generally follows the MVVM (Model View ViewModel) pattern, though it's not strictly limited to this approach. Vue's architecture utilizes Single File Components (SFCs) that encapsulate template, script, and style in a single file, providing an intuitive development experience while maintaining the benefits of the MVVM pattern.
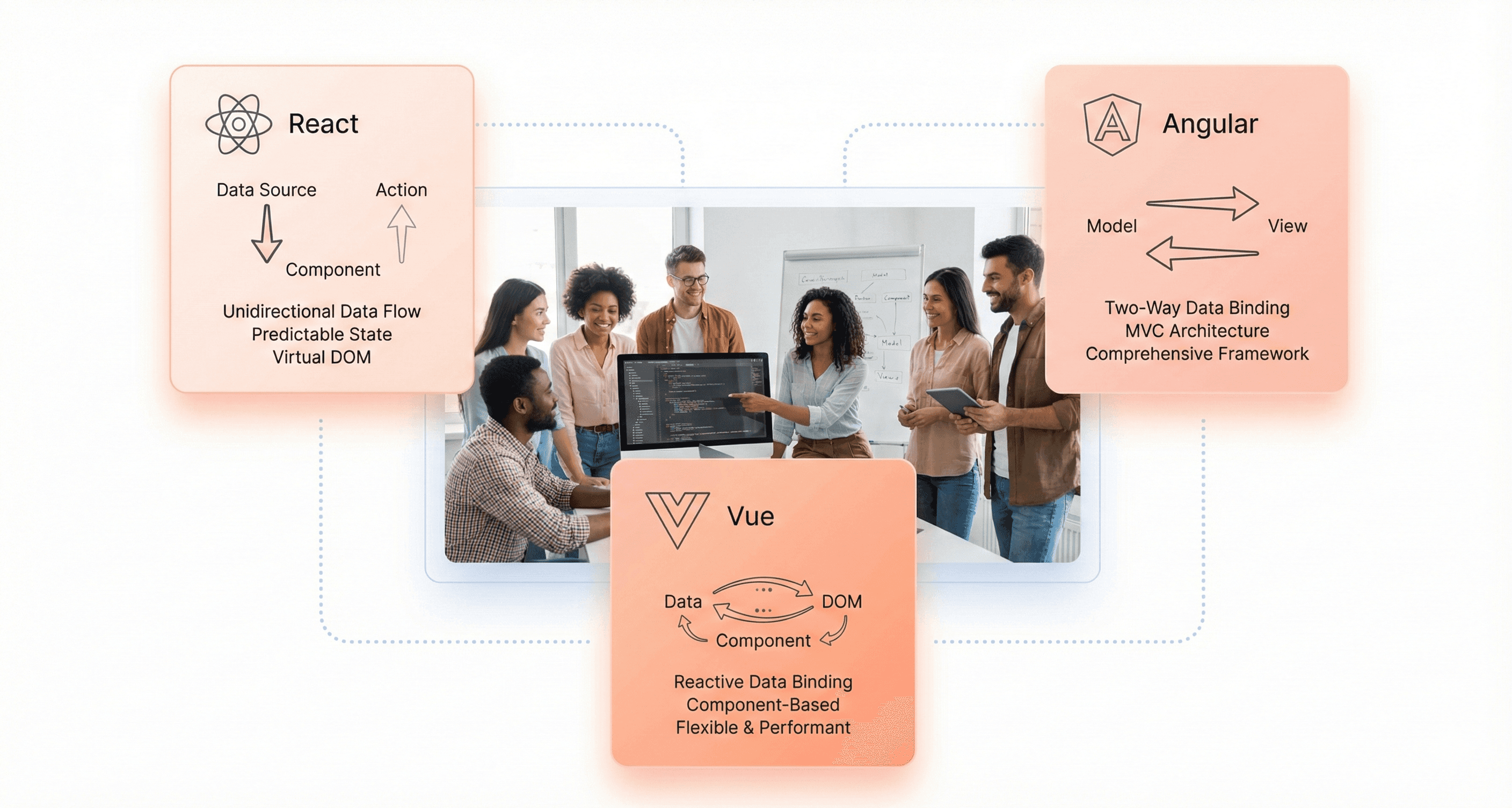
Data Binding Methods: One-Way vs Two-Way
The data binding approaches in these JavaScript frameworks comparison reveal significant differences in how data flows through applications. React uses one-way (unidirectional) data binding, which enhances code predictability by ensuring data flows in a single direction from parent to child components. This approach makes debugging easier and helps developers understand how data changes propagate through the application.
Angular utilizes two-way data binding, ensuring that changes in the model are immediately reflected in the view and vice versa. This automatic synchronization can significantly reduce boilerplate code for form handling and user interactions, though it can sometimes make data flow harder to track in complex applications.
Vue employs bidirectional data binding through its reactive system, combining the benefits of both approaches. Vue's reactive system automatically tracks dependencies and updates the DOM when data changes, while still maintaining clarity about data flow patterns.
Flexibility vs Opinionated Structure Trade-offs
The balance between flexibility and structure varies significantly across these front-end framework options. React offers high flexibility with a minimalistic view-layer focus, allowing developers to choose external libraries for various functionalities such as routing, state management, and HTTP requests. While this flexibility empowers developers to build applications exactly as they envision, it can lead to inconsistency across projects without strict guidelines and coding standards.
Angular provides a comprehensive and opinionated architecture with built-in tools and strict guidelines. This opinionated approach ensures consistency for large teams and enterprise applications but offers less flexibility in architectural decisions. The framework includes everything needed for full-scale application development, from dependency injection to comprehensive testing utilities.
Vue offers high flexibility with more opinionated guidelines than React, striking a middle ground between the two extremes. Vue provides a structured approach with built-in support for state management and routing, yet remains relatively lightweight compared to Angular. This balance makes Vue particularly appealing for developers who want guidance without feeling constrained by overly rigid architectural decisions.
Ecosystem, Tooling, and State Management
Framework | DOM Type | Performance Notes | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
React | Virtual DOM | Fast re-rendering, strong optimization tools | Dynamic, interactive UIs |
Vue | Virtual DOM | Lightweight, good for small–mid projects | Progressive web apps |
Angular | Real DOM | Slower for frequent updates, optimized via AOT | Large enterprise SPAs |
Built-in Features vs Third-Party Dependencies
When evaluating the JavaScript frameworks comparison for ecosystem and tooling capabilities, each framework takes a distinctly different approach to providing functionality. React's ecosystem is vast, relying extensively on a wealth of third-party libraries and community plugins for essential functionalities.
Developers working with React typically need to integrate external solutions for state management (such as Redux or Recoil) and routing (like React Router). This approach offers tremendous flexibility but requires more decision-making from developers regarding which libraries to incorporate into their projects.
Angular stands in stark contrast by offering a comprehensive, built-in ecosystem that includes integrated tools for HTTP requests through HttpClientModule, routing via Angular Router, and state management capabilities. This provides developers with a complete, out-of-the-box solution that reduces the need for external dependencies. However, this comprehensive approach can sometimes feel less flexible compared to React's modular ecosystem.
Vue strikes a middle ground with a smaller but rapidly growing ecosystem that features official libraries like Vuex for state management and Vue Router for routing. This provides developers with a well-integrated and opinionated experience while maintaining reasonable flexibility. The framework's official tooling ecosystem ensures better compatibility and smoother integration compared to relying solely on third-party solutions.
All three frameworks provide robust development tools, including React Dev Tools, Angular CLI, and Vue Devtools, which significantly enhance the developer experience and debugging capabilities.
State Management Solutions Available
State management represents a crucial aspect of the React vs Vue vs Angular debate, with each framework offering distinct approaches to handling application state. React provides multiple state management solutions to accommodate different project needs and developer preferences.
The Context API serves as a built-in solution for simpler state management scenarios, while Redux remains the most popular third-party option for complex applications requiring predictable state management. Recoil represents Facebook's newer experimental approach to state management, offering more granular control over state atoms.
Angular utilizes RxJS and NgRx for state management, leveraging reactive programming principles. RxJS provides powerful operators for handling asynchronous data streams, while NgRx implements the Redux pattern specifically tailored for Angular applications. This combination offers robust state management capabilities but requires developers to understand reactive programming concepts.
Vue's official state management library is Vuex, which follows a similar pattern to Redux but is specifically designed to work seamlessly with Vue's reactivity system. Vuex provides a centralized store for all components in an application, with clearly defined rules ensuring that state can only be mutated in a predictable fashion.
Mobile Development Extensions and Cross-Platform Options
The mobile development landscape showcases significant differences between these front-end frameworks, making this a crucial consideration in the React vs Vue vs Angular market share discussion. React supports mobile development through React Native, which has become one of the most popular solutions for cross-platform mobile development. React Native allows developers to create native iOS and Android applications from a single codebase while leveraging their existing React knowledge and skills.
Angular enables cross-platform mobile applications using NativeScript, which provides direct access to native APIs while using Angular's familiar development patterns. Additionally, Angular is closely associated with Ionic, a popular framework for building hybrid mobile applications using web technologies wrapped in native containers.
Vue offers mobile development extensions via Weex, though this option has less market adoption compared to React Native or Angular's mobile solutions. Weex allows Vue developers to build native mobile applications, but the ecosystem and community support are more limited compared to the alternatives offered by React and Angular.
These mobile development capabilities significantly impact the overall value proposition of each framework, particularly for organizations planning to develop both web and mobile applications using consistent technology stacks.
Testing, Scalability, and Team Collaboration in React, Vue, and Angular
Framework | Built-in Testing | Test Runner | Setup Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
Angular | Yes (TestBed) | Karma | Easiest setup |
React | No (requires Jest + RTL) | Jest | Moderate setup |
Vue | Partial (via plugins) | Jest | Easy setup |
Built-in Testing Tools and Frameworks
When evaluating React vs Vue vs Angular for testing capabilities, each framework approaches testing setup differently, which significantly impacts the developer experience and project maintainability.
Angular stands out with its comprehensive testing approach, automatically generating test files with a .spec.ts extension alongside every application file during project creation. This framework leverages the powerful @angular/core/testing module and TestBed utility, providing developers with a robust foundation for unit testing components, services, and other Angular constructs. The TestBed creates a testing module that mimics the Angular runtime environment, making it easier to test components in isolation while maintaining dependency injection capabilities.
React takes a more flexible approach, requiring developers to install additional testing libraries such as @testing-library/react and jest-dom to create a complete testing environment. Test files typically follow the *.test.js naming convention, and developers have the freedom to choose their preferred testing utilities and assertion libraries. This flexibility allows teams to customize their testing stack according to project requirements.
Vue.js strikes a middle ground by offering @vue/cli-plugin-unit-jest and @vue/test-utils as its primary testing solutions. The framework supports both *.test.js and *.spec.js file naming conventions, with Jest serving as the most common test runner. Vue's testing utilities provide specific methods for mounting and interacting with Vue components, making component testing intuitive and straightforward.
Test Configuration Requirements
The execution of tests varies across these JavaScript frameworks, reflecting their different philosophical approaches to tooling and developer workflow.
Angular simplifies test execution through its integrated CLI system, allowing developers to run comprehensive test suites using the straightforward ng test command. This command automatically configures the testing environment, watches for file changes, and provides detailed feedback through the browser-based Karma test runner.
Both React and Vue follow a more standard Node.js approach, utilizing the npm test command after properly installing the necessary testing dependencies. This approach requires developers to ensure all testing libraries are correctly configured in their package.json files and that the testing scripts are properly defined.
Real Device Testing Considerations
Modern web application development demands thorough testing across various environments, and all three frameworks, Angular, React, and Vue, provide robust support for real device testing scenarios.
Each framework supports running tests on actual devices, enabling developers to validate application behavior under authentic user conditions. This capability proves essential for identifying performance bottlenecks, touch interaction issues, and device-specific rendering problems that might not surface in desktop browser testing environments.
The emphasis on real device testing becomes particularly crucial when considering the diverse ecosystem of mobile devices, varying network conditions, and different operating system versions that end users encounter. Thorough testing under these real-world conditions ensures a seamless end-user experience across the entire spectrum of deployment environments, regardless of whether the application is built with React, Vue, or Angular.
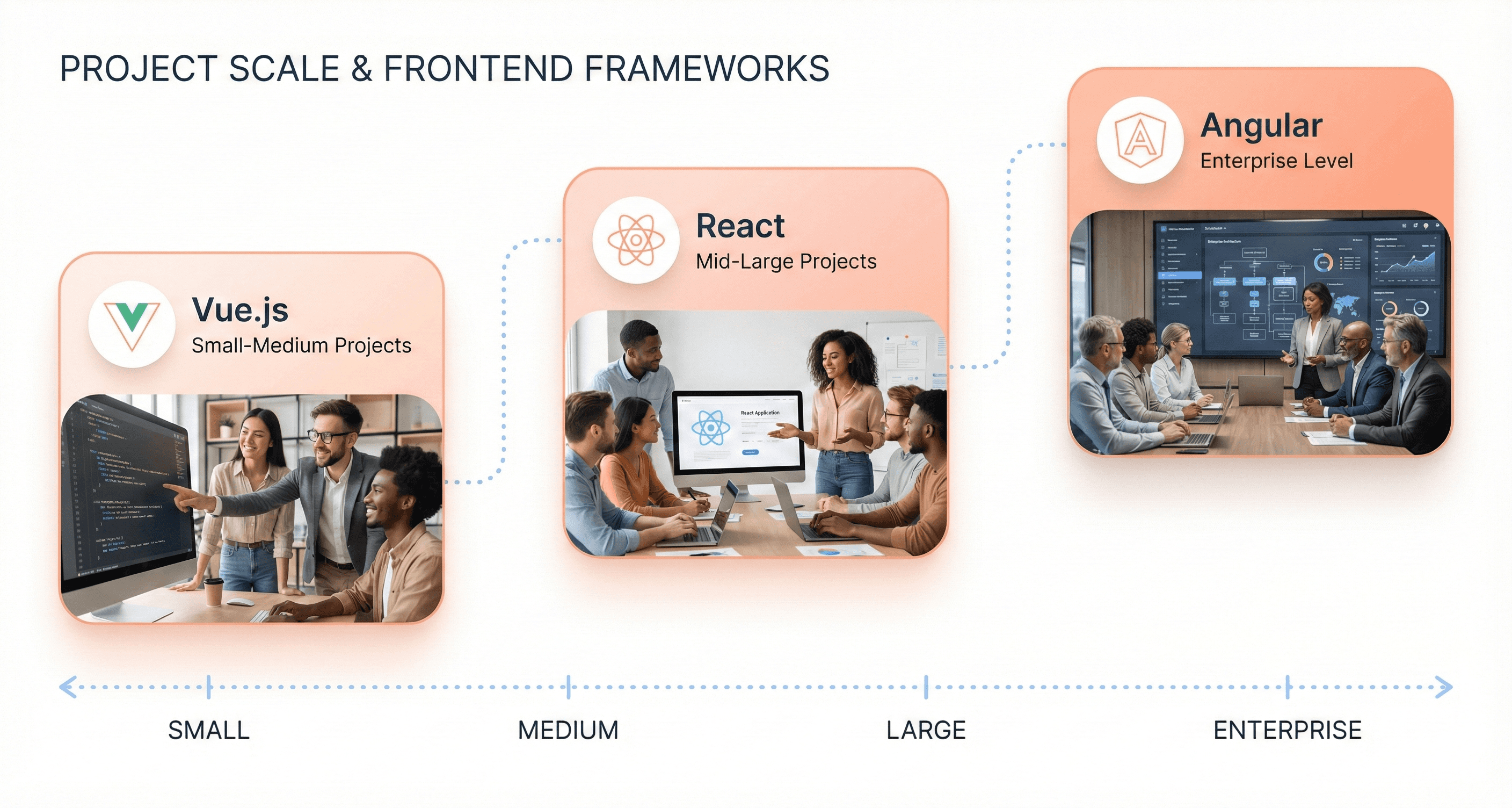
Scalability for Different Project Sizes: Small Apps to Enterprise Systems
Project Size | Best Framework | Why |
|---|---|---|
Small–Medium | Vue | Lightweight, quick to learn |
Mid–Large | React | Flexible, scalable |
Enterprise | Angular | Full-featured, structured |
Small to Medium Project Suitability
Vue.js emerges as the clear winner for small to medium-sized projects, thanks to its lightweight and flexible nature that delivers efficient updates without the overhead typically associated with larger frameworks. This makes it an excellent choice when you need to build applications quickly while maintaining optimal performance. The framework's gentle learning curve and minimal setup requirements allow developers to get productive faster on smaller projects.
React demonstrates impressive scalability across project sizes, performing efficiently in small to mid-sized applications while maintaining the flexibility to grow with your needs. Its component-based architecture provides a solid foundation that works well regardless of project complexity, making it a versatile choice for teams uncertain about future scaling requirements.
Angular's comprehensive nature presents unique considerations for smaller applications. The framework's full-featured approach can introduce unnecessary complexity and overhead for simple projects, potentially making development more cumbersome than needed. However, this limitation becomes less significant as project requirements grow more complex.
Enterprise-Level Application Requirements
When evaluating JavaScript frameworks comparison for enterprise-level applications, Angular stands out as the ideal choice for large-scale, enterprise-level applications. The framework provides a full-featured development environment with a highly scalable architecture built-in from the start. Angular's strong structural foundation and Google's backing instill confidence for long-term maintenance in large applications, making it a trusted choice for enterprises planning multi-year development cycles.
React scales effectively for large applications, leveraging its component-based architecture and inherent flexibility. This approach allows development teams to build complex applications while maintaining code organization and performance. The framework's modular nature supports the demanding requirements of enterprise-level development.
Vue, while excelling primarily in smaller projects, demonstrates adaptability for larger applications when paired with appropriate state management libraries like Vuex. This combination enables Vue to handle the complexity demands of enterprise applications, though it requires additional architectural planning compared to Angular's out-of-the-box enterprise readiness.
Many growing SaaS teams adopt Vue for scalability but eventually require structured VueJS migration services to refactor legacy UI architecture and improve long-term maintainability.
Team Collaboration and Code Maintainability
Angular promotes highly scalable team collaboration and code maintainability through its consistent and readable codebase structure. The framework's architecture ensures that minor changes don't necessitate updating the entire project structure, which proves invaluable when multiple developers work simultaneously on different features. Angular's strict guidelines and built-in tools guarantee consistency across large teams, reducing the likelihood of code conflicts and maintaining high code quality standards.
React's reusable components contribute significantly to reduced complexity and clearer, more maintainable codebases. This component-driven approach allows teams to build modular applications where individual pieces can be developed, tested, and maintained independently, facilitating better collaboration among development teams.
Industry Adoption, Popularity, and Job Demand
Corporate Backing and Long-term Support
Understanding which framework has the strongest backing is crucial when considering React vs Vue vs Angular for long-term projects. React enjoys robust support from Facebook (now Meta) alongside a massive open-source community, ensuring its continued development and widespread adoption. This corporate backing provides developers with confidence in React's stability and future roadmap.
Angular benefits from Google's extensive resources and commitment, making it a trusted choice for enterprise-level applications requiring long-term maintenance. Google's backing gives Angular significant credibility in the JavaScript frameworks comparison, particularly for organizations prioritizing reliability and sustained support.
Vue presents a different scenario, having been created by a former Google employee but maintained by a smaller core team. While Vue relies primarily on community support rather than major corporate backing, this has created some perception challenges regarding its trustworthiness among certain audiences, though its growing ecosystem continues to address these concerns.
Popular Companies Using Each Framework
The industry adoption patterns reveal interesting insights into React vs Vue vs Angular usage across major corporations. React dominates among tech giants and innovative companies, with Facebook, Uber, Airbnb, Netflix, Yahoo!, The New York Times, Amazon, and Twitter all leveraging its capabilities for their dynamic user interfaces.
Angular's enterprise focus is evident in its adoption by Google, Wix, PayPal, Samsung, Upwork, and MS Office. These implementations demonstrate Angular's strength in handling complex, large-scale applications that require structured development approaches.
Vue's growing market share is reflected in its adoption by notable companies including Alibaba, GitLab, UpWork, Netflix, Nintendo, and Grammarly. This diverse range of users showcases Vue's versatility across different industries and project types.
Developer Demand and Career Opportunities
Career considerations play a vital role in determining which framework to master in the current job market. The choice between React vs Vue vs Angular should align closely with individual career goals and market demands.
Angular offers exceptional opportunities for developers targeting large-scale application development, providing a comprehensive framework structure that appeals to enterprise environments. Mastering Angular positions developers well for roles requiring robust architectural knowledge and complex system management.
React presents ideal career paths for those passionate about creating dynamic user interfaces and working with cutting-edge frontend technologies. The framework's popularity in startups and established tech companies creates abundant opportunities across various sectors.
Vue provides an excellent entry point for developers seeking to build scalable projects with reduced overhead. Its straightforward learning experience makes it attractive for developers transitioning into frontend development or those working on projects requiring rapid development cycles.
How to Choose the Right Framework for Your Project (Startup, SaaS, or Enterprise)
Project Size and Complexity Considerations
When evaluating React vs Vue vs Angular for your specific project needs, the scale and complexity of your application should be the primary determining factor. Angular emerges as the clear choice for large-scale, structured, and enterprise-level applications that demand a comprehensive toolset and strict architecture. Its robust framework provides the necessary scaffolding for complex applications with multiple teams and extensive feature requirements.
React proves ideal for dynamic, high-performance, interactive user interfaces, particularly when building real-time applications and single-page applications (SPAs) that demand quick rendering and frequent updates. The framework's virtual DOM and component-based architecture excel in scenarios where performance and user interaction are critical.
Vue.js stands out as the optimal solution for small to medium-sized projects that require efficient updates, customizable UI components, and high interactivity without the overhead associated with heavier frameworks. Its lightweight nature and progressive adoption capability make it perfect for projects that need to balance functionality with simplicity.
Team Expertise and Timeline Factors
The selection of a JavaScript framework should strategically align with your team's existing expertise and project timeline constraints. Vue offers the most straightforward learning experience among the three, facilitating quick adoption for development teams, especially those with beginners or mixed skill levels. This accessibility translates to faster project initiation and reduced onboarding time.
React presents an easy learning curve for developers already familiar with HTML and JavaScript fundamentals, allowing for relatively quick ramp-up periods. Teams with solid JavaScript foundations can typically achieve productivity with React in shorter timeframes compared to Angular.
Angular's steep learning curve and TypeScript requirement present significant considerations for timeline planning. Teams without prior TypeScript experience may need to invest considerably more effort and allocate longer timelines for skill development and framework mastery.
Long-term Maintenance and Support Requirements
For front-end framework comparison considerations, long-term viability becomes crucial for project sustainability. Angular's backing by Google provides substantial confidence in its long-term maintenance and support infrastructure, particularly valuable for large-scale applications requiring extended lifecycles and enterprise-grade reliability.
React's development approach involves constant updates that require developers to continuously adapt and relearn new patterns and methodologies. This ongoing evolution implies a sustained maintenance effort and the need for teams to stay current with frequent framework changes and best practices.
Vue relies heavily on strong community support and comprehensive forums for long-term maintenance and learning resources. While this community-driven approach provides extensive knowledge sharing, it places greater responsibility on development teams to actively engage with community resources for problem resolution and framework updates.
Final Verdict: React vs Vue vs Angular (Which Should You Choose?)
Choosing between React, Vue, and Angular ultimately comes down to aligning the framework's strengths with your project's specific needs and your team's expertise. React excels in building dynamic, high-performance user interfaces with its virtual DOM and component-based architecture, making it ideal for interactive applications and teams that value flexibility.
Angular provides a comprehensive, enterprise-ready solution with built-in tools and strict structure, perfect for large-scale applications that require consistency and long-term maintainability. Vue offers the best of both worlds with its gentle learning curve and progressive nature, allowing developers to start small and scale up as needed.
Rather than declaring one framework as definitively superior, the key is understanding that each serves different purposes in the development ecosystem. Consider your project's scale, your team's background, performance requirements, and long-term maintenance needs when making your decision.
Regardless of which framework you choose, thorough testing across real devices and browsers remains essential to ensure your application delivers a seamless user experience. The JavaScript framework landscape continues to evolve, but React, Vue, and Angular have proven themselves as reliable choices that can power everything from simple websites to complex enterprise applications.

About the author
Author Name:
Parth G
|
Founder of
Hashbyt
I’m the founder of Hashbyt, an AI-first frontend and UI/UX SaaS partner helping 200+ SaaS companies scale faster through intelligent, growth-driven design. My work focuses on building modern frontend systems, design frameworks, and product modernization strategies that boost revenue, improve user adoption, and help SaaS founders turn their UI into a true growth engine.
Is a clunky UI holding back your growth?
Is a clunky UI holding back your growth?
▶︎
Transform slow, frustrating dashboards into intuitive interfaces that ensure effortless user adoption.
▶︎
Transform slow, frustrating dashboards into intuitive interfaces that ensure effortless user adoption.






