Legacy applications are slowing down your enterprise, frustrating users, and draining IT budgets. If you're an enterprise IT leader, CIO, or digital transformation manager struggling with outdated systems that can't keep up with 2026's business demands, this comprehensive report tackles the UX challenges in legacy application modernization head-on.
This 2026 Enterprise Report examines the critical intersection where aging technology meets modern user expectations. You'll discover actionable insights on three key areas that make or break modernization success: first, the emerging UX trends shaping 2026 modernization strategy, including AI-embedded interfaces and mobile-first design for deskless workers; second, a comprehensive legacy UX audit process that identifies pain points through stakeholder interviews, heuristic evaluation, and accessibility checks; and third, strategic implementation approaches for maximum ROI that balance technical debt reduction with user adoption.
Drawing from real enterprise modernization projects and industry best practices, this report shows you exactly how to transform clunky legacy interfaces into intuitive, productive tools that drive business results rather than hinder them.
AI-Powered Legacy Modernization Report 2026 for Enterprise Applications
Core Definition and Strategic Approaches
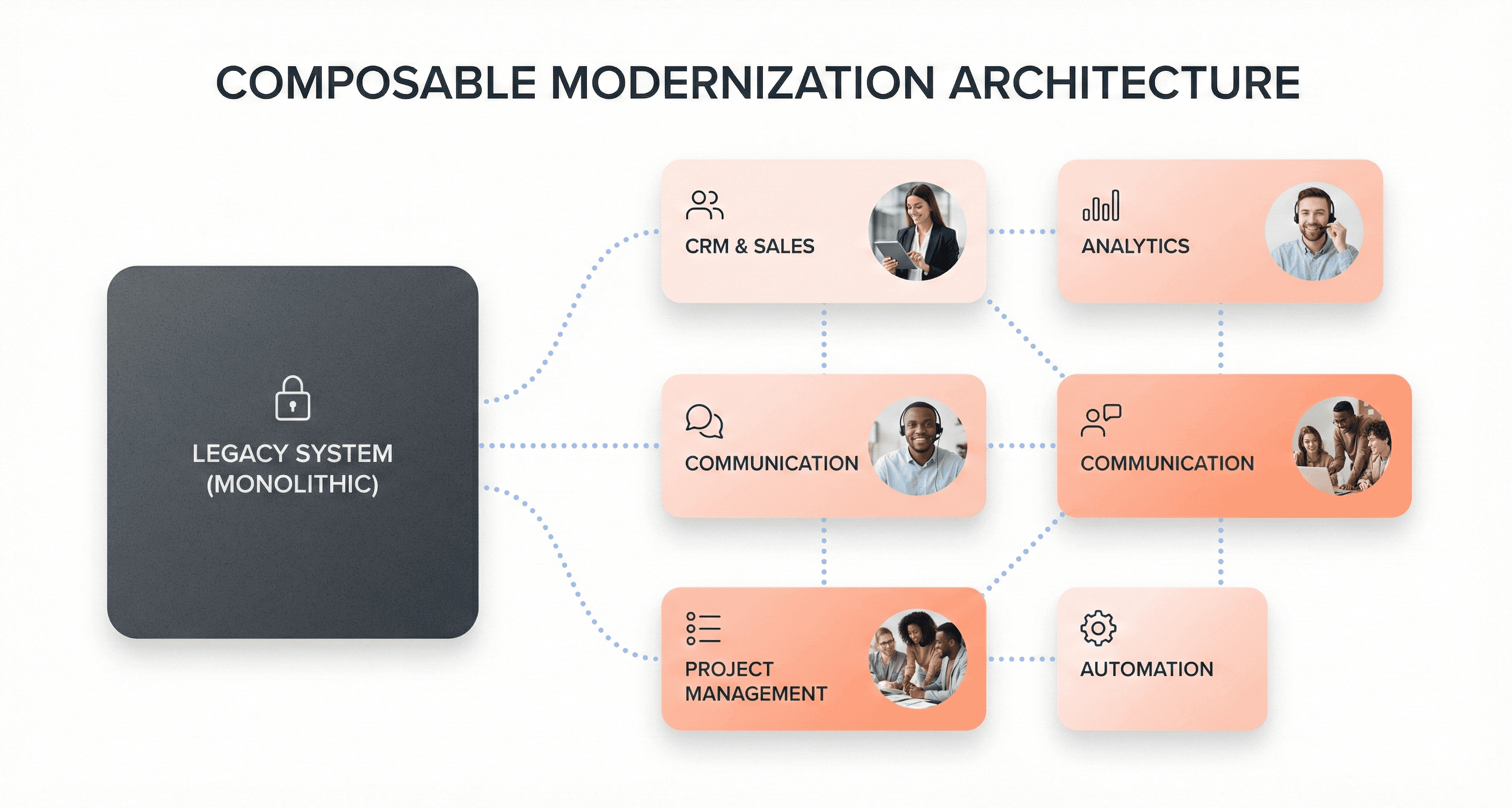
Legacy application modernization for 2026 enterprises represents a strategic business transformation that goes beyond simple technical upgrades. This process involves updating outdated systems, interfaces, and user experiences that have accumulated significant technical debt over years or decades of operation. The modernization encompasses everything from cloud readiness foundations to domain-oriented architectures that replace monolithic cores.
The strategic approach centers on composable modernization - a methodology that breaks down large-scale transformations into discrete, measurable increments. Rather than attempting disruptive "big bang" overhauls, enterprises are adopting iterative improvements that coexist with existing systems while delivering early returns on specific business needs. This approach reduces risk and allows organizations to maintain operational stability throughout the transformation process.
Modern legacy UX modernization strategy emphasizes security by design, embedding identity, access, and observability controls into new components from the outset rather than retrofitting them later. Zero-trust principles increasingly shape how systems are structured and integrated, influencing architectural decisions far beyond traditional security functions.
Key Differences Between Application and IT Modernization
While IT modernization focuses primarily on infrastructure upgrades and hardware replacement, legacy application modernization addresses the fundamental business logic, user interfaces, and data architectures that directly impact customer experience and operational efficiency. Application modernization specifically targets the software layer where users interact with enterprise systems, requiring careful attention to UX design principles and business process optimization.
The distinction becomes critical when considering that enterprises report losing approximately $370 million annually due to outdated technology and technical debt burdens. This staggering cost includes maintenance overhead, failed modernization attempts, and operational drag that legacy environments impose on innovation and performance. Application modernization directly addresses these pain points by improving user productivity, reducing training requirements, and enabling faster feature deployment.
IT modernization typically involves replacing servers, upgrading networks, or migrating to cloud infrastructure - changes that may be invisible to end users. In contrast, application modernization transforms how employees and customers interact with enterprise systems, making it a more visible and impactful business transformation that requires stakeholder buy-in and change management strategies.
Identifying When Systems Require Modernization
Enterprise systems reach critical modernization thresholds when they begin constraining business growth and operational efficiency. Key indicators include escalating maintenance costs, security vulnerabilities that cannot be adequately addressed through patches, and inability to integrate with modern data analytics platforms required for AI capabilities.
Technical debt accumulation serves as a primary signal for modernization needs. When systems require extensive workarounds, manual processes, or custom integrations to support basic business functions, the hidden costs begin impacting EBITDA and operational metrics that matter to investors and stakeholders.
User experience degradation represents another critical indicator. Legacy interfaces that require extensive training, cause frequent user errors, or cannot support mobile access patterns signal immediate modernization requirements. Modern customers and employees expect responsive, intuitive interfaces that legacy systems were never designed to provide.
Real-time data requirements also trigger modernization decisions. When business operations depend on immediate access to current information for decision-making, automation, or customer service, batch-oriented legacy systems become operational bottlenecks. Event-driven architectures and streaming data capabilities require foundational changes that legacy systems cannot accommodate without significant re-engineering.
The convergence of these factors - cost escalation, security exposure, user experience limitations, and data architecture constraints - creates a compelling business case for strategic modernization initiatives that align with 2026 enterprise digital transformation objectives.
Benefits of Enterprise Legacy Application Modernization
Cost Optimization and Productivity Gains
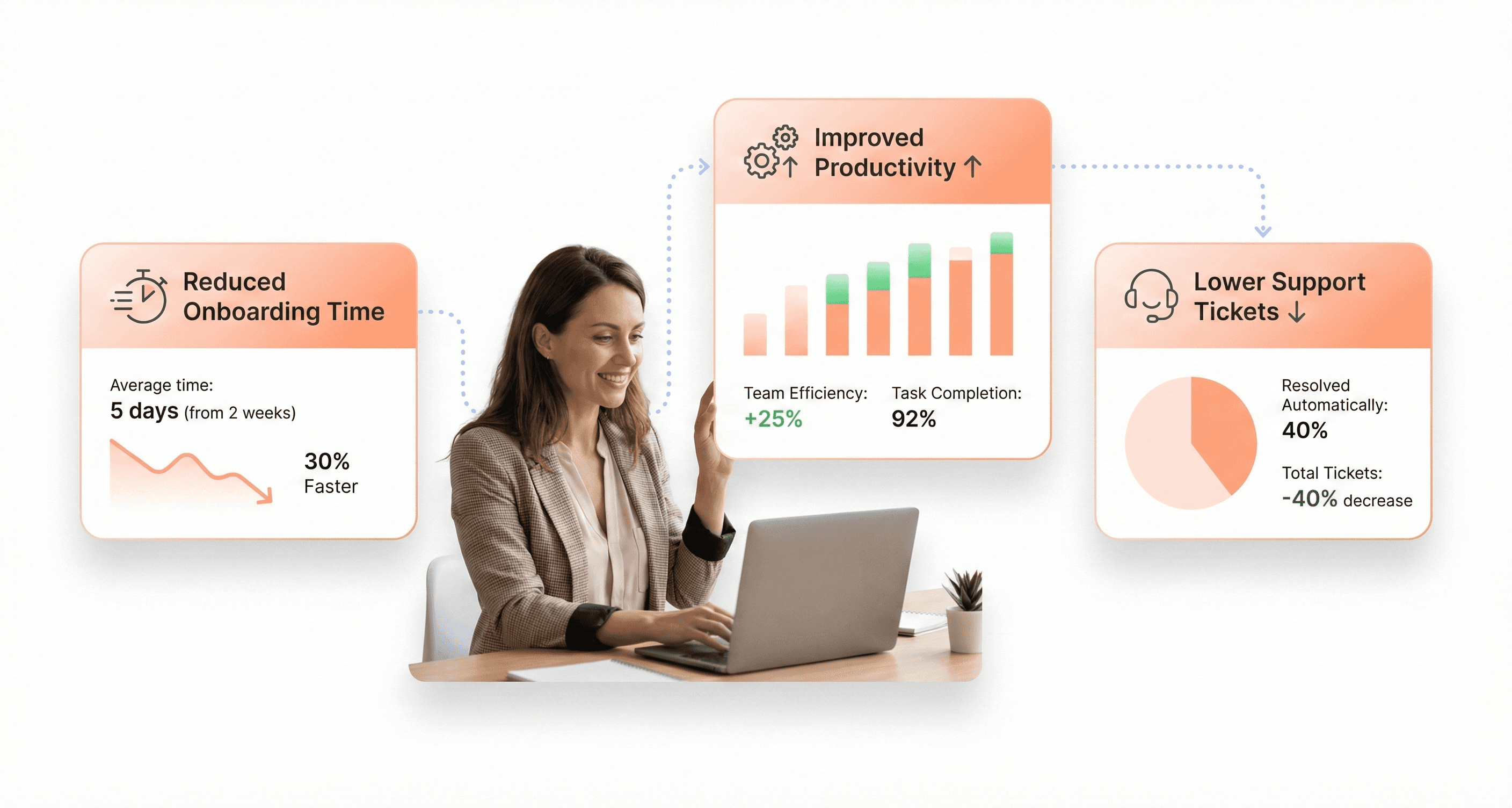
The financial impact of legacy application modernization extends far beyond initial development costs, delivering measurable returns that compound over time. According to Forrester research, every $1 invested in UX modernization generates an average return of $100, representing an extraordinary 9,900% ROI for enterprise organizations.
Reduced Training and Support Expenses
Legacy systems with poor UX design create cascading cost increases across the organization. When enterprise applications are unintuitive, companies require longer training programs, more detailed documentation, refresher sessions, and dedicated support staff. For organizations with high employee turnover or seasonal hiring patterns, these expenses become recurring burdens that significantly impact operational budgets.
Modern UX design dramatically reduces time-to-value for new employees. Well-designed systems require minimal training and support, enabling new hires to become productive faster. The difference between two weeks versus four weeks of training becomes material when scaling operations or onboarding large teams across multiple locations.
Elimination of Productivity Drains
Poor UX in legacy applications creates daily productivity losses that compound across the enterprise. If sales teams spend an extra 10 minutes per transaction due to clunky CRM interfaces, that lost time multiplies across hundreds of users and thousands of transactions, directly impacting revenue generation capacity.
Organizations that prioritize UX modernization consistently report significant productivity improvements. One retail company redesigned their store operations platform and measured a 35% reduction in transaction time, while a logistics provider improved their driver app and saw fuel efficiency gains because drivers could navigate routes more effectively.
Lower Support and Maintenance Costs
Intuitive design reduces helpdesk ticket volumes substantially, allowing support teams to focus on genuine technical issues rather than explaining basic task completion. For large enterprises, this difference can mean operating with a support team of 10 people instead of 30, representing substantial ongoing cost savings.
Enhanced Security and Compliance Standards
Modern UX design directly impacts enterprise security posture and regulatory compliance by embedding best practices into user workflows. When processes are clearly built into the user experience, employees naturally follow established protocols, reducing compliance violations and strengthening audit readiness.
Improved Data Quality and Governance
Well-designed interfaces include validation prompts, helpful guidance, and clear workflows that ensure cleaner data entry. This results in higher data quality, which translates to better decision-making capabilities, more accurate reporting, and enhanced automation opportunities. Poor data quality costs enterprises millions in manual cleanup efforts, incorrect decisions, and missed business opportunities.
Reduced Error Rates and Risk Exposure
Confusing interfaces increase mistake rates across all business functions. In financial services, these errors can be costly; in healthcare, they can be dangerous; in manufacturing, they disrupt entire operations. The cost extends beyond fixing individual errors to include downstream impacts on customer relationships, regulatory standing, and organizational reputation.
Built-in Compliance Features
Modern UX approaches incorporate compliance requirements directly into the user interface design, making it easier for employees to follow regulations naturally rather than requiring separate compliance training and monitoring systems.
Improved Employee Satisfaction and Retention
The quality of internal systems directly impacts employee experience and organizational competitiveness in talent markets. People expect to work with modern, well-designed tools, and legacy systems that feel outdated affect job satisfaction and retention rates.
Competitive Advantage in Talent Acquisition
When internal systems appear antiquated, it creates negative impressions during recruitment processes and impacts the organization's ability to attract top talent, particularly for technology and business-critical roles. Modern, intuitive systems become a differentiating factor in competitive talent markets.
Reduced Change Management Resistance
Organizations with well-designed systems experience smoother technology adoption cycles. When employees associate internal tools with efficiency rather than frustration, they become more receptive to system updates and new feature rollouts. This reduces change management costs and accelerates the realization of technology investments.
Higher User Adoption Rates
Systems designed around user needs achieve significantly higher adoption rates, ensuring that technology investments actually deliver their intended business benefits rather than being circumvented through shadow IT solutions or manual workarounds.
UX Challenges in Legacy System Modernization
Organizational Silos and Bureaucratic Resistance
Knowledge silos exist in 83% of companies, with 97% of workers acknowledging that silos harm their business operations. In legacy application modernization projects, these organizational barriers create significant disconnects between IT departments and business teams. Each function maintains siloed knowledge within their domain, making effective collaboration challenging during enterprise modernization initiatives.
IT teams possess technical expertise about system architectures and modernization capabilities, while business teams understand operational requirements and user needs. This separation creates an incomplete picture that leads to unforeseen issues and missed opportunities throughout the modernization process. The bureaucratic resistance often stems from departments protecting their existing processes and reluctance to share critical information necessary for successful UX transformation.
Operational Biases and Disconnected Decision Making
Many enterprises fall into the trap of shaping their modernization approach according to vendor limitations rather than prioritizing organizational needs. This vendor-driven decision making results in ill-fitting approaches that don't effectively scale or adapt as businesses evolve. The rigidity of vendor-dictated modernizations clashes with composability requirements—the ability to flex, add to, retool, and rearrange IT infrastructure to fit evolving business needs.
According to Gartner research, high-composability enterprises can expect greater revenue increases compared to low-composability enterprises. When decision making becomes disconnected from actual business requirements, modernization projects fail to deliver the anticipated value and may even hold companies back from potential revenue gains.
Low Change Adoption Culture Among Employees
Enterprise modernization represents a significant cultural and operational shift that extends far beyond technological evolution. Applications support business functions, meaning every modernized app creates substantial changes for developers, engineers, and the broader organization. Only 25% of employees report that AI implementation is actually improving efficiency, indicating that the path from implementation to improvement isn't straightforward.
If change management isn't well planned, managed, and supported, teams cannot work effectively with newly modernized applications, removing substantial value from modernization projects. The cultural transformation demands specialized change management expertise that supplements technical skills. Without bringing teams along the transformation journey, even well-planned modernization initiatives struggle to achieve their strategic goals.
Substantial Technical Debt and System Complexity
Legacy system upgrade challenges have intensified as tech stacks become increasingly complex while IT budgets remain static or shrink. The majority of organizations now wholly depend on digital technology to operate, with many businesses being defined by their technological capabilities rather than merely dependent on them. This creates pressure on IT leaders to demonstrate measurable ROI while managing substantial technical debt.
System migration projects exemplify this complexity challenge, with 72% of IT leaders reporting that migrations take longer than planned, while 75% of cloud migrations exceed budget projections. The prolonged and complex nature of these processes makes anticipated ROI elusive. Additionally, only 29% of IT leaders claim their organizations are at the forefront of data, analytics, and machine learning capabilities, highlighting the struggle to keep pace with rapidly evolving technologies while managing existing system complexity.
2026 UX Trends in Application Modernization
Role-Based Interfaces for Personalized User Experiences
With this in mind, next we'll examine how role-based access control (RBAC) is evolving beyond traditional security frameworks to become a cornerstone of personalized enterprise UX. The traditional approach of static interfaces that serve all users identically is rapidly being replaced by adaptive systems that recognize user roles and customize experiences accordingly.
Role-based interfaces in 2026 modernization strategy leverage AI-powered personalization to create context-aware environments where each user sees only what's relevant to their specific job function. For example, a CEO accessing an ERP system will see executive dashboards with high-level metrics and strategic insights, while a data entry clerk encounters streamlined forms optimized for rapid input. This isn't merely about hiding certain buttons - it's about fundamentally restructuring the interface architecture to match cognitive workflows and daily task patterns.
The implementation of role-based interfaces addresses the critical challenge of information density that plagues many legacy applications. Instead of overwhelming users with comprehensive data sets, these personalized systems use progressive disclosure techniques, presenting information hierarchically based on role requirements. A finance manager might see budget variance reports prominently displayed, while the same data appears as summary metrics for operations staff.
Modern role-based systems also incorporate behavioral learning, adapting interface elements based on usage patterns. If a user consistently ignores certain features, the system intelligently reorganizes the layout to prioritize frequently accessed functions, reducing cognitive load and improving task completion times.
AI-Embedded UX Integration Throughout Workflows
Previously, I've discussed how enterprise applications are transitioning from static dashboards to intelligent co-pilots, and this transformation represents perhaps the most significant shift in 2026 modernization strategy. AI-embedded UX integration moves beyond simple automation to create contextually aware interfaces that anticipate user needs and provide proactive assistance throughout complex enterprise workflows.
The evolution from traditional dashboards to AI-powered interfaces fundamentally changes how users interact with enterprise systems. Instead of requiring users to interpret graphs and identify patterns manually, AI-embedded systems proactively surface insights. For instance, rather than a logistics manager studying supply chain data to detect disruptions, the system automatically alerts them with contextual information: "Northeast region deliveries are delayed 23% due to weather conditions. Here are three alternative routing options."
Multimodal AI integration enables these systems to process and output information across various formats seamlessly. A single interface can ingest video data from warehouse cameras, generate written reports, create voice summaries, and produce visual dashboards - all within one cohesive workflow. This omni-modal approach eliminates the need for users to switch between multiple applications to complete complex tasks.
Trust remains the primary UX challenge in AI-embedded systems. Enterprise users need transparency into AI decision-making processes, requiring interfaces that provide clear data lineage and allow users to verify AI-generated insights. Successful implementations ensure users maintain access to underlying data and can understand the reasoning behind AI recommendations, building confidence in automated suggestions while preserving human oversight capabilities.
Mobile-First Design for Deskless Workers
Now that we have covered personalization and AI integration, the third critical trend shaping 2026 modernization strategy addresses the growing population of deskless workers who require enterprise functionality beyond traditional desktop environments. Mobile-first design for enterprise applications represents a fundamental shift from responsive design adaptations to native mobile workflows optimized for field operations, remote work, and on-the-go productivity.
The traditional approach of shrinking desktop interfaces to fit mobile screens fails to address the unique constraints and opportunities of mobile enterprise usage. Effective mobile-first design recognizes that mobile users often work in challenging environments - poor lighting, network connectivity issues, gloved hands, or noisy surroundings - requiring interfaces optimized for these real-world conditions.
Cross-platform continuity becomes essential as users frequently transition between devices throughout their workday. A field technician might start a service request on their mobile device, continue documentation on a tablet, and complete reporting on a desktop system. Seamless state preservation and synchronized data ensure users can resume exactly where they left off regardless of device switching.
Voice and natural language processing integration proves particularly valuable for mobile enterprise interfaces, enabling hands-free operation in field environments. Workers can dictate reports, query inventory systems, or update project status through voice commands, maintaining productivity while managing physical tasks.
The mobile-first approach also emphasizes offline functionality, recognizing that deskless workers often operate in areas with unreliable connectivity. Robust caching, local data storage, and intelligent synchronization ensure critical workflows remain functional regardless of network availability, with seamless data reconciliation once connectivity resumes.
Enterprise UX Audit Framework
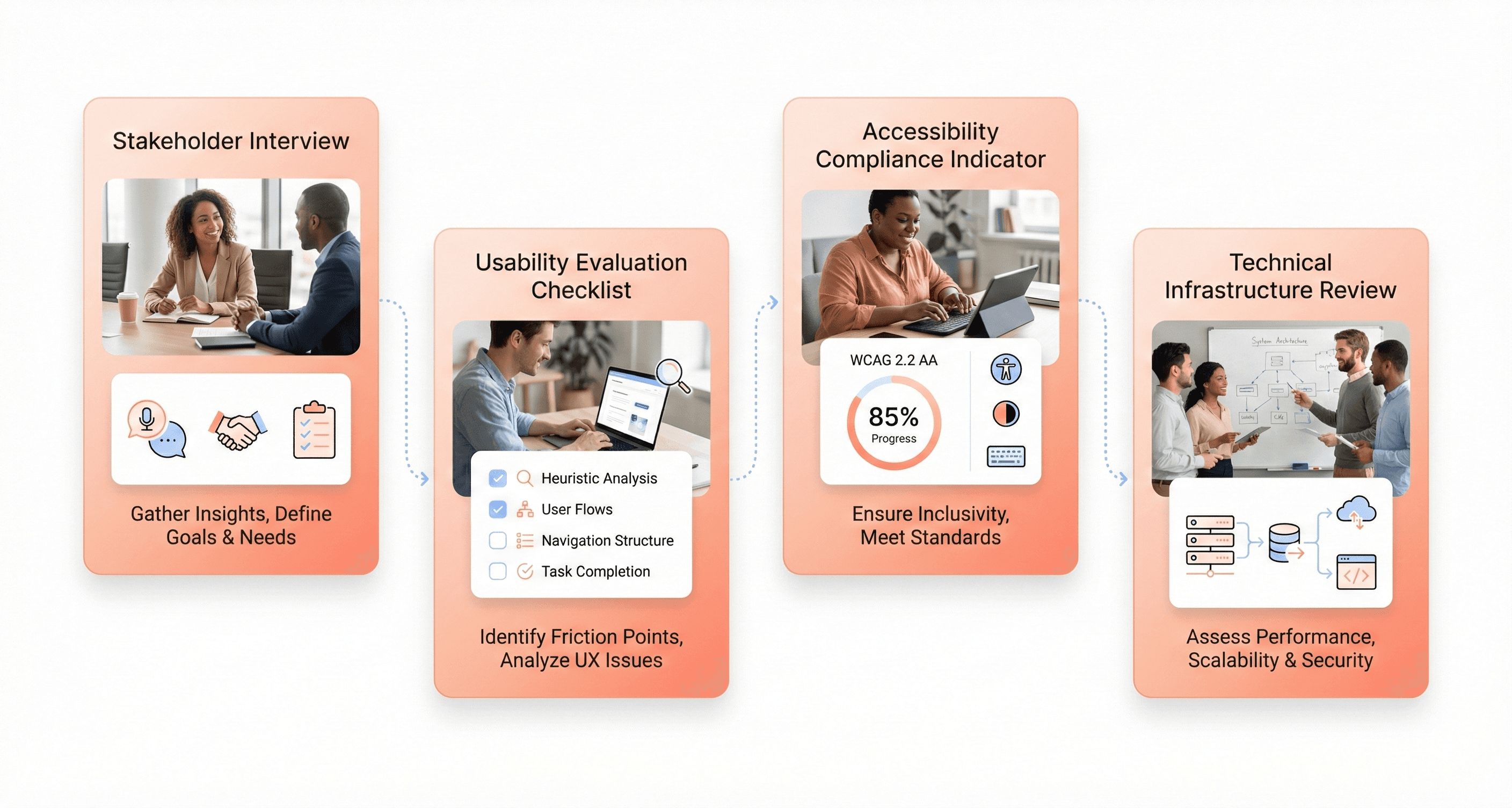
Stakeholder Interviews and User Pain Point Analysis
The foundation of any comprehensive legacy UX audit begins with understanding the human experience behind the software. Stakeholder interviews provide critical insights into how different user groups interact with legacy systems and where friction occurs. This process involves conducting structured conversations with end-users, administrators, IT personnel, and business stakeholders to map out pain points that may not be visible through analytics alone.
During stakeholder interviews, audit teams should focus on identifying specific workflows where users create workarounds or abandon tasks entirely. For example, if field sales representatives avoid entering notes into a CRM system because the save button is difficult to find, this represents a critical usability failure that impacts business productivity. Similarly, when employees maintain separate worksheets outside the system to store data or perform manual calculations, it signals that the legacy application is forcing users to devise compensatory mechanisms.
The interview process should also uncover context-dependent usage patterns. A B2B software firm's CRM system might see poor engagement from mobile users because touch targets and load times weren't optimized for on-the-go usage. Understanding these contextual factors ensures that modernization efforts address real-world usage scenarios rather than theoretical interface improvements.
Heuristic Evaluation Against Usability Standards
Following stakeholder insights, a systematic heuristic evaluation examines the legacy application against established usability principles. This structured assessment identifies interface inconsistencies, navigation problems, and design violations that contribute to user frustration and decreased productivity.
The evaluation process should focus on identifying specific instances where the interface fails to meet modern usability standards. For instance, a logistics company's shipment tracking module that forces users through too many screens while loading slowly represents multiple heuristic violations. The audit should document whether these issues stem from outdated feature design, poor information hierarchy, or technical limitations that require infrastructure updates.
Heuristic evaluation becomes particularly valuable when examining design system consistency across legacy applications. If a payroll product displays two different button styles for identical actions, this creates cognitive load and potential user errors. The audit must determine which version aligns with current standards and recommend consolidating components to eliminate confusion.
Click-Stream Analysis and User Behavior Tracking
With this foundational understanding established, click-stream analysis and user behavior tracking provide quantitative validation of qualitative insights gathered through interviews and heuristic evaluation. This data-driven approach reveals patterns in user interactions that highlight specific areas where legacy applications create friction or confusion.
Heat maps and click tracking data serve as powerful indicators of user struggle points within legacy interfaces. When users repeatedly click disabled buttons or consistently backtrack while completing routine tasks, these behavioral patterns signal clear opportunities for interface improvement. Support ticket analysis complements this data by revealing recurring issues that users encounter but may not articulate during interviews.
The analysis should particularly focus on user flow completion rates and abandonment points. If users consistently drop off during account setup or abandon forms at specific fields, the audit can pinpoint whether these issues result from compliance requirements, interface design problems, or underlying system limitations that need addressing during modernization.
ADA Accessibility Compliance Assessment
Now that behavioral patterns are understood, accessibility compliance assessment ensures that legacy application modernization creates inclusive experiences for all users. This evaluation examines how well current systems serve employees and customers with disabilities, identifying barriers that may exclude significant user populations.
The assessment should evaluate contrast ratios, screen reader compatibility, keyboard navigation capabilities, and touch target sizing across the legacy application. For example, a data entry tool that works adequately for younger staff might create significant challenges for employees with vision impairments due to insufficient contrast or poor screen reader support.
Accessibility auditing becomes particularly crucial for enterprise applications where diverse employee populations interact with the same systems. The evaluation must consider not just compliance checkboxes but real-world usage scenarios where accessibility failures impact business productivity and legal compliance requirements.
Technical Debt and Infrastructure Compatibility Review
Previously established user experience issues often stem from underlying technical constraints that limit modernization options. The technical debt and infrastructure compatibility review examines the legacy system's architecture to understand which UX improvements are feasible within existing constraints and which require more substantial technical investments.
This assessment should evaluate integration capabilities with modern systems, scalability limitations, and architectural patterns that may restrict interface modernization efforts. For instance, monolithic legacy systems might prevent seamless integration with contemporary tools, forcing users into inefficient workflows that impact overall productivity.
The review must also assess whether the existing technical foundation can support modern UX patterns like responsive design, real-time updates, or progressive enhancement. Understanding these technical boundaries ensures that UX modernization recommendations are realistic and align with available development resources and infrastructure capabilities.
Strategic Implementation Approaches to Improve Application Modernization ROI
Seven-Level Modernization Technique Selection
With this in mind, next, we'll see how strategic modernization approaches deliver maximum ROI by balancing speed, cost, and risk while aligning with business objectives. Not all modernization approaches deliver equal value, making technique selection critical for enterprise success.
The seven-level approach to legacy application modernization provides enterprises with a structured framework for transformation:
Level 1: Rehosting (Lift and Shift)
Migrating applications to the cloud without modifying code
Fast and cost-effective implementation
Limited cloud-native benefits but immediate infrastructure cost reduction
Level 2: Re-platforming
Optimizing applications for cloud environments while retaining core functionality
Moderate investment with improved scalability and performance gains
Level 3: Refactoring
Restructuring code to improve efficiency and scalability
Enables better integration with modern tools and frameworks
Higher upfront costs but significant long-term operational benefits
Level 4-7: Progressive Enhancement
Each level involves deeper architectural changes and AI integration
Supports advanced analytics, automation, and real-time responsiveness
Maximum transformation potential with corresponding investment requirements
The key to maximizing application modernization ROI lies in selecting the appropriate technique based on system criticality, business impact, and available resources.
Modular Rollout Strategies for Risk Mitigation
Now that we have covered technique selection, implementing modular rollout strategies becomes essential for managing modernization risks effectively. The incremental versus full-scale modernization debate centers on balancing immediate value delivery with comprehensive transformation needs.
Incremental Modernization (MVP Approach)
Prioritizes high-impact areas first, such as customer-facing applications or critical internal systems
Quickly demonstrates value to stakeholders and secures continued investment
Reduces implementation risk by limiting scope and complexity
Enables continuous learning and adjustment throughout the modernization journey
Strategic Phased Implementation
Organizations should focus on areas delivering the highest business value:
Customer experience touchpoints for immediate revenue impact
Critical operational systems affecting productivity
Security-vulnerable applications requiring urgent attention
Integration points that enable broader system connectivity
This approach allows enterprises to maintain business continuity while systematically addressing legacy UX challenges and technical debt. Each phase builds upon previous successes, creating momentum and organizational confidence in the modernization process.
Design Systems and Consistency Standards
Previously, we've established the importance of phased approaches, but maintaining consistency across modernization efforts requires robust design systems. Modern applications must support personalized interactions, real-time responsiveness, and seamless omnichannel engagement to deliver enhanced customer experiences.
Design systems provide the foundation for consistent user experiences across all modernized applications by establishing:
Component Libraries and Style Guides
Standardized UI components that ensure visual consistency
Defined interaction patterns for predictable user experiences
Accessibility standards compliance for inclusive design
Responsive design principles for multi-device compatibility
UX Consistency Standards
Unified navigation patterns across applications
Consistent data presentation and visualization approaches
Standardized form designs and validation messaging
Harmonized notification and feedback systems
These standards become particularly crucial when managing multiple modernization projects simultaneously. They ensure that users experience a cohesive interface ecosystem rather than fragmented applications with conflicting design languages.
AI-Powered Code Analysis and Migration Tools
With this framework in mind, next, we'll explore how AI-powered solutions are reshaping the modernization landscape by dramatically reducing implementation timelines. Traditional modernization efforts can take years, but innovative AI tools are revolutionizing how organizations approach legacy system transformation.
Advanced Code Analysis Capabilities
AI-powered platforms leverage extensive enterprise code libraries and generative AI agents to provide comprehensive software engineering capabilities. These tools can:
Analyze existing codebase complexity and dependencies
Identify modernization opportunities and potential risks
Generate migration recommendations based on best practices
Automate routine code transformation tasks
Timeline Compression Benefits
The most impressive feature of AI-powered modernization tools is their ability to dramatically compress modernization timelines, potentially reducing time to modernization by 60 to 70 percent. This massive efficiency gain addresses primary concerns for CFOs and decision-makers regarding time and resource requirements for significant technological overhauls.
Comprehensive Migration Support
By blending advanced code generation with agentic AI and robust code libraries, these platforms enable engineering teams to create high-impact solutions supporting everything from initial modernization to ongoing development and testing. They serve as strategic accelerators that transform the entire software development lifecycle, making enterprise modernization more achievable and cost-effective.
These AI-powered tools represent a quantum leap in accelerating technological upgrades, offering compelling solutions to the challenges of legacy system transformation while maintaining quality and reducing risk.
Modernization Best Practices for Enterprise Software Modernization Success
Future-Proofing Documentation and Support Systems
Building robust documentation and support systems is critical for modernization best practices that ensure long-term success. Organizations must establish comprehensive documentation frameworks that capture not only technical specifications but also business logic and architectural decisions made during the modernization process. This documentation should include detailed roadmaps, including timelines and resource allocation, to help in executing future modernization efforts effectively.
Modernized applications require automated compliance checks and streamlined reporting features that help ensure adherence to regulations while reducing the administrative burden on compliance teams. These systems should be designed to evolve with changing regulatory requirements, allowing enterprises to stay ahead of regulatory changes with minimal disruption. The documentation must also address data integrity protocols, particularly crucial during migration phases where meticulous planning and testing prevent data loss or corruption.
Support systems should incorporate AI-driven features such as predictive analytics and intelligent automation to add significant value, allowing enterprises to optimize operations proactively. By establishing clear communication plans and phased rollout procedures within the documentation, organizations can minimize operational disruption during future updates and ensure business continuity.
Employee Onboarding and Change Management
Managing the human aspect of modernization transitions requires comprehensive change management strategies that address resistance to change and ensure smooth operational shifts. Effective change management includes clear communication protocols, structured training programs, and phased rollouts to minimize disruption and encourage adoption across the organization.
Enterprise digital transformation success depends heavily on stakeholder engagement, ensuring that all relevant parties are involved from the outset. Continuous communication and feedback loops throughout projects help align expectations and quickly address issues that arise. This collaborative approach fosters a sense of ownership and commitment among all parties involved, which is essential for long-term success.
Training programs should focus on helping teams understand the complexity of modernized systems, particularly when transitioning from monolithic to microservices architectures. Employees need support in managing numerous independent services and understanding potential issues with orchestration, communication, and consistency across systems. Organizations should also address the developer experience, as developers building, maintaining, and evolving software face friction with technical debt and unfamiliar language frameworks that can slow innovation and productivity.
Creating Ownership Culture Among System Users
Developing a culture of ownership requires balancing multiple stakeholder interests with differing priorities and objectives. Achieving consensus and buy-in across departments demands effective communication and collaborative decision-making processes that align stakeholder goals with the overall modernization strategy.
Ownership culture development involves ensuring that teams understand their role in maintaining system integrity and driving continuous improvement. This includes providing visibility into application architecture through comprehensive monitoring tools that help teams visualize dependencies and assess the complexity of ongoing modernization efforts. Real-time insights enable teams to prioritize which components to update first and understand the impact of their decisions.
Organizations must foster an environment where employees feel empowered to contribute to modernization success by providing them with the tools and knowledge necessary to make informed decisions. This includes access to architectural observability platforms that offer deep insights into existing application structures and help identify interdependencies that could impact future development efforts.
Continuous Monitoring and Optimization Strategies
Ongoing monitoring is essential for identifying issues early and ensuring legacy application modernization success over time. Enterprises must continuously track performance and gather feedback to adapt their modernization approaches effectively. This adaptability is key to maintaining the relevance and effectiveness of modernized applications, allowing for iterative improvements based on real-world data.
Continuous monitoring strategies should include automated systems that provide advanced data processing and analytics capabilities, enabling enterprises to derive real-time insights and make informed decisions. Enhanced data visibility supports better strategic planning and operational efficiency, helping businesses identify trends, optimize processes, and predict customer needs more accurately.
Organizations should implement monitoring frameworks that track both technical performance metrics and business outcomes. This comprehensive approach ensures that modernization efforts continue to deliver enhanced customer experiences through user-friendly interfaces and improved functionality. The ability to quickly identify and fix issues that impact user experience is crucial for maintaining customer satisfaction and retention in competitive markets.
Optimization strategies must also focus on cost management, as modernized systems should require less maintenance and demonstrate greater resilience over time. By continuously monitoring resource utilization and system performance, organizations can achieve significant cost savings while maintaining operational excellence and supporting future innovation initiatives.
Conclusion
Legacy UX modernization represents one of the most critical investments enterprises can make in 2026. As we've explored throughout this comprehensive analysis, the challenges are substantial—from navigating complex technical debt to overcoming organizational resistance—but the rewards far outweigh the risks. Companies that successfully modernize their legacy interfaces see productivity gains of up to 90 minutes per employee daily, achieve remarkable ROI of $100 for every $1 invested in UX, and position themselves for sustainable competitive advantage in an increasingly digital marketplace.
The path forward requires a strategic, user-centered approach that combines thorough auditing, phased implementation, and emerging technologies like AI-embedded interfaces and mobile-first design for deskless workers. Success hinges not just on technical execution, but on fostering a culture of digital adoption and maintaining consistent stakeholder alignment throughout the modernization journey. For enterprises ready to transform their legacy systems, the time to act is now—waiting only increases technical debt and widens the gap between current capabilities and user expectations that define modern digital experiences.

About the author
Author Name:
Parth G
|
Founder of
Hashbyt
I’m the founder of Hashbyt, an AI-first frontend and UI/UX SaaS partner helping 200+ SaaS companies scale faster through intelligent, growth-driven design. My work focuses on building modern frontend systems, design frameworks, and product modernization strategies that boost revenue, improve user adoption, and help SaaS founders turn their UI into a true growth engine.







